The hottest year: 2010 * The nine hottest years were recorded in the 21st century, plus 1998. The natural fluctuations do not allow us to see continuous warming from year to year, but definitely show warming from decade to decade
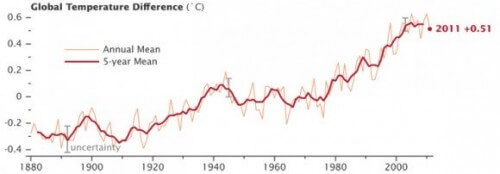
The average temperature of the Earth's surface in 2011 was the ninth warmest since 1880. This is according to data published by the American space agency NASA. The findings continue a trend whereby nine of the ten warmest years in the modern meteorological record have occurred since 2000.
NASA's Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS) in New York, which monitors global surface temperature on a continuous basis, has released an update showing the temperature around the world in 2011 compared to the average temperature since the mid-20th century. The comparison shows that the Earth continues to experience warming compared to the situation several decades ago. The proposed surface temperature in 2011 was 0.51 degrees Celsius warmer than the mid-20th century baseline.
"We know that the planet absorbs more energy than it emits," says GISS director James Hansen. "So we continue to see a trend of rising temperatures. Even under the influence of the cooling effect of La Niña and low activity of the sun in recent years, the year 2011 was one of the ten warmest years in history."
The difference between 2011 and the year that was the hottest in the GISS records - 2010 - is 0.12 degrees Celsius. This highlights the emphasis that scientists place on the long-term trend of rising temperatures. Because of the great natural variability of the climate, scientists do not expect a continuous increase in temperatures from year to year. However, they do expect a continuous rise in temperature from decade to decade.
The first 11 years of the 21st century experienced significantly higher temperatures than the middle and late 20th century, Hansen said. The only year in the 20th century that entered the list of the ten hottest years was 1998.
Higher temperatures are maintained due to the increasing concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, especially carbon dioxide. These gases absorb the infrared radiation emitted by the Earth and release the energy into the atmosphere instead of allowing it to escape into space. As the concentration of greenhouse gases increases, the amount of energy captured through these gases will lead to a further increase.
The concentration of carbon dioxide was 285 parts per million in 1880, when temperature measurements began. In 1960, the concentration rose to 315 parts per million and today it has already reached 390 parts per million and continues to rise at a rapid rate.
The GISS data is collected from over a thousand meteorological stations around the world, satellite observations of sea surface temperature, and measurements from research stations in Antarctica. An open computer program makes it possible to calculate the differences between the surface temperature in any given month and the average for that place and that month in the years 1951-1980. The average of these three decades functions as a baseline for analyses.
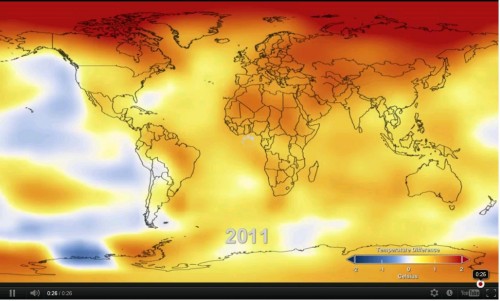
The result obtained is very similar to those obtained by the Hadley Office of Meteorology in Great Britain and the Climate Research Center of NOAA - NASA's equivalent agency for oceanography and atmosphere. NOAA asked to change its name to the "National Climate Agency" but Republican officials in Congress claimed that it would thereby transform from a scientific agency to an agency with an agenda that promotes the claim (remember, for the Republicans this is a claim not a fact) that the Earth is warming.
Hansen expects to see more records in the next two to three years due to the increase in solar activity and the expected return of El Niño, which raises the surface temperature in the Pacific Ocean. The hottest years on record were 2005 and 2010 in a virtual tie.
"It's always dangerous to make predictions about an El Niño, but it would be safe to say that we will see one in the next three years," says Hansen. "It doesn't take a particularly strong El Nino to raise temperatures above those of 2010."

3 תגובות
Abby - what's the deal with Steve Jobs now?
Nonsense.
Global warming is a result of dark matter.
According to the video, in 1955 there was a jump in the temperatures in Antarctica.
I wonder why ? Maybe after the second war they began to vigorously produce everything they destroyed?
Question for thought