Hayadan > Computing and technology > nano-tech
nano-tech
- The Voice of Science website - the Israel National Science Foundation
- April 25, 2024
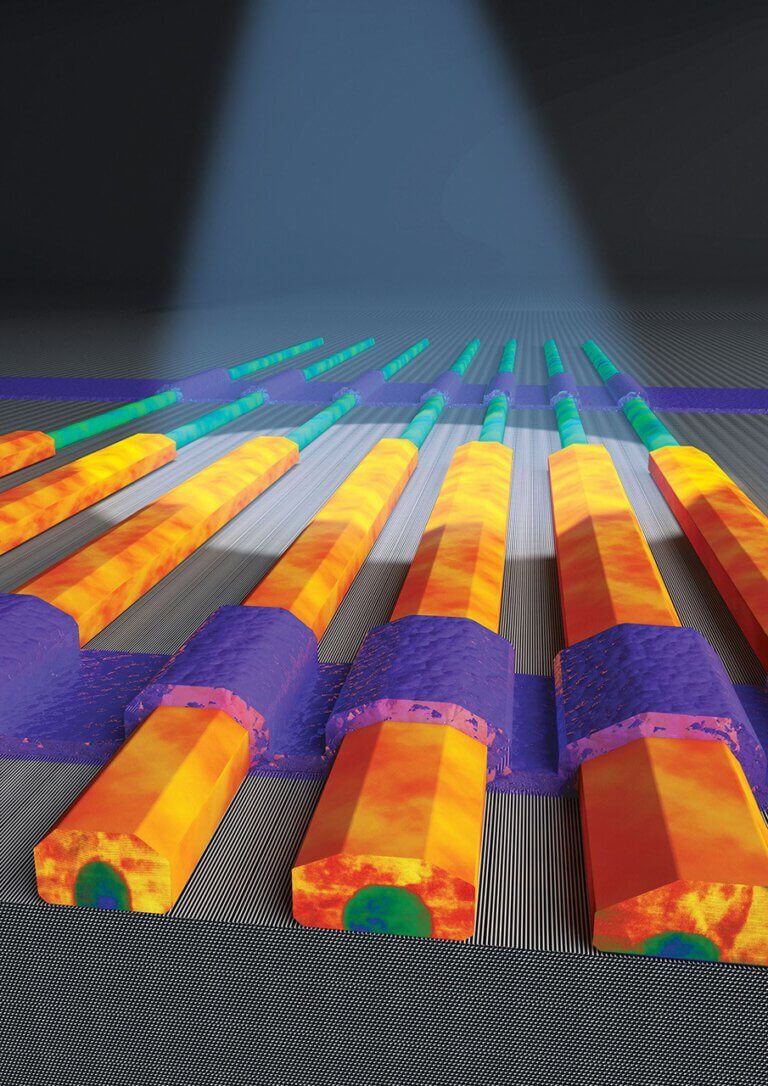
Researchers aim to launch the second revolution in the field of spintronics - and significantly increase the amount of memory in our electronic devices
- Tel Aviv University
- April 23, 2024
A new development may accelerate the use of graphene in the nanoelectronics industry and be used in many technological applications
- The Technion
- April 22, 2024
- One response
The applicability of the new technology is demonstrated in the contexts of local cell transplantation, drug transport for controlled local release over time and 3D bioprinting. The mechanical properties of the scaffolds can be adjusted according to the target tissue and the desired drug release rate
- Tel Aviv University
- April 21, 2024
The team of researchers explained that the uniqueness of the smart liquids is that, as a result of their chemical properties, the liquids maintain separation from each other, thus creating distinct droplets
- The Voice of Science website - the Israel National Science Foundation
- March 6, 2024
It turns out that the shorter a crack in brittle materials - the more resistant they are to it, which can help in the design and use of applications that are based on brittle materials
- Bar-Ilan University
- January 20, 2024
Prof. Rachela Popobzer from the Faculty of Engineering and the Institute for Nanotechnology and Advanced Materials at Bar Ilan University won a grant of 150 euros, for research aimed at making drug treatment more efficient and targeted
- Dr. Moshe Nahamani
- November 29, 2023
- No comments
The smoothness of a surface can be adjusted by changing its roughness at the molecular level - this is how researchers from Finland demonstrate
- Dr. Moshe Nahamani
- October 31, 2023
- One response
Before the successful synthesis, it was not clear if it was even possible to create such a molecule and keep it stable long enough to study its structure and its electronic properties.
- The Technion
- August 8, 2023
- No comments
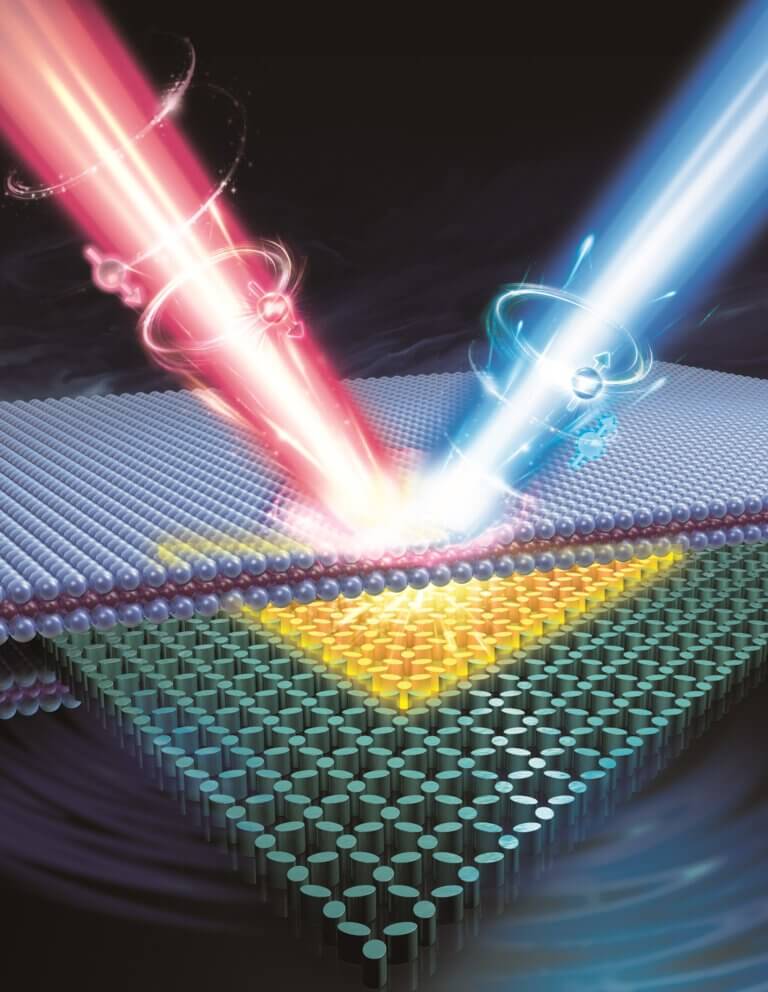
Researchers from the Technion have challenged the limits of what is possible in the field of spin-optics at the atomic level. They developed a spin laser from a single atomic layer - a device that does not require magnetic fields or low temperatures
- Tel Aviv University
- August 7, 2023
A new material created from natural materials can move quickly through water and carry up to 40 times its own body weight
- The Technion
- July 5, 2023
- One response
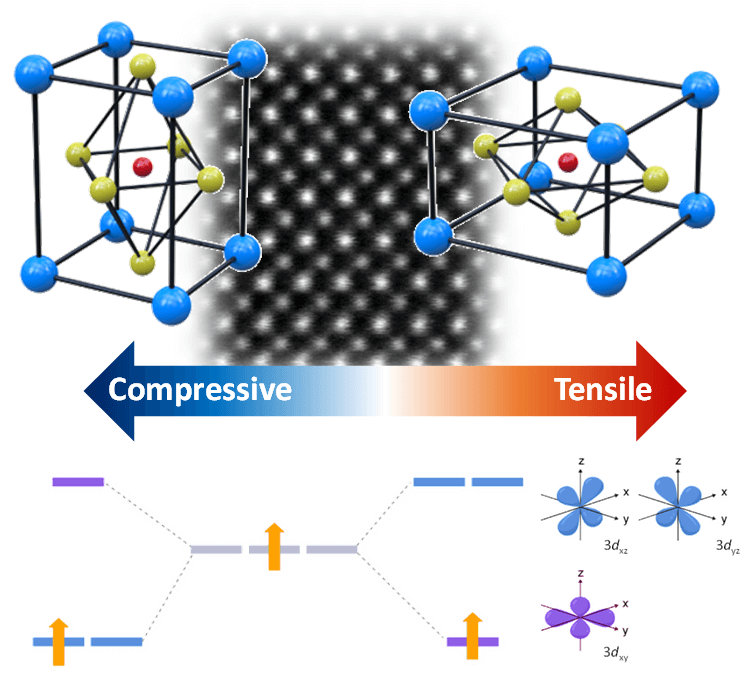
Researchers at the Technion have engineered a material that may replace silicon in the world of electronics in the future; Through the stretching of the material at the atomic level, they gain control over the material's conduction and insulation properties, thus progressing towards turning it into a fast and efficient switch
- Dr. Moshe Nahamani
- May 12, 2023
- No comments
First-of-its-kind pioneering demonstration points to the possibility of a greener future for the electronics sector
- The Voice of Science website - the Israel National Science Foundation
- April 18, 2023
Researchers built surfaces that direct the growth of nanowires and nanotubes and watched their growth process in real time. The forecast for the future: building advanced devices, such as tiny solar cells
- Angle - a news agency for science and the environment
- April 16, 2023
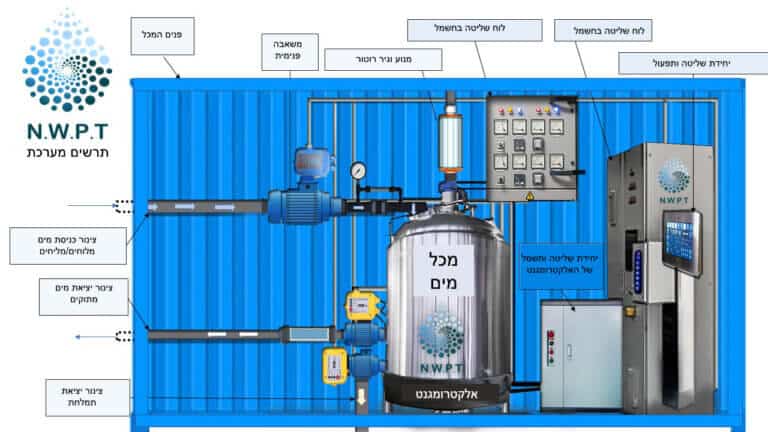
Futuristic water purification? An Israeli company is developing a new desalination method in which nano-robots will clean seawater of problematic salts; This, without removing from them substances that are important for our health
- Tel Aviv University
- March 28, 2023
Meet the hybrid microrobot: innovative technology tiny at 10 microns (the size of a biological cell)
- Dr. Moshe Nahamani
- March 24, 2023
- No comments
Researchers from the University of Santiago in Chile, working in the field of machine learning, have succeeded in developing an innovative method for identifying organic compounds based on the refractive index at a single optical wavelength
- The Hebrew University
- March 19, 2023
- No comments
A team of researchers from the Hebrew University has developed a device that is able to easily and quickly measure the properties and thickness of surfaces 35 times smaller than the diameter of a human hair. The method is expected to significantly optimize the production of solar cells, flat screens and a variety of futuristic technologies
- Weizmann Institute
- February 20, 2023
Weizmann Institute scientists present a new method for imaging a single electron
- The Technion
- February 6, 2023
- No comments
These watches have unique features including small volume and weight and low energy consumption - essential features because they are mobile components powered by batteries. The tiny clock has uses similar to those of normal atomic clocks used for example in navigation systems (GPS), synchronization between communication systems and computer systems.
- Dr. Moshe Nahamani
- January 29, 2023
- 2 תגובות
An international team of researchers succeeded in developing the most stable and porous zeolite known so far composed entirely of silica, which they named ZEO-3
- Avi Blizovsky
- January 27, 2023
- One response
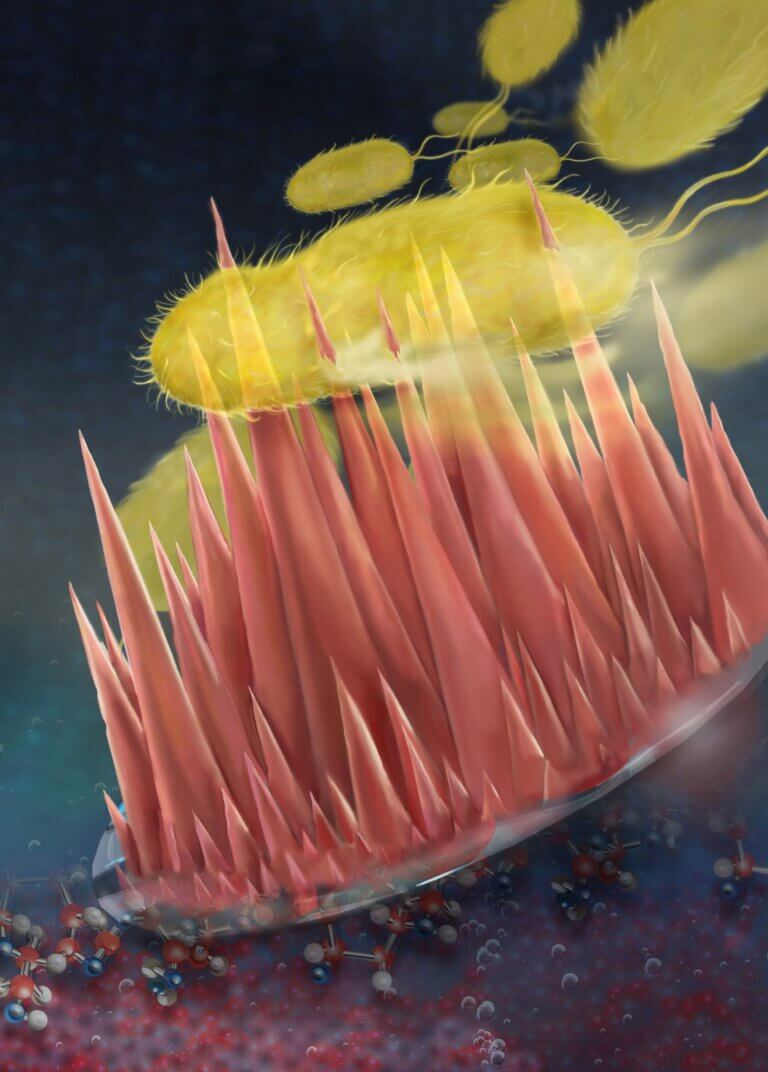
Long and dense spikes formed by a sulfated polysaccharide substance found in red algae were discovered by a research group from Ben-Gurion University of the Negev to have biological activity against bacteria and fungi
- Avi Blizovsky
- December 27, 2022
- 4 תגובות
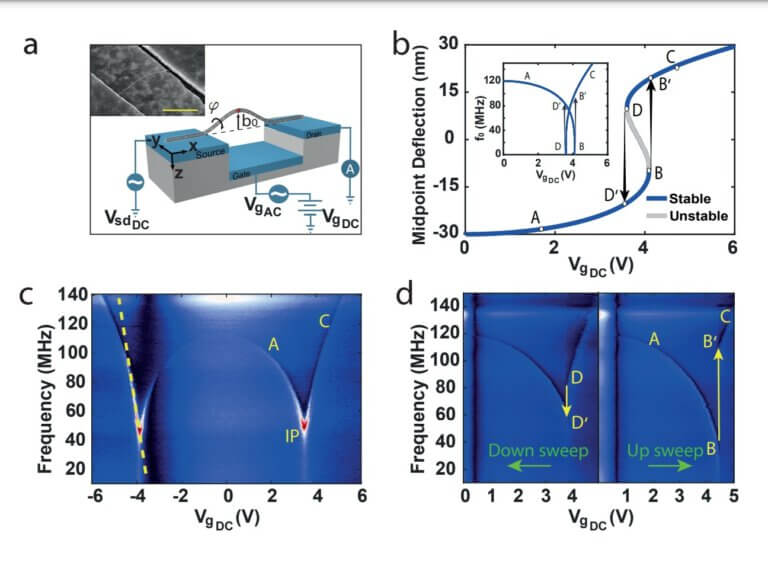
Schematic of the measurement circuit (a), theoretical model (b) and resonant frequencies as a function of the gate voltage (c, d).
- The Technion
- November 25, 2022
- No comments
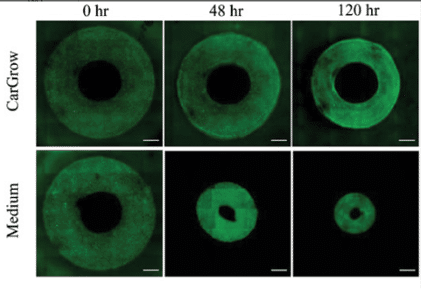
The technological innovation suppresses the typical shrinkage of printed tissues in the period before transplantation
- Tel Aviv University
- November 23, 2022
- No comments
- The Voice of Science website - the Israel National Science Foundation
- October 29, 2022
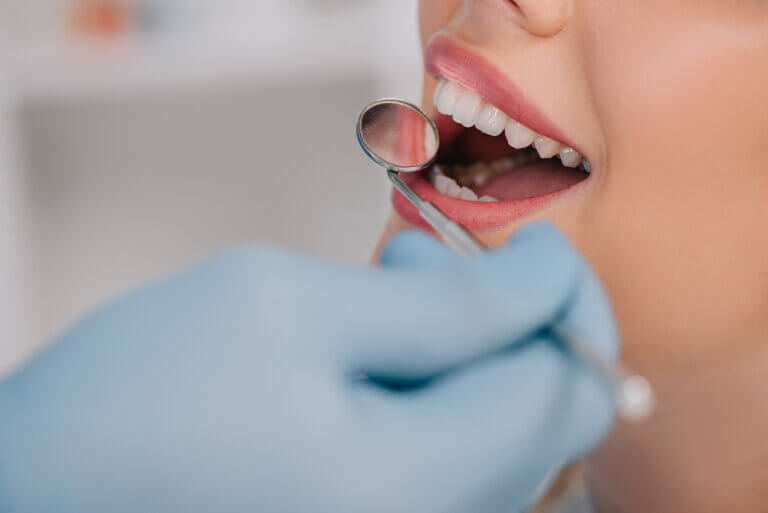
Volatile molecules may characterize diseases such as tooth decay and gum disease





![Computer simulations showed that changing the coverage of the monolayer changed the smoothness of the surface. Both low coverage and high coverage produced very slippery surfaces, but for different reasons. [Source: Sakari Lepikko et al 2023]](https://www.hayadan.org.il/images/content3/2023/11/530361_s415570230134636_981234.jpg)




![The image of the structure of the material zeo-3, an innovative silica zeolite with extremely large pores [courtesy: ICMM-CSIC]](https://www.hayadan.org.il/images/content3/2023/01/researchers-create-a-n-768x485.jpg)