The effort to get rid of the 19th century metal cylinder that still defines a kilogram is scheduled to end in 2018

- Since 1889 the definition of the kilogram has been based on the weight of a single cylinder of platinum and iridium alloy kept in a vault near Paris. This is the only measure that is still tied to a physical object.
- But the original kilogram loses its mass. This is one of the reasons for the decision made by the International Conference on Weights and Measures in 2011 to give the kilogram a new definition that will be related to a constant in quantum mechanics.
- In 2017, the redefinition process entered its final stage. The official metrology laboratories of five countries participate in the process and it involves some of the most difficult scientific measurements to perform.
John Pratt He felt the tension rising in him as he approached the security checkpoint at Dallas International Airport in Washington. In the camera bag he was carrying were four metal cylinders. Such objects could not fail to attract the attention of the suspicious security personnel. The weight of each cylinder was exactly one kilogram. The value of one of them, a cylinder of platinum and iridium alloy the size of half a can, was at least $40. (The price of platinum now hovers around $1,000 pertroy ounce, a common measure for precious metals.) The other three were stainless steel cylinders produced by a meticulous mechanized process.
Pratt's mission was to bring them to his colleague in the suburbs of Paris safely and without anyone touching them on the way.
Pratt had documents fromStandards Institute of the USA which are intended to make it easier for him to pass the security checks. The documents explained that it carried four official US kilograms: the masses used as the basis for all US weight measurements. They further clarified that it is forbidden to touch the kilograms or take them out of the containers protecting them.
Pratt, a former punk-rock musician, directs the quantum measurement department at the institute's laboratories in Gaithersburg, Maryland. "The guy from security at the airport gave me some trouble, but after reading all the documents it became the story that made his day." After a few minutes, Pratt was allowed to continue on his way and he boarded the seven-hour flight to Paris, where he had to face another dilemma: what would he do with his valuable luggage when he had to get up from his seat? Should he keep the case with him at all times, as some of his colleagues advised him to do? "I admit I left the bag under the seat in front of me while I went to the bathroom," says Pratt. "He was out of my sight for a short time, during which someone could have touched the pound and filled it with dirt."
Touching the cylinders would have spoiled many months of careful work devoted to measuring these kilograms to an accuracy of a few parts per billion. Pratt was on his way with the cylinders to the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BEEP) in the town of Sur near Paris. A few months later they compared Metrologists Between these metal cylinders and between identical metal cylinders from three other countries, as well as between them and a very pure silicon ball produced inThe National Metrological Laboratory of Germany. This was the last step taken as part of a historic process of changing the way masses are measured in the world.
In 1889, the year the Eiffel Tower was inaugurated, the kilogram was defined by the mass of a cylinder made of an alloy of platinum and iridium that was placed under three glass bells and kept in a locked safe room at the headquarters of the International Bureau of Weights and Measures. The international standard kilogram, or Le Grand K (the big K), as it is called, is the prototype of the kilogram on which all other national mass standards are based. At the end of 2018, the Grand-K will lose its status. In its place, the kilogram will receive a new definition based on Planck's constant: a constant number in quantum theory related to the amount of energy carried by a single light particle, a photon.
Why was it decided to retire the Grand-K? For many years, metrologists have wanted to create an accurate and reliable international standard for mass that would be based on a fundamental constant in the universe instead of a block of metal kept from any guard since the Victorian era. But there is a more pressing reason for the change: the Grand-K seems to be losing its mass. Once every 30 years or so, the Grand-K is taken out of the vault for cleaning and comparison to six official copies, the temoins ("witnesses") kept with it. When comparing the first two "witnesses" to the Grand-K in 1889, both matched the original. But in measurements made shortly after World War II, and again in 1992, it turned out that the weight of the copies was slightly greater than that of the Grand-K. The hypothesis that the mass of copies just increased while the Grand-K remained unchanged seems implausible. There is, of course, a more plausible explanation: "One can assume that the standard international kilogram is losing its mass," says Michelle Stock Director of the Department of Physical Metrology at BIMP. This uncertainty is one of the reasons for the decision made in 2011 bThe General Conference on Measures and Weights, the body that manages the International Bureau of Weights and Measures, to establish a new mass standard.
No one knows why the Grand-K is losing weight. His value was too high to allow him to undergo the tests that could have found this out. This mystery creates a real problem. With the advancement of technology in the coming decades, it is expected that mass measurements on a molecular scale and even on a scale smaller than that will be commonplace in many fields. "We'd like to have ways to measure microgram-scale masses with at least three-digit accuracy," Pratt says, "and with a physical standard kilogram there's a lot of uncertainty on such a small scale."
The problems associated with Grand-K are not limited only to the field of mass measurements. Units of power and energy are also derived from it. "We are now at a point where we could see changes in the value of fundamental constants because the international standard kilogram is changing, and that doesn't make sense," says Stock.
A new standard
Of the seven basic units of the metric system, the kilogram is the unit with the closest update date, but it will not be the last unit to change. Besides the kilogram are included inInternational System of Units (SI) Also these units: meter, ampere (unit of electric current), second, candela (a measure of the luminous intensity of a light source), mole (which relates the weight of a substance to the number of atoms it contains) and the Kelvin degree (temperature).
Two of the units in the international system were redefined a few decades ago. The meter was redefined in 1983. Until then, it was defined by the distance between two lines engraved in a platinum-iridium ingot kept in the same guarded and locked room where the Grand-K is kept, while in its new definition, the meter is the distance traveled by light in the 299,792,458th part of a second. Following the improvement of the accuracy of atomic clocks in the 60s of the 20th century, the second was also redefined. Its old definition was as part of the day, while its new definition was made in terms of the particular frequency of the microwave radiation emitted by a cesium atom. Like the kilogram, the mole, the kelvin and the humper are also slated to be updated in 2018.
Hamper's current situation is particularly strange. Its official definition includes two wires of infinite length, one-dimensional and massless. This is such an abstract definition that it cannot be accurately created in a laboratory. This situation will change in 2018, when the ampere will be defined in electron charge terms. This progress was made possible thanks to the development of nanotechnological devices capable of counting single charged particles passing through an electrical circuit.
"If we think about new definitions that will be established in the future, they may include the unit of illumination, the candela, which will be defined in terms of quantum mechanics, and perhaps an optical definition of the latter instead of the microwave definition," says Alan Steele, Canada's chief metrologist. "But these changes will only happen in at least 15 years, maybe more."
The redefinition of the kilogram is at the center of an effort to create a truly universal system of measurements that will not be limited to local conventions or those that will be limited only to our own world. In principle, the new units could be understood by intelligent beings anywhere, from here to the Andromeda galaxy. This is an important period in the world of metrologists. "This kind of thing happens once in a lifetime," says Steele. "The last time we tried to do something on such a fundamental level was when the meter was redefined. Trust me, it's times like these that you should be a chief metrologist. It's not like achieving world peace, but it's pretty cool."
the safe
The Grand-K is not the first official kilogram. Its predecessor was created during the French Revolution, with the birth of the entire metric system. Before the revolution, almost all measures of weight and length used in France depended on local customs. Different sizes were accepted in different cities and this awkwardness burdened the state. In total there were more than 700 different units of measure in France. GodTawaz, for example, was a measure equivalent toFathom The English defined as the distance between the tips of a person's arms when they are spread out to the sides. But a tawaz in Paris (which was equal to 72 poises or inches) was not necessarily the same as that used in Marseilles. The Savants, as the French then called the scientists among them, tried to bring order to the chaos by creating a new system "for all times, for all peoples", as the motto proclaimed on a medal from the period.
"Their idea in 1791 was that the standard would be based on natural and unchanging phenomena," says Richard Davis, former director of the mass department at the International Bureau of Weights and Measures, the department charged with keeping the Grand-K. According to him, "we are still doing the same thing". The difference is that now the metrologists want to base the standards on natural constants that really don't change.
We are sitting in Stock's office inPavillon de Breteuil, an elegant building from the 17th century standing on a green hill inSt. Cloud Park The viewer on the river Seine. The park used to be a hunting reserve for the kings of France and Marie Antoinette's rose garden is still carefully cultivated here. It has been the seat of the International Bureau since the Meter Convention of 1875, an agreement signed by 17 countries.
"When you crossed the bridge towards Sver, did you notice the island on the left?" Davis asks. On the island, according to him, there used to be a factory of the Renault company where tanks were built for the German army in World War II. American bombers tried to hit it many times. After one of the bombings shook the Pavillon de Breteuil, the Grand-K was placed in a special shockproof container. The "witnesses" were indeed moved to an underground vault in the French bank and remained there for most of the war years, but according to the meter convention, the Grand-K had to remain in the bureau.
After the war, in 1946, when the Grand-K was taken out of the safe for the purpose of cleaning and comparing it with the six copies, it was found to be 30 micrograms lighter than the "witnesses". When the next cleaning date came, 45 years later, the difference increased to 50 micrograms - the weight of a fly's wing.
"Fifty micrograms in a hundred years," says Stock and we look at the graph showing the changes on the computer screen in his office. "You can see the difference is small." For now this difference does not create practical difficulties, "but if we continue like this, one day it will eventually lead to problems."
In the world of nanotechnology, 50 micrograms is a considerable weight. Moreover, the uncertainty about the mass of the kilogram will spread and affect a long list of other basic units. The metric unit of force, the newton, is defined in terms of kilograms; Newton, in turn, defines the joule, the unit of energy; whereas the joule defines the watt, and so on. In the end, a small question mark may stick to almost every measurement made in the physical world.
The cleaning and comparison between the Grand-K and test masses are not routine operations. They have only been made four times since 1889. To remove the first Grand-K from its caveau, that is, from the safe room where it is kept, three people must be present who have to open three horizontally arranged locks. Inside this locked room is another large safe with a combination lock, and inside the inner safe lies the Grand-K under the three glass bells placed one on top of the other. The six copies are also kept in this safe. The director of the International Bureau of Weights and Measures, the director of the National Archives in Paris, and the president of the International Conference of Weights and Measures, which oversees the work of the bureau, are the only three people in the world who have keys to the vault room. Since each key is different, all three must be present to open the saved room.
"In the history of the 1875 Meter Convention, I am only the second person from outside Europe to be elected president of the International Conference on Weights and Measures," says Barry Inglis, an Australian electrical engineer. "I asked what would happen if I flew home and the plane crashed over the Indian Ocean. How will they manage without the key? But I'm sure there is a locksmith who can open this old lock without too much effort."
Few of the bureau's employees got to see the Grand-K with their own eyes, and there are rumors that his official photographs are those of a duplicate. "I saw him once," says Susan Picard, who has worked at the office since 1987. The three key holders open the safe once a year to see the Grand-K, without touching it, just to make sure it's there.
After entering the Grand-K's sanctum sanctorum when it's time to clean and weigh it, a technician picks up the gleaming cylinder with tongs lined with fine leather and takes it to a cleaning station where it is polished with a leather cloth soaked in alcohol and ether and then rinsed with double-distilled water. A final blast of nitrogen gas removes the last remaining drops from him. The whole process takes about an hour. The bureau tried other cleaning methods on experimental masses, which included, among other things, the use of ultraviolet radiation. But it turned out that these methods cleaned the alloy too much. "They seem to remove more dirt than our method," says Stock. "But after such cleaning, the mass becomes unstable because as a result of the cleaning that is obtained, the tendency of the surface to react with the environment greatly increases." Such a situation would have reduced the credibility of the Grand-K as a standard, so the bureau continues to use its old method, cleaning with a soft leather cloth and washing with water.
After the washings, the Grand-K and the "witnesses" are taken to a clean room and put into a device called "compares essays". It's a $500,000 device that can measure mass differences as small as a single microgram. The mass comparator and ten "work bodies" of the standard kilogram weight are the "workhorses" of the mass department of the International Bureau of Weights and Measures. They are used in the day-to-day calibration work, while the Grand-K and the "witnesses" go out into the world only once every few decades for the purpose of verifying the weight of the official kilograms of different countries.
After my conversation with Davis and Stock goes on for some time I ask them if I can see from the outside the vault room where the Grand-K resides. I know there is no chance to see the noble Galilee in its own right. They burst out laughing and shaking their heads: "No, no, no, no!"
"This is not the first time we have been asked to see the safe," says Davis.
"She's here, in this compound, right?"
"Yes," Davis replies, "that detail is not a secret."
Difficult measurement
Soon, when the new international mass definition will be based on Planck's constant, the Grand-K will become an item whose value will be mainly historical. The definition of Planck's constant includes both energy units and time units, and it can be expressed in terms of mass based on the equation E=mc2. same as the gravitational constant, G, also Planck's constant, h, is an entity derived from the theory, but its numerical value can only be determined experimentally, and thanks to better instruments, the degree of precision with which the natural constants can be measured is getting better and better.
To move to the new quantum standard, the International Bureau of Weights and Measures developed a two-part strategy. First, the national metrology laboratories of five different countries determine the numerical value of Planck's constant. After that, their official national kilograms are weighed according to the value that will be obtained and finally the degree of compatibility between the different measurements of the kilograms is compared. These tests were conducted by the Bureau in the summer of 2016. The results are expected to be received in early 2017, and if they are satisfactory, the laboratories participating in the study will begin a reverse process, in which they will use the official kilograms held by the various countries to further improve the accuracy of measuring Planck's constant. At the end of the process, the new and more accurate value of Planck's constant will be used to formulate the final definition of the kilogram.
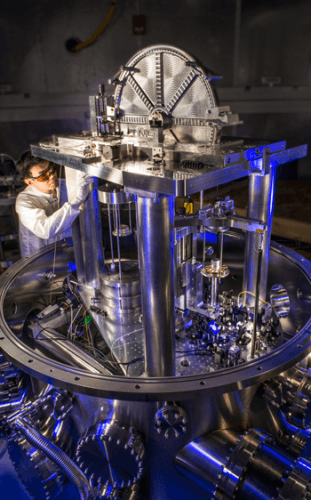
Most of this work is done with the help of a very complicated device called "Kibal balancers". Until 2016, this device was called "Watt balances", but the metrologists decided to change its name after the death in 2016 of the physicist who invented it, the British Brian Keeble. It is so difficult to conduct experiments on Kibble balances that in 2012 the journal Nature listed them among The five most difficult tasks in physics, alongside the discovery of the Higgs boson or gravitational waves.
In May 2016 he drove me Stephen Schlaminger From the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) to a two-story white building at the edge of a wooded campus that covers about 24 dunams. Kibble scales are installed in this building, the older of the two facilities owned by the institute. Since the newer model was completed in 2014 the older facility is not in use. "This place is like a 'little house on the prairie,'" Schlaminger jokes when we stop in front of the isolated building. This is where most of the institute's measurements were made to determine the value of Planck's constant, and the new model will operate more or less in the same way.
Any resemblance to the little house on the prairie disappears when we enter the building. From the inside, it looks like the setting of a novel from the era of the industrial revolution, full of steam engines. The walls are covered with copper sheets up to the ceiling of the second floor. "Do you see that all the devices are made of brass?" asks Schlaminger. "There is no iron here." The copper and brass shield the device from external magnetic fields. But the magnetic fields created inside the building are strong enough to erase credit cards. In the middle of a room on the first floor stands a tall support column with a superconducting magnet at its base. When it is running, it is cooled with liquid helium.
The measuring facility itself is located on the second floor. It consists of an aluminum wheel standing perpendicular to the ground with weighing scales hanging on both sides. During measurement, a kilogram mass is placed on one of the scales. A coil of wire hangs directly below this spoon on a pole three to four meters long. In the spoon on the other side of the scales there is a counterweight and an electric motor. In order to find all the necessary values for the equation that relates the mass to Planck's constant, the scales need to be operated in two different ways. In "weighing mode", the downward force of gravity exerted by the test mass is exactly balanced by a magnetic field created by an electric current transmitted in a coil below the spoon. In "speed mode" the test mass is removed from the handle and the motor in the other handle lifts the coil at a constant speed through the magnetic field created by the superconducting magnets of the device, which generates an electric voltage in the moving coil.
It is so difficult to conduct experiments on Kibble balances, that in 2012 the journal Nature listed them among the five most difficult tasks in physics, along with the discovery of the Higgs boson and gravitational waves.
The current measured in the weighing mode and the voltage occurring in the speed mode are placed in the equations of quantum theory that link electric current, voltage and resistance to Planck's constant. In short, in Kibble scales, the starting point is one kilogram, by which the device can determine Planck's constant. Then, when we have an accurate value of Planck's constant, we can use balances to measure mass without the need for any physical weights for comparison.
To reach accurate results, Schlaminger and his colleagues had to take into account local fluctuations in air pressure and gravity, as well as the shaking the earth and the ocean tide. "If you don't correct the results according to the tide, a deviation of about 100 parts per billion is created," Schleminger explains. Despite its complexity, this facility reminds him of things from another era. When his team was busy measuring Planck's constant, they had to open and close valves in a strict order and constantly monitor the pressure inside tanks filled with liquid helium. "It felt like driving a locomotive from the days of steam trains," says Schlaminger, "but in truth, these experiments measured dimensions in quantum mechanics!"
Farewell to the Grand-K
The continuation of the course of things depends on the results of the experiments from 2016. The kilogram measurements of three of the five participating national metrology laboratories must be nearly identical; The difference between them must not exceed 50 micrograms. This is the current uncertainty regarding the mass of the Grand-K. After the results of the preliminary study are published, the serious work on the new definition will begin.
If everything goes well, the kilogram will be defined at the end of the process in terms of Planck's constant. The International Bureau of Weights and Measures established strict standards: not only that the measurement differences must not exceed 50 parts per billion, but in one of them the uncertainty must be less than 20 parts per billion. The Canadians have already achieved this level. For the new definition to come into effect in 2018, the new measurements of Planck's constant must be accepted for publication by July 1, 2017.
And what about the Grand-K? It will stay in his safe. Since kibble scales are a very complex device, it can be assumed that we will continue to see physical standard kilograms. Instead of continuing to make arduous measurements on balance scales, for the next decades the metrology laboratories will continue to use a new generation of standard models in their daily work. The Bureau is already planning these models, but their exact calibration will be done using Kibble scales, and not according to the Grand-K.
Is this the end of the story? Do we finally have a kilogram "for all times, for all nations?" Stock is still not ready to commit.
"One of my predecessors in this position, Nobel laureate Charles Edouard Guillaume, thought that the current kilogram would serve us for 10,000 years," he says. "It was an overly optimistic vision, of course. I'm not convinced this will be the final setup, but it will be good for some period of time. Maybe not for the next 10,000 years.”

284 תגובות
On another topic,
Another article on inflation theory
https://www.forbes.com/sites/startswithabang/2017/09/28/is-the-inflationary-universe-a-scientific-theory-not-anymore/#6351ba08b45e
All arguments with Yehuda are a blessing in disguise. Leave him alone
Shmulik
An elastic mechanism cannot produce any gravity. No need to mess with light 🙂
Yehuda,
Unlike what is written here, I absolutely do not understand how an elastic mechanism produces light gravity. Why do elastic collisions bend a light beam but not produce refraction similar to a rainbow or the colors of the atmosphere.
In addition, I would be more than happy to know how much the light should bend, according to your formula: as Newton predicts or relativity or is it time for something completely different?
Dis is detind cili
Israel
Le Sage disagrees with Yehuda...
Yoda
What is an experiment for? Does anyone disagree with you that pushing creates gravity?
The question is if this is what is happening in reality, are Sage particles the ones that attach us to the earth.
Why not try replacing particles with radiation? You will get the same gravity as in pushing, but most of the classic problems of pushing will be solved.
Albanzo
I was surprised by your comments in your last comment.
Isn't the theory of relativity "the key to gravity"?
Is general relativity an outdated theory of gravity?
I'm already thinking that maybe I'm just trying to understand her. Maybe it's worth building the pushing regardless of general relativity and we'll see where we end up, I think I'll work at the same time on planning my experiment
I am planning an experiment that can show once and for all if the gravity pushing idea works and if it does so in elastic collisions. Patience again
Yehuda
There is also waiting for Yehuda. I think she got stuck because I used the word forbidden (a form of government that was practiced in pre-World War II Italy. Don't panic, the word wasn't directed at anyone). Hope you will be released soon.
It is clear that the theory of relativity is not "the key to gravity". More or less from the day of its publication, people realized that it cannot describe processes at very short distances (Planck length) or at very high energies. General relativity is a classical theory, and just as Newtonian mechanics is a classical theory that does not correctly describe our world but is an excellent approximation under certain conditions, so general relativity is an excellent approximation at low energy scales. And when I say low, I mean "still much higher than the energies we reach even with advanced accelerators". Therefore, although from a theoretical point of view general relativity is an outdated theory of gravity, it is the most advanced that has been tested experimentally - simply because we do not have the ability to test quantum gravity phenomena with the existing technology.
By the way, in recent years there is an understanding that in black guys there are differences between classical and quantum gravity, which are not only quantitative (and therefore below the measurement resolution) but also qualitative and therefore can really lead to different behaviors. That's why quantum black holes have been a terribly hot research topic for the past five years.
Yehuda
What I say is also true in very thin gas. There will be particles that will bounce off the earth like stones on water, nullifying the effect of those that were blocked.
And of course you ignore the rest...
Yehuda,
When light passes through the atmosphere, it is colored blue due to the scattering of light in the atmosphere
Why don't your particles color the sky? Your particles are simulated as a gas and they are good enough to bend the beam but not enough to do dispersion?
Below are your questions:
Question: And what does gas do to light? Answer bends it according to its density.
Question: I would love to receive an answer to my question, which is not just asked: Answer: Please.
Question: If all your particles are doing is elastic impact, why is light being bent by them?
Answer: The curvature does not occur because of the elasticity of the particles but because of their density.
Question: And if light nevertheless bends, does it bend as Newton predicts or as relativity predicts and if as relativity does, how does this miracle occur? Answer: This is the million dollar question. And that's what I'm learning right now.
Happy day and happy new year
Yehuda
Yehuda,
And what does gas do to light?
I would love to get an answer to my question, which is not asked for nothing: if all your particles do is elastic impact, why is light bent by them? And if light nevertheless bends, does it bend as Newton predicts or as relativity predicts and if as relativity does, how does this miracle occur?
I have already explained that in normal gas under normal conditions the phenomenon of gravity will not be seen because the average free path of the gas particles is very short relative to the distance between the bodies. Thus, external particles will hit the gravity-creating particles and they will lose their direction. To increase the free path we need a thin gas at low pressure whose distance between the particles is greater.
Yehuda,
Very funny that you complain about having to repeat the same claim several times. If I had a dime for every time I had to just repeat the same thing over and over and over again because you're ignoring me, I'd be a millionaire. For example - how many times have I already explained to you that the formula you propose explicitly contradicts general relativity? The fact that you say the words "there is no contradiction between my formula and general relativity at short distances" is worth nothing. It's like I say "there is no contradiction between classical physics and quantum physics" or "there is no contradiction between fascism and democracy". You can say it as much as you want - it's still bullshit.
The formula you propose contradicts the theory of relativity in an explicit way that is not ambiguous even at short distances. The fact that you do not understand the theory of relativity and know nothing about it does not give you the permission to invent fantasies in which it behaves as you please.
Yehuda
They say that every problem has a simple, elegant ... and wrong solution.
If the collisions are elastic then a lot of particles will hit me after they hit the earth. Think of particles coming from the horizon at a flat angle.
According to what you describe then the air above me should also have pushed me to the ground, but this is not happening. And what I say is true for both compressed gas and very thin gas.
LaSage realized this, and so he argued that collisions are perfectly inelastic. The problem that then arises is enormous warming.
Another problem is that your model requires high transparency for the material, so the shape of the body has no effect. But - how do you explain that the weight of an atomic nucleus is a simple product of the number of particles in it?
How do you not see all the contradictions between your model and the theory of relativity? According to your model space has no properties, but according to the theory of relativity these properties are the source of gravity and persistence. According to your Torah there is no reason for the rate of time to change, for the curvature of light or for the existence of speed c.
The theory of relativity explains other things, such as why a charge in motion produces a magnetic field. She explains how, after all, there are bodies that are faster than the speed of light, and we also see them!
Without the assumption that the theory of relativity is true throughout the universe, there is no point in talking about the big bang, or even about the science of cosmology. It is better to assume that the stars are points on the sky.
Because Feynman was mentioned, he scolded his wife in 1962: "Remind me not to participate in lectures and meetings about gravity anymore, I too can write formulas that no one understands."
But if strings are the key to gravity, then doesn't that mean relativity isn't? Or maybe Einstein saw the future in his vision?
Miracles
It's a shame that after months of discussion you still don't understand the simple gravity pushing principle. A person standing on the earth receives less particles from the direction of the earth than from the direction of his head, therefore he is pushed to the ground. Really simple.
Happy day and happy new year
Yehuda
Yehuda,
No one else is stopping you from studying. In fact everything was quiet until you answered answers that answered nothing. The fish on the plate because he opened his mouth.
You can't resist relativity because it doesn't exist for you. There is no film in which relativity exists and neither does your formula, therefore you have no theoretical basis to take insights from relativity. You have no reason for gravity to move at the speed of light except as an arbitrary condition you decided on because you understand that it is not worth arguing with relativity because relativity has successfully predicted predictions that have come true for 100 years.
What is your prediction about the bending of light near masses? Like Newton or like relativity and if like relativity, how does this miracle happen?
Shmulik
In my understanding, if the collisions are elastic then there is no "gravity". And it doesn't matter how much Judah denies this detail.
Shmulik Nissim and others
You are interfering with my learning the material and insisting on just asking questions. For example, a question was asked, does gravitation move instantaneously like Newton or at the speed of light like in relativity? I answered that it is clear that gravitation will operate at the speed of the particles which is apparently approximately the speed of light. This did not satisfy Nissim and he again asked a casual question on the subject so there is really no point in rambling and it is a shame that someone thinks I am wrong about such an obvious matter of the speed of the phenomenon of gravity. So here it is moving at the speed of light as in the theory of relativity. If the sun suddenly disappears, fewer pushing particles will still reach the earth than from the opposite side, which means that gravity will continue to work for approximately eight minutes. So an obvious thing to explain again and again?, in addition how many times do I have to say that the idea of pushing gravity has no objection to relativity at small distances. Regarding large distances there is no gravitation at all according to the simple universe. Be a little patient and we'll see what I understand about the general attribution.
So really I won't answer now until I have a more serious explanation on the subject of general attribution
Good night and good year
Yehuda
Yehuda,
I don't ask for nothing and miracles do not hold a deaf dialogue with you. It's not a matter of being suddenly offended or questioning my motives.
Why is this speed? How is the relationship between the speed of light and gravity? Under which framework is light the fastest speed for transferring information? It was explained to you that if you change Newton, you have lost a theoretical connection to relativity (both by Albanzo and by Steven Weinberg) and therefore any property you ask from relativity must come from something else because it clearly does not come from your formula. from what?
In any case, I would love to get an answer to a bucket question, which is not asked for nothing: if all your particles do is elastic impact, why is the light bent by them? And if light nevertheless bends, does it bend as Newton predicts or as relativity predicts and if like relativity, how?
for miracles
We are having a dialogue of the deaf, I don't feel like continuing. Decide what you want. I'm retiring. Bye.
Yehuda
Yehuda
So wrong it makes me want to cry….. If your particles are moving at a certain speed then gravity should also depend on speed.
You also need to explain why your persistence mass is equal to gravitational mass. You attribute different mechanisms to both. Basically you are ignoring the problem that you have no explanation at all for why there is persistence mass.
You are ignoring gravitational pull.
You ignore the change in the pace of time.
You avoid the problem of friction (why is there not much light?).
All of these are solved in one equation system of general relativity (actually one equation, which is not too complicated to understand).
to Shmulik
Gravitational changes move at roughly the speed of light because this is the speed of the particles that determine gravitation. So simple it makes me cry.
And when you say that there is no connection between me and relativity, you are wrong, the connection is at least like Newton's and I have no objection to relativity at short distances. I feel like I'm repeating myself. Let us understand the general attribution and we will move on. I have a feeling you're just asking. And by the way, I clicked on the link and got a random caption, I'll check later why that is.
Happy New Year
Yehuda
Yehuda,
Click on the resulting link and see the cartoon
Yehuda,
I mean, you didn't answer anything.
The power "2" is not popular with me... it's Newton and with Einstein it emerges as a result of approximating the equations of the theory of relativity under certain conditions. If I had seen the YouTube I sent, you would have heard Steven Weinberg say that. He also said that there is no way to play with the equations of relativity without destroying it and the idea behind it. Maybe the physicists are wrong but it seems to me that you need to study relativity well to be able to say that. don't you think
Again I will repeat what I already wrote, and it seems that you agree: you not only contradict relativity but also destroy Newton because while he did not propose a mechanism for gravity, you do propose a mechanical mechanism for gravity and therefore you must explain why changes in gravity only move at the speed of light, what is special The speed of light with you (remember, there is nothing to do between you and the theory of relativity) and why gravity acts on light the way it does and, in particular, why light bends the way it does in the presence of your gravity. Why is the light not spread everywhere?
Regarding the aurora, again, the moon has no atmosphere and therefore, if you look at the sun from the moon, you will see it as a glowing circle in dark space. Since your particles interact a lot with the sun - create gravity - and also bend the light (just decide like who) you can't tell me that they don't damage the light. If they hit the light, how come they only deflect the light and yet not produce the same effect of dust and laser beam, i.e. glow?
Since it seems to me that you will be forced to play with your formula, then note what Albantezo wrote to you about it: "...it is only under certain conditions. For example, for light even in a weak field there is a fundamentally different behavior between relativity and Newton." So when you engineer your formula, how would you rather engineer it, like Newton or like Einstein?
Application = study
for miracles
I tried to enter the cartoon and failed. I hope she is not too insulting. My formula is based on the premise that if it is correct then it has an advantage over Newton's formula which was obtained inductively. The fact that it was derived from Kepler's laws, which were also derived from Tycho Brahe's data, does not make it true for the entire universe, but only for the measurements on which it is based. At other large or small distances the formula may be falsified.
Why am I not allowed to "play" with my formula??, I'm allowed! For example, I am allowed to see that it solves the precession of the planet Hema without relativity. And that seemed like a nice thing to me. I don't try to solve everything with her, I just like science and try to understand more about the topics I read.
And of course I could be wrong. I will continue my pursuits. There is a lot of material and I am not sure that I will succeed. so please do not disturb ())
Please do not respond in the coming hours. This is where you learn.
Yehuda
Yehuda
You have no problem with the formula, because it is a formula. It does not describe the world - rather it gives results that are close to observations under certain conditions. The same is the case with Newton's formula. Newton's formula is the result of a mathematical analysis of the observation that the orbits of the planets are elliptical. To be precise: from Kepler's second law it follows that the force is central, and from the third law it follows that it depends on the square of the distance (following in a weak sense of course).
What I don't understand is, why do you think you are allowed to play with your formula to solve any problem that comes up? This reminds me of an old cartoon:
https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=images&cd=&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=0ahUKEwiH-smKiL_WAhVJwGMKHSfRDj8QjRwIBw&url=http%3A%2F%2Fscripting.com%2Fliveblog%2Fusers%2Fdavewiner%2F2016%2F02%2F10%2F1000.html&psig=AFQjCNG65X2Kp8ysf6o7wbnitIxOJfe0sA&ust=1506385139473887
Can't you understand that you might be wrong?
Miracles
I know that I have no mistake in my formula, but my question is why according to you my formula cannot under certain conditions be a result of the theory of general relativity?. And I have two approaches to the answer:- the first, which I don't prefer, which can indeed stem from the theory of general relativity and you are wrong (perhaps, don't get angry), or (second option) that you are not wrong but there is also the possibility of making a small change. For example, an addition assumes a possible disturbance in the gravitational field which is similar to the addition in my formula. I am currently finishing the repetition of the theory of special relativity with its two basic assumptions which are a constant speed of light in inertial systems and the laws of nature are the same for an inertial system. Regarding the general, I am looking for material and so far not with much success. And the calculus of tensors is not simple and is new to me. I also have a problem that my formula can under certain conditions solve the precession of the planet Hema even without attribution. Doesn't this create duplication with attribution and the benefit actually causes a serious deviation? A question is asked: what about the factions of the other stars.?, in short, …..I'm interested!.
So for now bye. I continue with my attributions.
So please respond gently and patiently.
Happy New Year
Yehuda
I will take a little break from memorizing and answer my friends.
Shmulik, I'm using Newton's formula, my change is not in the 2nd power which is so popular with you. My addition is different, it multiplies the whole formula by a certain member. What does it mean? It seems to me that the relativity formula with the curvature of space refers to space as something "pure" and without flaw, my addition gives relativity a certain "turbidity" that would actually be more suited to cosmology as I understand it. Right. The addition will be damaged by the infinity of gravitation and will create an inconsistency with the existing attribution, but perhaps it is better to marry a bride who is a little less than a perfect beauty.
In addition, there is a great difference between the pushing particles and the dark matter and they are completely different. My particles have all the properties that real particles have with friction and the like. Imagine that I would ask for the "right" that you allow the dark matter the right to be without friction? I would have solved the friction problem for myself a long time ago but in my opinion this right given to the dark matter is not "fair" and it would also be unfair of me to use such a right.
Another thing is that my particles are not swallowed by the material and if they are swallowed, they must of course be expelled. I prefer the elastic collision only. But, the idea of Israel is very interesting and I will think about it.
I'm also amazed at your statement that there is no glow near the sun, well there's no need to run into space, it's enough to observe a solar eclipse and see the glow around it.
I also want to respond to the miracles so I will end here.
Please respond gently and happy new year
Yehuda
Yoda
Science is for scientific reactions. Facebook is for sharing personal experiences. If you have a scientific response, respond. Spare us the course of your life. Not very interesting.
Yoda
Science is for scientific reactions. Facebook is for sharing personal experiences. If you have a scientific response, respond. Spare us the course of your life. Not very interesting.
Yehuda
That is not the intention. You have no mistake in the formula.
I have just finished Newton's and Kepler's laws of mechanics and now I am in gravity and after special relativity and after general relativity only then will I check a possible change with my formula. There is still time. I am currently babysitting my granddaughter. so good night
Yehuda
To understand general relativity, it is very useful to understand tensors well.
albentezo,
Thanks so much for the explanation,
Yehuda,
Successfully
I still continue to study the material. patience. Hope to finish by Yom Kippur.
Happy holiday!
Yehuda
Shmulik,
The phrase you are talking about is not a phrase with a name associated with someone. What it shows at the beginning is a naive calculation of the scattering amplitude of 4 gravitons (which is a bit confusing, but actually what it represents in reality is the probability that two gravitons will collide with each other and after the interaction there will be two gravitons left that will scatter from each other with a certain momentum and a certain angle). This is a calculation made naively by "promoting" classical gravity theory to be quantum. The formula looks a bit intimidating to people who are not knowledgeable in the field because it uses very convenient and compact notations that are simply not familiar to the general population (the triangular and square brackets).
The second formula he presents is also nameless as far as I know, and is the string equivalent of the same calculation from earlier. As he explains, it gives the same result at low energies but at high energies regularizes the dissipation. In principle, this is a very common phenomenon that is a cornerstone of string theory - due to the fact that the string has a finite length, in all calculations there appears a minimum size or distance in the interaction that eliminates infinity (because in field theory the infinities usually come from the fact that particles can approach each other up to a distance of 0 and exchange infinite momentum).
Like I said, these specific formulas (before and after the regularization) don't have a name that I know of and I think you'll have a hard time finding information on them, but you can look at something similar. The Veneziano amplitude is a similar scattering amplitude (not talking about gravitons but about other particles) and it was the first time that people noticed such phenomena, of the vanishing dissipation and connection to strings. In fact, its calculation by Gabriele Veneziano is considered by many to be the birth of string theory. I'm pretty sure there is an explanation for this equation even on a level that doesn't include a lot of math that can be found on the internet.
albentezo,
A question that is not related to the discussion but to string theory,
In this lecture Na'ah talks about a formula whose interpretation is a string: minutes 53-55. What is the name of the formula? If you have anything to add about the formula, that Wikipedia would be too complicated, I'd love to hear it
https://youtu.be/U47kyV4TMnE
I returned home. It was fun to be with my family and grandchildren. The stomach is full beyond measure. Please give me a few days to study the subject of gravity and attribution. Albanzo and Shmulik. I also took your last comment into consideration. Let us understand the spirit of relativity. Hopefully I'll find a book on the subject among the hundreds I have.
Good day and happy new year!
Yehuda
Yehuda,
I will try to explain: relativity and Newtonian gravity are different. They are two different theories with different equations, therefore they explain different phenomena and do so in different ways. If you take the theory of relativity and look at it in a certain area (where the energy density is very low) for certain conditions (massive particles), then you get *approximately* Newton's equation. But note a few things:
1. It is only under certain conditions. For example, for light even in a weak field there is a fundamentally different behavior between relativity and Newton.
2. This is only an approximation. Approximation means that the results are *different*, but that to notice the difference you have to look closely. This is a very important detail because with the help of accurate measuring devices it is easy to differentiate between two theories, even if they give roughly the same equations.
The theory you present approximates Newton. But Newton and relativity are two different things, and she does not give any approximation of the theory of relativity. For example, the two examples that came up here - its relation to light is like Newton's (and not like relativity), that is, a wrong relation. The second example is the change in time with the change in the field - again, for you it's like Newton, but Newton and relativity are different. In relation, clocks at different heights show a different time, and this is indeed what is seen in the experiment.
Yehuda,
If you had only seen the five nice minutes on YouTube that I sent, you would have heard Steven Weinberg say that relativity stems from one central idea and from that idea derives its field equation. These equations, when approximating slowly moving bodies, converge to Newton's equation and in particular to the square of the distance. There is no choice but to accept the 2nd power and there is no way to play with the field equations without destroying the basic idea behind relativity (in his words: it would lead to nonsense). Albantezo also wrote similar things. So for the umpteenth time, there is no point in playing with the equations just to get the result you want.
Ironically, you who are so opposed to dark matter, propose another dark matter that not only does not explain phenomena that are well documented but even destroys classical physics. Newton from whom you derive his equation (why from him, because that's what you know and that's why you dressed up. There's no other reason). While Newton never offered an explanation for gravity (see his famous saying) from his theory it follows that the effects of gravity are instantaneous (and not at the speed of light) but in principle there is no problem accepting that light bends near a mass beneath it (light bends because it bends, I don't know why Newton would say .just not enough relative to relativity, in the case of the planet Mercury). With you, since you propose a mechanism of mechanical collisions, there is no way to explain why light bends near a mass, because small billiard balls hitting the light will not simply deflect it in the right direction. The light is not football and the particles of Judah are not goalkeepers who work together. When a rainbow is formed in the sky, it is because the water arranges itself in a unique way so that if the sun is at your back, the reflection of the light creates a beautiful rainbow. With you, the particles move randomly in every direction and there is no reason for the light to always bend in the way it actually bends. We would expect to see a different curvature of light each time, much more random
If your particles do hit the light and the light scatters, I don't understand why near the sun there isn't a glow that fills the sky uniformly (similar to what the atmosphere does). Looking from the moon towards the sun, I would expect the sun not to be a glowing point in dark space but to be a uniformly diffused glow. I would be happy to hear a reference to this.
Yehuda
If the collisions are perfectly elastic then there will be no "attraction" between two bodies. On the one hand, there will be particles that will not hit body A because of the hiding of body B. But, there will be particles that will hit A precisely as a result of the return from B.
In particular, their concentration will not change.
In the case of a plastic collision, in my opinion, there will be a decrease in the concentration of particles in the body area.
To Albanzo and miracles. Thanks for your detailed answers. There is apparently something in principle that I do not understand. Why, if the formula of the simple universe is almost identical to the Newtonian formula at small distances, does relativity not allow it to be a substitute?. Apparently Albanzo is right in that I need to complete knowledge of relationships. And a question for miracles, if the collision of the particles will be completely elastic, will their concentration near the bodies be greater? Food for thought. So please be patient and thank you for your answers and patience, and most importantly have a good year!?
Yehuda,
You keep repeating that the correction you propose to Newtonian gravity does not contradict the theory of relativity at short distances. You have to understand that he is. At short distances, the theory you propose (if you can call it that) gives Newton's equations. Relativity does not. You have to sit down for a moment, concentrate and understand it. In relativity there are other equations called Einstein's field equations. They are *not* Newton's equations, and they are the ones that allow relativistic effects such as gravitation of bodies with 0 mass (like a photon), changing the flow of time a bit, etc. You cannot say that for you the equations of gravity are like Newton's double exponent, nor that they do not contradict relativity - because they explicitly do contradict relativity.
sit down a minute Listen. Digest, then respond. Until you accept that, no one will get anywhere. Don't you think that before you say your theory is consistent with short distance relativity, you should learn a little bit about what relativity is all about? If you had made an effort to study the subject you have been talking about so much for years, it would have been clear to you too that what you have proposed so far is in direct contradiction to relativity. Therefore, there are three possibilities: either your model is wrong (which is of course the correct possibility, as we have already seen by presenting an infinite amount of errors that you choose to ignore), or your model is right and relativity is wrong (of course this is an invalid possibility because relativity satisfies all the experiments have been for 100 years), or that miraculously your model explains the same phenomena seen in the experiment such as changing the flow of time, the effect of gravity on photons, etc., but in a different way. In this case the onus of proof is on you, and instead of evading, you must answer the miracles once and for all and explain to him how your "theory" explains these phenomena.
Yehuda
Nor did you explain how your experiment differed from the Cavendish experiment.
And another nagging question - how does your gravity deflect light rays, but not slow them down?
Yehuda
Are you trying to have your cake and eat it too? 🙂
Your explanation should also work over short distances. Otherwise, my cup of coffee would now be running alone in the room.
Why would there be a high concentration of particles in the mass area? It should be the other way around - some of the particles are swallowed, or at least a few within the mass. If I place a block of palladium in a container containing hydrogen, the concentration of hydrogen in the area of the block will decrease.
What does it mean that a photon has energy equivalent to mass? Your explanation is mechanical, and not based on all kinds of delusional conversions of physics by the ignorant scientists 🙂
Yehuda - I don't understand how you don't see the contradiction in saying that a photon's trajectory is accelerating "because it has mass." It's like saying my cup of coffee is attracted to the earth because it has mass. Do you really not see the problem??
So we finished with the cakes as well. Let's move on to the eyes of gravity. Why does a light beam bend in the passage near Mesa? For the same reason you are thinking of, relativity. After all, pushing gravity has no resistance at small distances to the theory of relativity. But in addition the beam can also be curved due to an above average concentration of pushing particles in the area of the lens mass. A third possibility is that the photon has energy equivalent to the mass and it is the one that is attracted to the sun and the entire beam is bent. A fourth possibility is a thin gas found around the sun or any mass. A total of four is possible for traction and curvature, who is more and who is less. I am not ruling out any possibility. So I don't see any problem with Idus. Note that gravity pushing also has the possibility of negative repulsion if the beam passes through a low pressure area. So far. Happy New Year. Please respond gently. Yehuda
Happy holiday!!!
Dear friends, I am at a delicious holiday dinner. A bit more fun than pushing promises to respond afterwards. Bon appetit to me and happy holidays!
Yehuda
Why don't you pay attention to what I say?
Yehuda,
Like miracles, I don't understand your explanation. Why does a beam of light bend in a mass?
Can you explain again what exactly is going on there? How to think about what is happening there? What kind of scattering of light goes through the encounter with these particles?
albentezo,
I understood the explanation. Thanks.
Albanzo. Maybe write an article about string theory for science?, that sounds like an interesting theory! I heard that it is sloped in dimensions, 10 or even more. I wonder why. Happy New Year!
Shmulik,
It's a bit of a semantic matter. I personally study mathematical physics and believe that there is no reason why any process that occurs in nature can be explained using classical intuition (for example, colliding balls). Therefore, I do believe that it can be said that general patronage explains gravity (up to the barrage of endless why questions, as you said). But it is also clear to me that most people - even among physicists - make a sharper distinction between intuitive explanations and explanations that derive from mathematics. Mechanical gravity (whether classical like the one that Judah and Israel talk about, or quantum like in string theory) explains the origin of gravity by collisions of particles, something that is very easy for us to understand and imagine. String theory even explains this in more depth, because it also gives an answer to the question of where these particles come from and why they exist at all (they are simply closed strings - like rings made of wire. Each string can be torn into two strings, one of which closes on itself, and this will be understood on My hands as a particle that released a graviton - that is, a particle that performs a gravitational interaction with its environment. The explanation of string theory is very beautiful and very accurate, for example it shows why gravity will always exist in any system and every two particles will perform a gravitational interaction, in contrast to, for example, electromagnetism which does not exist in every system and not every particle necessarily performs such an interaction).
I think there is a fundamental difference between the global law of gravity which is not based on a gravitational model, and mechanical gravity which is based on a model. Between general relativity and mechanical gravity the difference is thinner, but still exists, because the source of the interaction between the energy density of a particle and its environment (=gravitational force) in general relativity stems from abstract mathematical considerations. To me they are no less good, but it is hard to deny the aesthetic value of a theory that explains the phenomenon with simple visual means. If only it wasn't wrong...
Ok everyone now knows that the principle of gravity by pushing gravity works and since it doesn't work with air particles under normal pressure and will work in thin air so I hope everyone will agree to my gravity formula of the simple universe which is Newton's formula with the addition.. Do you accept miracles?
Yehuda
I did not understand what you are measuring. We know that there are gravitational forces between nearby bodies. There are experiments that have to take these forces into account, for example in the measurements of the Casimir wind.
So you're saying we'll see attraction between bodies? Cavendish measured such attraction in the open air - 200 years ago. Are you saying this experiment was not done?
Yehuda
The explanation is from the quantum theory, and also the theory of relativity. Even in the glass the photons move at speed c. But, the photons are absorbed by atoms on the way and after a short time are emitted again. This process continues and at the end a photon is emitted from an atom at the end of the track. Due to the conservation of momentum, the photon's path changes when entering and exiting the glass, and therefore there is a refraction phenomenon.
In the theory of relativity, a particle with no rest mass must always move at c, otherwise it would have no momentum (and then there is a problem of what happens when it collides with another particle).
You do not accept the assumptions of the theory of relativity and therefore you cannot use what I wrote "against me".
By the way - we see spectral lines in light from distant bodies. If the speed of light was different in the past then we should see a shift in these lines. In addition, if the speed of light was discussed in the past then chemistry should also have been different, because the electromagnetic force is directly affected by c. This alone should invalidate your claim about the change in the speed of light...
Miracles, the air in my experiments must be thin so that the average free path of the air particles is longer than the distance between the bodies creating the gravitation. If not, no
Almost gravity will be created between the bodies. I wonder if you understood this hand waving. Happy New Year.
Miracles, and how do you explain the speed problem you brought up? And please, gently, without waving your hands.
Yehuda
You are the wizard of waving your hands 🙂 What do you mean that "Newtonian gravity" is an explanation for Idush? After all, you claim to have an explanation for gravity, and rather disdainfully dismiss any problem with your explanation.
Explain something really simple to me: a photon moves through the glass at 200,000 km per second, and as soon as it leaves - it is immediately at 300,000 km per second. How does your theory explain this?
Shmulik. Idush can be done in several cases. A, by the passage of light in areas of different density. B, in Newtonian gravity if photons have the property of matter. C, in relativistic gravity. I prefer A in the explanations, but I have no problem with the other two. Happy New Year.
Yehuda
What is this experiment? Show that there is an attraction between balls? The amount of air will not affect the attraction between the balls, because the collisions are elastic. Do you want to show that there is gravity?
The following is the Sabdarmish A. experiment. inside a laboratory where the air is thin to drop two balls. During the fall, the bodies are supposed to get closer due to the impact of the air particles that will play the role of the pushing particles. What does it look like now? A second and even simpler Sabdermish experiment, in a large container containing thin air hang two balls. The distance between them will be smaller than the distance between the hanging points. This will be proof of the beneficial action of the air particles. I moved the steaks deep in the freezer. Please respond gently. Happy New Year!
Yehuda,
Say, why does light bend under the influence of mechanical gravity?
albentezo,
Given the disregard of the achievements of the last 30 years, why is the explanation of the theory of relativity - the curvature of time-space - still not an explanation of the origin of gravity? Of course, you can always ask additional why questions, for example, why mass distorts space and keep asking why (until the only answer is shut up and eat your chips...to quote Louis CK). In the same way one can ask why questions about mechanical gravity.
Why questions are always problematic. Richard Feynman explains why
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3D2RaDVkylY
Yehuda
And the worst - who puts a steak in the freezer?
Yehuda
I didn't think for a second that it would convince you...
Please explain to me, how is it possible that we see galaxies that are moving away from us above the speed of light? In general, why in your theory does light move in a vacuum at speed c? And how is it possible that particles can indeed move faster than the speed of light?
Miracles. The emission is a result of a light beam that passes close to the mass and then bends. It doesn't matter where it comes from, that's why it's proven to be fresh from a close pass and not billions of light years. It is also possible that the contamination was created by something else, such as the passage of the light beam in the concentration of the gravitational pushing particles. I decided at this point to leave the steak in the freezer. Happy New Year. Please respond gently.
Israel, my experiment with thin air in a vessel when the air particles will act as the pushing particles seems more convincing to me if it is required to be done in weightlessness and it is more expensive. I will try to plan an experiment on earth.
Miraculously the light beam passes by the lens body I believe at a distance of a few light years and bends. This is proof of gravitation for single light years and not for billions
Yehuda
You did not fully understand your explanation of why the gravitational acceleration of a vagus at a distance of 8 billion light years, by a galaxy at a distance of 4 billion light years, does not confirm that general relativity works even at very large distances. I would appreciate it if you could elaborate on what you explained.
By the way - in my opinion cosmic radiation also confirms the theory of relativity. Otherwise - why do all these energetic particles move precisely (almost) at the speed of light of our time? If they were created a long time ago then they should have been slower - then it doesn't make sense that they sped up along the way.
Seasoned Beth
waiting A tremor that indicates, going to sleep.
Yehuda
Why air? This can be done by simple mechanical means.
We will take two large, perforated metal discs. The disks are exactly opposite each other.
We will put the device into a chamber where small balls fly from all directions, the speed of which we can direct as we wish. An image for Lesage's idea.
Lesage and logic tell us that the discs will cover some of the balls, so they will move towards each other. We got lasage gravitation.
The problem is that if a disc moves relative to the cell, the balls will exert an opposing force on it. This is Feynman friction.
Now instead of discs, we will use plasticine. (It is desirable and possible to use electrically charged bodies that the balls can penetrate without distortion, but flexible plasticine that allows the balls to pass through it without distortion will also do the job).
Because according to the principle of the ballistic pendulum above a certain speed the force exerted by the balls on the plasticine decreases significantly, so this time we will not encounter friction. The balls should not be at infinite speed, but high enough to allow gravitation.
N.C. claims that gravitation will be canceled when the disks move above a certain speed, which is true but not relevant. To see this, let's assume that DHA only reacts to particles whose speed relative to it is in the range of speeds 1-1000,000 m/s. So when it moves around the sun its speed is about 30,000 m/s. Gravitation is slightly reduced but definitely not eliminated. Not to mention the moon whose speed is much lower.
In my opinion, we might also get inertia: as long as a disc moves at a constant speed, the force on it balances out. When it goes from one speed to another, the sum of the forces on it is not equal to 0 and resets only when it reaches a new constant speed. But I'm really not sure about it.
This is what I still haven't understood about the Higgs field: how does it know that a body is accelerating? Why only then does he resist it and not at a constant speed?
I directed the question to a professor from San Diego who explained that the Higgs field is like an ocean that resists the ships sailing in it. He only said that I found the expression in his argument, but did not explain what the solution was.
Israel,
If you read my response again you will see that its content has nothing to do with where you heard this quote. For me, it could have been said by a 6-year-old child with a developmental delay or by Juan Maldesana and it would not have changed what I said. If you expect me to be impressed because the person who said this is a physicist, I have news for you… 80% of the people I talk to are physicists who work on gravity and none of them are above talking nonsense every now and then. Not that I am claiming that the claim is nonsense, I think I made it very clear in my response that I think it is inaccurate because it ignores massive and very fruitful studies because they have not yet been proven in the laboratory. Yes, if you take string theory out of the picture, I think the claim is true. But to me it seems funny to take out of the picture one of the greatest achievements of theoretical physics ever. Five years ago, was it correct to ignore the standard model as if it did not exist and say that there is no understanding of the behavior of matter and the fundamental forces in nature, just because the Higgs boson (which is an essential component of the model) has not yet been found in an experiment? To me that's a wrong approach, but if that's what you want to believe, your right.
albentezo,
And what is the speed of the dwarves? Regarding mass, I thought that while there are particles with zero mass but I was wondering if there is a theoretical limit on how light a mass can be if it is greater than zero
Miracles,
Nice YouTube. Shouldn't this border also affect the particles of Judah?
Yehuda,
If you don't believe Steven Weinberg who says in his voice that under the time-space assumption the equations of relativity are determined and that the equations of relativity have no possibility except to reach a coefficient of 2 in the appropriate approximation, then why should you believe my translation? I don't believe so no.
Say, why does light bend under the influence of mechanical gravity?
Good morning to all my friends wherever they are
I will respond briefly to your latest intelligent comments
Israel
The laboratory model you are talking about is interesting, but there are two important things to do. The first to use thin air to get particles with a relatively long mean free path relative to the distance of the gravitating bodies. My calculation for the required pressure is ten to the minus eight atmospheres. Secondly, the Earth's gravitation will interfere with the experiment, conclusion: the experiment must be done in a space station which, in its rotation around the Earth, will give the direction of rotation of the mini solar system that can be done in the experiment. And if anything... Maybe the rotation of the sun and the galaxy, they are the ones that help to overcome the friction...?
Of course I agree with your request that pushing gravity should be given the honor as the only theory that tries to explain the nature of gravity.
Miracles
Believe me I am not ignoring any observation that may/may show a deviation from pushing gravity. Besides, I don't understand how it is that for the purpose of explaining gravity people are ready to bend the whole universe but not ready for some careful billiard balls running around....
Albanzo
Your dwarves brought a smile to my throat but why go for dwarves. Walk on God and angels. You will have many more fans. Our Minister of Education for example. And regarding string theory, I have no opinion.
So good day my friends
And happy new year
Yehuda
http://yekumpashut.freevar.com/
Cause of gravity
Mon, Sep 18, 2017 6:42 pm
snuz2001 snuz2001@aol.comHide
To //////////@mit.edu
Hello mr Bertschinger.
I was present at a lecture you gave in UCLA a few years ago, and if I remember correctly, you presented a writing on the board that said:
Scientists do not know the cause of nature's most obvious phenomena: gravity.
1. Is my memory correct?
2. Is this still the situation?
Thanks,
Israel Shapira.
Sent from AOL Mobile Mail
The recipient was at the time head of the physics department at MIT
Miracles
What are you arguing with Yehuda for? Isn't it a waste of time? These are futile arguments.
Mechanical gravity is not the only theory that explains the origin of gravity. There are many other theories that do this, for example: space is full of invisible dwarfs. They like everything close, because they are dwarfs and it is difficult for them to walk long distances (short legs). So they are constantly trying to push things to be close together. As two bodies are already quite close, it increases their motivation and more dwarves come to help them, that's why the attraction is stronger.
Although this theory is more retarded (much) than mechanical gravity, it is just as wrong. In other words, I fail to understand why one should "give her the respect she deserves" for explaining the origin of gravity if it is a wrong doctrine. There are endless wrong theories that explain the origin of many phenomena. As I said earlier - for all its aesthetic value, at the end of the day mechanical gravity is a model that fails in trying to describe gravity as we understood it 350 years ago, let alone modern gravity.
I agree with the claim that the model produces gravity, and agree that if its problems were miraculously solved (although I insist that the solution proposed here is not really a solution because it is not physical), it would produce gravity consistent with the measurements we had before general relativity. Can't understand what the value of this is today for research (it has entertainment value, and maybe also a pedagogical value about building models).
I completely disagree with the claim that scientists do not understand the origin of gravity. This claim is only true if you ignore the most fruitful field of research in gravity in particular (and in my opinion in physics in general) in the last thirty years. String theory gives an excellent explanation for the origin of gravity, it is consistent with all modern measurements, and it is not only not theoretically disproved (like mechanical gravity) but also has quite a lot of theoretical evidence. It is important to remember, and this is why I said I do not fully agree instead of saying I completely disagree, that it is still on paper and has not been proven in the laboratory.
In my opinion, it is wrong to say such bombastic statements about what we understand and what we don't while ignoring the huge amount of research on the subject, even if it is only on paper at the moment.
is nothing. We're not supposed to do anything about it either. It is enough to show that it is possible to build a computer model of gravity for Sajit or even a laboratory facility.
This would show that the theory works, much to Yoda's delight. Is this what happens in reality? Apparently not, relationships, etc.
What's in Washington? I don't get out of bed for vibrations of less than 5.
Good night.
Israel
I am in Washington State, a little far from San Andreas….we have our fault line….
Israel
Lesage explains gravity by assuming momentum and persistence. He requires plastic collisions but does not know how to explain their nature. It requires a sea of particles but does not give an explanation for their origin. He does not explain how bodies are not excited by slowing down the particles. He does not explain what the origin of c is, and the other phenomena of the theory of relativity.
He does not explain why gravity is limited to c, and on the other hand, he predicts "gravitational waves" from every supernova. He does not explain how there are particles without mass but yes with momentum.
So, he gives a simplistic explanation for gravity? What will we do with it?
Did you feel the tremor?
Why don't you take a look at Lesage?
You still haven't addressed what I wrote:
"It is possible to build a model in the laboratory where we will get systems similar to our solar system, with gravity whose strength we can direct as we wish"
Agree or not?
Israel
How does she explain exactly? Why do particles exert a force on other particles? Elastic collisions? momentum transfer? What is the explanation?
Miracles
Let's agree that there is no explanation for gravity. Is that why we have to insist on an explanation that is less good than what we have?'
Maybe you meant what we don't have 🙂
So do you agree with the statement I brought in English? I sent it to MIT for confirmation just to be sure. Let's hope they respond soon.
But Pushing does explain the source of gravity, without cleverness and without if so then so. Let's give her the respect she deserves as the only theory that does this.
Israel
You know I know that….
In my understanding, the theory of general relativity explains exactly gravity. Mass distorts space. Now you will ask "but - what is the reason Damsa distorts the space", and this is a correct question. And after they answer each of these questions, another question will come, and another question.
And by the way, (special) relativity explains magnetism, but it doesn't explain electric attraction (to my understanding).
Of course that's not the whole story, because it doesn't fit with quantum theory.
But, let's agree that there is no explanation for gravity. Is that why we have to insist on an explanation that is less good than what we have?
Miracles
The GPS clock does not move faster - the clocks in Israel move slower due to proximity to a massive body.
The theory of relativity does not explain the cause of gravitation, it describes and quantifies it. Newton did that too. I don't believe - Gegal.
How about the following sentence:
Scientists do not know the cause of nature's most obvious phenomena: gravity.
Israel
A GPS satellite clock runs faster than a clock on the ground. This is a non-negligible phenomenon, about 45 microseconds per day.
The explanation of relativity for gravity is the curvature of space due to mass inventions, combined with movement in space-time. Think that the earth is swelling at an increasing rate - what you will feel is exactly like gravity.
I know this is an explanation far from reality, but it satisfies my intuition. In any case, it is closer to reality, in my opinion, than imaginary particles that move at any possible speed and contradict all the laws of physics.
To match these particles to observations, simply …. Adapt them to observations. And all this for what? Because we haven't discovered the dark matter particles yet.
And when an observation is shown that contradicts the basis of the idea of particles, it is ignored.
Miracles
What is the shortening of time?
What is the explanation of the theory of relativity or any other theory besides pushing to the source of gravity?
What is a hangover?
Shmulik/Albanzo
look at this:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=osvOr5wbkUw
A particle with the energy of a baseball 🙂
Yoda
For nothing.. The fact that pushing can theoretically produce gravity, it still does not mean that this is also what is really happening. Even a government without ultra-Orthodox can theoretically be stable..
I think we're having fun.
I believe that no one here except Yehuda claims that pushing is indeed the cause of gravitation. The question as I understand it is: does pushing theoretically work?
The answer is yes, as long as the masses are static. Otherwise you get Feynman friction, which is why Feynman spoke of it as disqualifying pushing outright.
If Feynman friction is overcome (I suggested a way), then pushing also works with dynamic masses.
When I say working, I mean that a model can be built in the laboratory where we get systems similar to our own solar system, with gravity whose strength we can direct as we wish. Is there anyone other than the Israel National Police, you evade, pretend you don't understand and don't listen and you have a logical error and that's why I don't answer you anymore, I don't agree?
"After all, the theory has been tested by almost every serious scientist in the last three hundred years and it was found to work except for the known problems: friction, heating, aspiration.."
no no no. There is a consensus that mechanical gravity is a very elegant and interesting explanation for the origin of Newtonian gravity (which, as mentioned, fails due to several important points). I have never heard a single person claim that relativistic results can be reproduced with it, which we know for sure to be true. In other words, this is a very nice theory of gravitation, but it fails to reproduce gravity as we understood it 350 years ago, let alone modern knowledge. If anyone has a way to reproduce Einstein's field equations with the help of mechanical gravity (which is not quantum, because that is what we do in string theory as I explained before), I would love to hear it - good luck.
Shmulik - it is indeed customary to measure masses of elementary particles in electron volts, but there is no particular reason to do so. It's also possible in grams, it's just inconvenient because everyone will have a mass that starts with lots and lots of zeros. Regarding the mass, no. There is a quantity called the Planck mass and it is of great importance in physics, but it does not play a role similar to the Planck length in gravitational theories (the length from which classical theory began can no longer faithfully describe reality because quantum effects become comparable to gravitational forces). There is no obstacle for a particle to have a mass smaller than the Planck mass. After all, we all know quantum particles with mass 0 such as the photon, the gluon and the graviton. In fact, all elementary particles have a mass less than the Planck mass.
Israel
If mass is the result of particle collisions, then it makes no sense to say that particles have mass. If the particles have mass then this mass increases at high speeds, unless you completely dismiss the theory of relativity.
You cannot solve the gravity problem by saying "particles have mass and that's it".
The speed of the particles is very relevant to explain gravity. I don't understand, I thought we had a real explanation for an observed phenomenon. According to what you are a nation then it's just hand waving. It takes a lot of chutzpah to dismiss all modern science like that.
Time both lengthens and shortens, see any GPS book. If you do not accept the assumptions of the theory of relativity, then you have to give another explanation for these phenomena.
I never talked about the LaSage model, because it is a much worse explanation than relativity. The "pushing gravity" is not different in principle from Ptolemy's universe - hanging on hanging on hanging. Even if LaSage's model didn't have a problem with friction that doesn't make it correct. Let's invent space octopuses that pull the bodies to them, and their hands weaken at great distances. Do you really want to go back to Greek mythology to understand the world?
The basis of the theory - "a simple universe" - lacks any grip on reality. Didn't we go through this phase 120 years ago?
Nissim will address Israel's comments. He is right.
Israel Thank you for your help in my difficult times. You earned your stake and your wife's with respect!
Happy New Year
Yehuda
Miracles
Definitely! And now explain the relevance of the following questions:
"How do your particles have mass?" - irrelevant. You will get gravity pushing even if the particles are small chocolate teddy bears and melt honey blocks that the teddy bears are trying to eat.
"What if time shortened and lengthened" - time lengthens, not shortens. Pushing does not pretend or is supposed to address this issue, although it has an alternative explanation.
"What is the speed of the particles?" is irrelevant, as long as it is high enough to produce gravitation.
You have not yet answered the question:
"You don't believe that it is possible to build a model in the laboratory that would produce Lasage gravity with simple materials but with one major problem and that is friction? And if the bodies simulating the masses in the model are not in motion then we will get gravitation whose strength we can direct as we wish?'
They tell you to organize the attack on Luxor airport, and you start to investigate: what are the bombs made of? (Irrelevant as long as they do what they are supposed to do, damage). How will you know if the range of planes comes from Hadar to Luxor? (We were already there in 67 and another 100 times after that). How does the lift on the wings work (works, works, what does it have to do with the mission?)
If you don't believe that the Lesage model produces gravity, then why do all the scientists claim that it does?
Israel
A scientific theory has to explain all the observations of all the theories it replaces. You do not agree?
Miracles
Most of your questions about Lasage particle properties appear and are at least partially answered in the Lasage article:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Le_Sage%27s_theory_of_gravitation#Predictions_and_criticism
After all, the theory has been tested by almost every serious scientist in the last three hundred years and it has been found to work except for the known problems: friction, heating, aspiration...
You don't believe that it is possible to build a model in the laboratory that will produce Lasage gravity with simple materials but with one major problem and that is friction? And if the bodies simulating the masses in the model are not in motion, then we will get gravity whose strength we can direct as we wish?
So what is all this two-and-a-half-hour investigation for, what are the particles made of, what are the particles that make up the particles, what are their properties, what are their plans, as if poor Yoda should know..
Yehuda
By the way - the neutrino is thought to have a mass of about 37-10 grams, so how does that fit with what you say? We should see collisions between them and your particles, shouldn't we?
Yehuda
You are not answering me….. I asked some questions. How do your particles have mass? What if time shortened and lengthened, what is the speed of the particles?
Yoda
You're right.. I actually thought about it 2 minutes after I sent the response, but I was already with my dogs in the mountains..
It's my fault!
Miracles
For you and your wife I will prepare, as you requested, a steak without fat, delicious and seasoned... from a dark mass, h h h h h, well, well, we'll get along.
And regarding your response, I do not calibrate, I established the idea of gravity pushing and understand that there is a mean free path and that is where everything comes from.
And for Israel, if r is very small relative to a, then r divided by a tends to zero and all the other part tends to one and the formula takes the form of Newton and comes to a redeemer's point (or gravitation) and then we have gravitation at small distances. In a gas under normal conditions there is no attraction because the average free path of the molecules of the gas is small relative to the distance between the bodies. If we dilute the gas, the free path will increase, and so will gravitation.
You didn't think about that.
Le Sage didn't think either.
That's why it's the "simple universe" and not "La Sage theory", and not "pushing gravity" for nothing.
to Shmulik
I have an idea, maybe you could translate the relevant part into the next comment? I'll go back in and see what it's all about.
Happy New Year
Yehuda
http://yekumpashut.freevar.com/
Yehuda,
He says it explicitly at 26:58. broke before? your reply?
The mass you calculated, is that their rest mass?
Yehuda
If, as you say, a is equal to the average free path of the particle about the size of 1.55 light years, then how do we get gravitation at short distances, say one meter?
In the original Lasage, there are no collisions between the particles, otherwise we would get gas (and not rise!), and gas, as we know, has no attraction as we can prove if we spread two sheets in front of each other..
Yehuda
I like with fat, but my wife won't let me...
In any case - you did not answer my questions. My understanding is that all you are doing is calibrating numbers to match your formulas to reality. The "2" in the Newton/Einstein equation has a meaning that derives from the assumptions of the model.
to Shmulik
I went to the link you sent me to. My English is not good, but I still understood something then:
A. Despite Bach's cute piece, I don't think that beauty is the "guide" to the correctness of theories. Although the example of deviation in the piece was jarring. Only measurements will determine the correctness of a theory.
B. I was not convinced that the 2nd power of R follows from the theory of relativity. Stephen also stated that this does not follow with certainty from Newton's words.
third. To your difficult question about the nature of my particles pushing gravity the truth. I don't know if I should give them systematic or quantum properties and I reserve the right to do so later, at the moment I treat them with Newtonian sensibilities. Like tiny billiard balls as you defined. If there is a constraint in the future I will change it. I also don't know if I have to give external theory properties to parts of my theory. Do I have to do relative calculations with them, I don't know. Maybe there is an evasion here but I really don't know.
for miracles
When we count then hydrogen really has one proton and I have ten fingers and even if I get 9.8 fingers in the calculation I will complete to 10. But what is the mass of each finger or each proton. It will always have uncertainty. What is the speed of a body there is certainly uncertainty. An example brought to me by someone from the academy told me that the same is true even with a spin that can only accept certain values, and if the calculation came out with a spin of 1.99, then it was clear to him that it was a spin of 2. (And maybe there could be a spin of 1.99??) There is no doubt that I need to upgrade the definition So that you can also receive things with absolute certainty. We will think about the holiday.
I believe that the speed of light was different in the past and not only me there are also many others who believe in its change. Let's not forget that a greater speed of light in the past would have obviated the need for an inflationary universe.
For my particles, this is the rest mass, but even in my blog there is a reservation about the above-mentioned size and the way it is calculated, mainly in terms of the required relativity or not. I'm allowed?.
I have a dilemma with attribution. I don't know if I have to put her in. Sometimes I can solve with my theory problems that were solved by the theory of relativity. For example. Let's take the addition (e^(-r/a)) which I multiply by Newton's formula to make it the simple universe formula. If I take a (to remind you a is equal to the mean free path of the particle) as the size of 1.55 light years, which is about 98,000 astronomical units, this would solve the precession problem of the planet Mercury, without consuming relativity. So what am I supposed to do now?, ignore it? Or maybe try to continue to damage every relative, petty idea. I have the feeling that I am treating a delicate structure and it is difficult for me to decide how to perform the next step. Especially when there are hungry wolves looking to grab some stack.
So that's it, I'll make me a coffee and just a question for the record, don't draw miraculous conclusions from this, but do you like steak with or without fat ()
Good evening and happy new year and please respond gently
Yehuda
http://yekumpashut.freevar.com/
Hebrew
Miracles
Too bad about the arguments with Yehuda. Go do more productive things. The feeling is getting stronger and stronger in me and probably in yours too, that Yehuda's knowledge and understanding of physics is, at best, loose.
Yehuda
In science can not be accurate? How many protons are there in the nucleus of a hydrogen atom? Let's be scientific - to how many precision digits do we know that the result is 1.0000000?
Regarding the constant c - first you need to understand that c is not a property of the light, but of the space itself. Because of the assumptions of special relativity, massless particles will always move with speed c. How exactly does this derive from your theory - I would be happy to receive a brief explanation. In addition, stability over time is related to bonds within molecules and probably the chemistry itself had to change over the years. We have billions of year old rocks on Earth and I don't think anyone thinks the chemistry was different when they were formed.
Yehuda - if you change an assumption of a theory then the theory changes. It's simple logic. I think that the non-invention of dark matter is not a good enough excuse to cancel the measurements of the size of the universe, the age of the universe and in general the whole big bang. A bit pretentious, isn't it?
In connection with the example I gave about gravitational acceleration we will observe: the newly observed body at a distance of 8.7 light years, and the body causing the acceleration is at a distance of 3.7 billion light years. Therefore - medium steak please.
You wrote that your particles have mass. It's a bit hard for me to understand how they have mass, if they create the mass. I would love to know how fast they move.
You still haven't explained to me how both speed and gravity affect time.
And another question - how can it be that a photon of long radio waves and a photon of X-rays move precisely at the same speed?
Yehuda,
I do not understand. What you calculated is their rest mass (or for you the mass does not depend on the speed)? Are they really, really small billiard balls (if that's even possible) or are they elementary quantum particles?
Steven Weinberg
The silent section starts at minute 18:20 and concretely from 22:20 until about 27:00
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x9Jqgxh6D2s
to Shmulik
It is absolutely not necessary that a device that is sensitive to natrino will also be sensitive to even tinier particles of P.G.
And in addition, particles can be weighed and if desired also in tons or electron volts. as you want. I preferred grams.
With your permission, I can't find Steven Weinberg's YouTube. Send me a link again. you are welcome.
Yehuda
albentezo,
Don't think for a second that I'm trying to drag you into a discussion, but I have two questions about something that Yehuda wrote that I'd love an answer to.
He wrote: "And regarding the size of the gravity pushing particle, I once did a calculation and got that my particle is of the order of magnitude of 6.3 times 10 to the minus power 37 grams much smaller than the estimated size of the neutrino. But the quantity is greater and it is the one that affects."
Does anyone even talk about elementary particles in grams, does it have meaning in relativistic velocities? Elementary particles are not always measured in (G)EV (sorry for the Hebrew, don't want to block them)
Another question: Is there a lower limit to the mass? That is, is there a lower barrier below which Planck wakes up and says so far?
Yehuda,
In the meantime, the response that bears your name has not been released. I will update when it is released
I did not understand. Obviously, according to your claim, the effect is *gravity* and it occurs by normal mechanical means: collision, like billiard balls. Neutrinos are created in the sun in huge quantities, but because they hardly interact with matter, it is very difficult to detect them, but an abundance of particles that produce gravity by collision, it is really requested that they appear in our detectors. There are many orders of magnitude more dark Judas particles than neutrinos, their effect is much more dramatic and therefore, you would expect them to show up in our detectors. this is not happening.
So to produce gravity by collisions in space yes, but to ask them to collide with detectors in underground mines protected from cosmic radiation no?
You wrote to Nisim that "...we disagree on whether the almighty Einstein changed the power from approximately 2 to exactly 2"
I don't think you bothered to watch the YouTube that Steven Weinberg made just for you. He says no, categorically and absolutely. Under the assumptions of the model there is no way to change from exactly 2 to about 2. It has nothing to do with uncertainty,
but to go where the pencil leads you after the assumptions of the model have been made. Change the assumptions, you will get a different theory, but it will have to reproduce all the successes of general relativity. Do you want me to give the YouTube link again?
for miracles
I was getting ready to eat breakfast but I see that I will have to eat lunch straight away. But after the current reaction to you, I'll go eat.
So we both agree that before Einstein Newton's 2nd power was in question. We disagree on whether almighty Einstein changed the power from approximately 2 to exactly 2. So in short I tell you that in science there is not and cannot be exactly. The measurements that will try to check the "accuracy" will always do so with a certain uncertainty, and I'm not just talking about Eisenberg's uncertainty principle. There is always uncertainty in the determination of facts in science. point.
What I want to do now, maybe next holiday we can do better, is it possible to add a fourth assumption of the "disturbance of space" to the three assumptions for the passing of the phenomenon. In our case the phenomenon of gravitation. And by the way, I already said that I don't accept the assumption of constant C and I apologize to Einstein. Each generation and its C. A change of XNUMX cm per second per year due to the expansion of our precious universe, and its cooling. But we'll see what we get on the holiday, maybe the ease of the holiday and my satisfaction with the food will make it easier for me to draw fateful conclusions in science. So here I said that the assumption of constant velocity C is not acceptable to me, but unlike you I am not sure that it will collapse the theory of relativity. But, we will have to accept that an atomic bomb dropped by North Korea in a year will produce less energy than today because the speed of light in a year will be smaller. We will wait for an explanation after the holiday.
And we have come to the last section of your response - the gravitational cooling that was discovered at a distance of 8.7 billion (!) light years.
First of all, calm down. Your stack hasn't even been bought yet. There is great uncertainty in your winning.
What you are showing here is not confirmation of gravitational acceleration to a distance of billions of light years that is billions of light years away. What is meant by this? I am ready to accept that, for example, a solar system that is billions of light years away will work the same way our solar system works - not that I have proof of this, it is just a friendly agreement given in a moment of weakness and hunger by a responsive person who reminds me of psychic stacks for a hungry person And impairs my gastronomic scientific mindset. This is a clearly unscientific method and I also say it is ridiculous. But it is what it is and these are your friends. Let's go back to the gravitational cycle. What you see there is a dot. Gravitational or not is another question. If it's convenient for you to add dark mass as the king's hand to make it a "gravitational waste" you will.
Enough, I broke down, I'm going to eat.
Please respond gently
Happy New Year and a pleasant Christmas dinner.
Yehuda
http://yekumpashut.freevar.com/
Shmulik
I am honored that you used my name in your pending response. I promise not to accuse you of plagiarism.
Neptune is not created by the sun alone, but you will be forgiven for that too.
And my answer to your question: "Why don't your particles wash away these detectors and the detectors that are used to find dark matter?" It is precisely my particles that have a wonderful effect on the detectors and... show gravitation! There is no other practical explanation for gravitation. You just have to believe.
And regarding the size of the pushing gravity particle, I once did a calculation and got that my particle is of the order of magnitude of 6.3 times 10 to the minus power 37 grams much smaller than the estimated size of the neutrino. But the quantity is greater and it is the one that affects.
You get encouragement from the fact that gravitational waves were only discovered after 111 years, so come and I will encourage you a little more, Kepler's laws were discovered over a thousand years after Ptolemy's geocentric thought, and Sabdarmish was discovered 6000 years after the creation of the world, the one whose birthday we celebrate this week. Is this a reason for encouragement?, I don't think so, but today I'm big, I'm ready to give the fans of the dark mass a few more hours to discover my wimp parts or whatever it may be. We wish good luck to the detectors that are being built for this purpose,
Have a good day and a happy holiday and a happy new year.
Please respond gently and smile!
Yehuda
Yehuda
You look at Newton's formula as if Newton guessed that the power was 2. But, that's not the case. Newton came out of Kepler's laws, and these formulas are the result of Tycho Brahe's measurements. If that was the whole story then it might be possible to say that 2 is an approximation. But, one gentleman named Albert Einstein came and showed the whole world that Newton's formula is based on 3 simple assumptions (equivalence of reference systems, constancy of c in any system of axes, and the principle of equivalence). That's it, 3 simple principles.
To say that Newton's formula is wrong, you have to show that one of these 3 assumptions is wrong. Which one (or which ones) do you think is wrong?
By the way - another case of confirmation for the theory of general relativity at large distances - gravitational acceleration - at a distance of 8.7 billion (!) light years.
I like steak medium….
Good morning miracles
You wrote that I wrote that the theory of relativity was proven by induction. God forbid I do this scoundrel act! What I wrote is about Newton's well-remembered gravitation formula, and of course I should have emphasized that. Below is the quote:-" I find it hard to believe that you still insist that a formula proven by induction on a small group will also be true for the entire universe??" End of quote. This is what I wrote, and I will emphasize again and explain: - Newton's gravitation formula was proven by induction on a small group - the planets in our solar system, and with all the faith we have in it since we were born, we must not draw conclusions about the entire universe from it. There are always uncertainties and inaccuracies in measurements, so you have to understand that a conclusion from measurements is not just one formula but an infinite number of formulas. For example, maybe the power of R is not 2 but 2.0000000001? And the universal gravitation constant is not exactly as written in the formula, and maybe Newton's formula with the tiny product of Judah (e^(-r/a)) is the correct one? more and more. And in addition, all of these infinite formulas are correct and match the measurements we made. And we won't be able to cancel any of them until we make a new series of more accurate measurements or for a longer range. Of course, until we do that, of all these formulas we must choose the simplest one, Newton's formula. (The choice according to Ockham's razor. And it is a choice of convenience!) A more exhaustive explanation in my blog article.
In addition, in your response you wrote that I myself gave an example that Newton's equation is valid even at large distances. You're right, you're right, you're right, I sinned, I sinned, but it came to me perhaps out of the joy of writing, or because of the tiredness of the quiet night of Herzliya at three in the morning. I should have emphasized that if Newton's gravitation formula is correct, then the escape velocity will be 11.2 km per second, but if another formula from the infinite number of other correctnesses is correct, then we might reach a different result by a few centimeters per second more or less.
So please respond gently
And may it be a good year for us and for all the people of Israel.
Yehuda
http://yekumpashut.freevar.com/
Miracles
I follow your discussions with Yehuda. Nothing came of it. Yehuda is a master at inventing loose theories. Really cool
Yehuda,
In my previous pending reply, I used your name by mistake
a question
According to what you claim, the moon rotates around Earth due to the pushing gravity. That is, some of your dark particles get stuck in the Earth, enough to produce gravity for the moon (if I understand correctly).
Neutrinos, which are produced only in the sun, and therefore their quantity is much smaller than your particles, pass through CdWA without blinking. Nevertheless, "once in a while" they get stuck in an atom and produce a flash of light, which is picked up by detectors specially built for this purpose.
Why don't your particles wash out these detectors and the detectors used to find dark matter?
By the way, they don't try to find dark matter for 80 years, much, much less. If I'm not mistaken, Zwicky (the one from spherical villains) proposed something like this and Vera Rubin strengthened it a lot by individual observations of individual galaxies, but only relatively recently are detectors built for you. I remind you that it took 111 years to find gravitational waves.
Yehuda,
If you want me to stop pestering, just say because it sounds to me like you're horribly underestimating the question about gravitational waves.
From what I read, Poincaré predicted that there must be gravitational waves traveling at the speed of light as early as 1905 because of the space-time geometry presented by special relativity. According to what is written, Einstein joined the idea after he published the theory of general relativity, although he was initially skeptical (still in Europe) and came to the conclusion that there must be gravitational waves.
See what a miracle, about 111 years later, these waves were discovered by the collision of two black holes at a distance of a billion light years from here (or a few hundred million light years, I don't remember), speaking of examining the theory at a great distance
So the fact that you don't understand what gravity waves are or barely understand why there are sea waves is nice but it doesn't exactly help you. As explained to you by Albantezo (and also by Steven Weinberg if you bothered to watch the YouTube I sent), the theory of relativity is based on a central idea from which elements that must exist and elements that must not exist are derived. Gravitational waves must exist and must not travel above the speed of light and this is exactly what was discovered. According to Newton, there must not be gravitational waves because the effect is instantaneous and since you are essentially proposing a Newtonian universe (you are in no way proposing a different geometry than Newton), you must not have gravitational waves, but they do exist. This is a contradiction.
http://www.science20.com/relativity_and_beyond_it/henri_poincare_predicted_the_existence_of_gravitational_waves_as_early_as_june_5_1905-165539
Yehuda,
Are you talking about the wavelength of the graviton...!? This is how it looks..
As if the gravitational effect, of the earth, ends at a certain distance... ok...
But, why would gravity work differently in other galaxies? (I can't understand the basis of your words)
Or are you talking about the power that lies between the galaxies?
That is, in the empty spaces of space. You claim that this empty space is filled with PG particles instead of dark energy/matter, yes?
Yehuda
Relativity proved by induction? what are you drinking there
You wanted proof that relativity works even at golden distances. May I ask why you ignore it?
You yourself gave an example that Newton's equation is valid even at large distances. May I ask why you ignore this too?
Miracles
I find it hard to believe that you still insist that a formula proven by induction on a small group will also be true for the entire universe?? I went into Stimatsky in Herzliya and all the books were made of paper, so can we conclude that all the books in the universe are made of paper?? Will you conclude that Morbi wrote his laws on paper because that's how it is with Stimatsky?
I don't understand you, we are wasting energy on an obvious thing.
And look what you did in addition you convince me that the formula I used is incorrect and in fact there is another and it is the correct one regarding free fall. Beautiful and even excellent. But imagine that I would tell you that you are wrong and that my formula is correct! It is true that I got 98 km per second, but 86.8 of them are dark and I didn't see them as transparent, and they have to be subtracted from the result. Then 11.2 km per second came out, which is exactly what should come out. Dark speed is just like your dark mass. What are you saying miracles?, eighty years looking for proof of the dark mass in Sarn, in America, and maybe also in North Korea, and not exactly finding it, do you want a few more hours to search?, I have no problem with that.
Good night and good sleep
I was wrong - Happy New Year
Please respond gently it's just science
Yehuda
http://yekumpashut.freevar.com/
Shmulik
Your question :- Why are there gravitational waves?
Answer :- I really don't know why there are gravitational waves, I don't understand the relativistic explanation for gravitational waves and I don't know if gravity pushing might support it or not. I hardly understand why there are waves in the sea. I apologize. I wasn't in that class in high school when they explained about gravitational waves.
So please don't make waves and respond gently
Yehuda
Yehuda
Calculating the escape velocity relies on the fact that at infinity the gravitational energy is 0, and that its strength at any distance is -
G *M*m/r^2. We perform integration and get that the potential energy is -
G*M*m/r-. From this we get that the escape velocity (or - as you said - the velocity that a body will reach due to falling from a long distance) is
(sqrt(2*G*M/R
Place data and you will get 11,200 meters per second. Change Newton's formula and you will get a different result. This is XNUMXth grade physics.
What are you doing, Judah? You say "You don't know what happens at great distances!!" And then you say "but I do know!"
And why - because they haven't found what the dark matter is to this day. that's it.
You dismiss relativity and quantum theory. You have no explanation for the relativistic time effects - effects that are not scientific curiosities - they are tools used by engineers. You ignore that there is indeed evidence for the correctness of the theory of relativity even at huge distances. In my understanding, the Doppler effect also exists for distant galaxies. Relativity has no effect on this effect?
Miracles
In your response you say: "The basis for this calculation is that Newton's formula is valid for any distance." End quote.
My answer is that there is not and cannot be a firm formula for any distance because the firmness of a formula can only be done by measurements and as we know there is no possibility of infinite measurements. So it is true that Newton said that gravitation works according to his formula at any distance. so he said Is that true??, absolutely not!. Did he test at any distance?, no!, could he test at any distance??, also no! Therefore the quoted sentence you said cannot be true! Is it understood?, it's really simple.
Let's go back to the example I gave. Say miracles, if you checked the gravitation formula in the solar system at a distance of less than a thousand light years, do you really think that it is possible to deduce from it the whole universe without measuring??? Newton determined his formula by induction, that is, he gathered all the measurements known at the time up to the planet Saturn and derived from that his gravitation formula up to a distance of about ten astronomical units from Saturn. As soon as he saw that the formula worked on all the known planets then for him it was the entire known universe, and he was happy to declare that his formula was true for the entire universe and was accurate because it was the universe that was known to him. But not for us. Our known universe is trillions of times bigger than Newton's universe and without measurements you cannot state that the formula is correct even to one light year. So it's true that measurements were made, in galaxies, at billions of times distances and it's a wonder that the famous Newton's formula is falsifying in the galaxy! It predicts gravitation too little, and you miracles tell me that "Newton's formula is valid for any distance???"
excuse me please Science is offended.
I hope the point is clear
Happy New Year, and please respond gently. It's just science.
Yehuda
http://yekumpashut.freevar.com/
Yehuda,
Why are there gravitational waves?
Albantezo wrote "In other words, the relativistic phenomena that Nissim questions you about are explained in relativity precisely by the correction that lies beyond the Newtonian approximation. You have a different correction, and therefore you cannot say that you explain relativistic phenomena in the same way as the theory of relativity.'
According to Newton, there is no such thing as gravitational waves and if I understand your work correctly, it is all contained in the Newtonian world.
Gravitational waves have been measured, while with you (again, if I understand correctly), there must not be anything like that (because with Newton there is none). Isn't this a contradiction to observations?
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gravitational_wave
On the kippak n.c., bay.
Yehuda
You didn't respond to my example.
By the way - the example you gave of blocked fall speed shows exactly the opposite of what you claimed 🙂 The basis for this calculation is that Newton's formula is valid for any distance.
anonymous
The "s" that appeared was my mistake, he saw it as a one-time mistake.
In addition, you asked why gravity would work differently at far distances.
The answer to this question has already been examined by the best philosophers (for example David Yom the Englishman) and the decision is that what we will examine is what exists. Deciding to go beyond that is a gamble.
I will give you an example:- v=g*t This is the formula for the speed obtained in free fall on the earth, for example after one second it is 9.8 meters per second and after two seconds the speed is 19.6 meters per second. What do you think the speed is after 10,000 seconds?, the speed according to you should be 98 km per second. But there is a problem with this because the free fall speed to the earth cannot be more than its escape speed which is 11.2 km per second. From here you have to understand that what works in the short term will not necessarily work in the big one.
The problem with the spread of gravitation in space is that they ignored a possible disturbance that could have to its progress in space something like turbidity that affects the spread of light intensity in space. Hence, the gravitation formula must have a term that expresses this disturbance e^(-r/a) where e is the natural number, r is the distance between the masses creating the gravitation, a is the mean free path of the two gravitational pushing particles (the collision between them reduces the formation of gravitation). Therefore, at distances r very small relative to a, the term e^(-r/a) tends to 1 and its multiplication in Newton's formula gives the Newton formula, on the other hand, at distances r very large relative to a, the term e^(-r/a) tends to zero and so on by multiplying it by Newton's gravitation formula.
I currently do not know the size of a, I believe it is over a light year.
And regarding your proposal to change the name of "The Simple Universe" I will do so when I change the name Sabdarmish
and miracles,
It would actually be nice to gather the company of scientists for a fun evening by the fire, with some astronomical observation.
and to Israel
It doesn't seem to me that anyone thought about my formula.
Happy New Year
Sabdarmish Yehuda
we
Yoda's idea is brilliant, and so did most scientists in history, from Newton to Feynman, but suffers from many problems, chief among them friction.
Yes. Ral, yes, you didn't understand again.. Understanding what you read is not something today, I recommend reading messages in their entirety and not just a part 🙂
Happy holiday and Regards from Atzevoni
N.C.
And I thought you wrote in the last comment that this is the last time you answer..
So once again I didn't understand?
chow Regards to blowing water.
Yehuda
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/SS_433
I'll settle for a good steak, thanks
By the way, Yehuda, would you consider changing the name of your theory to something more catchy, such as, for example, allow me to suggest the 'Tsunami model of particles'. What do you think? ?
Yehuda
Thanks.
At the same time, I fail to understand why gravity would 'work differently' at far distances. After all - these are the same materials and these are the same energies and these are the same physical conditions as in near space.
Our Israelis, say what you will about Yehuda's theory (O.S., as he decided to call himself now.. I will not be surprised if he suddenly decides to appear with a casket hat, a leather jacket, and a fashionable beard... :)) )
But, his idea is brilliant… ☺
to Albenzo
Thanks for your response. It seems I have no choice but to learn how relativity as we know it gives a weak field approximation of Newton's equation and then draw conclusions about my formula. I will delve into the subject and respond. I will have something to do on the holiday.
Thanks again Albanzo and Happy holidays.
Yehuda
Yehuda,
The theory of relativity as we know it gives in the weak field approximation the Newton equation. You can see this for yourself in any relationship book. If your model approximates a different equation, it is not the same model as relativity. It is quite possible that different models will give the same approximation. For example, string theory - this is a different model of gravity (very different, it's quantum at all), but it roughly produces the Einstein equations (that is, the general theory of relativity), and they roughly give the Newtonian equations.
In the case of two different models that give the same approximation, it can be said that all the phenomena (in the area where the approximation is valid) will be the same, assuming that they are local (not dependent also on other places where the approximation may not be valid). But with you there is something different - your equation of motion in a weak field is *different*. It gives the same approximation as general relativity only at the edge, but all relativistic phenomena are exactly the phenomena that are not explained by this approximation (if they were explained by this approximation, they would be part of Newtonian mechanics). In other words, the relativistic phenomena that Nissim is questioning you about are explained in relativity precisely by the correction that lies beyond the Newtonian approximation. You have a different correction, so you cannot say that you explain relativistic phenomena in the same way as the theory of relativity.
In conclusion - the theory of relativity explains certain phenomena and also gives an approximation of Newton's equation. You have another model, which also approximates Newton's equation. This does not mean that it explains the things that sponsorship explains. You must show this explicitly, or face your model contradicting the observations.
I'm starting to get a little tired, especially from having to type details over and over again. Those who are still interested can see the explanations in the same article from five years ago:
https://www.hayadan.org.il/astronomers-reach-new-frontiers-of-dark-matter-130112/comment-page-17/#comment-327356
out of it:
"Bottom line, the purpose of all this discussion was to reach the point that there might be particles similar to Lasage particles with the following property: when they hit matter, they transfer momentum to it without wasting it in the form of heat, but above a certain speed they pass through the matter without affecting it or them.
Get on the freeway.
The Autostrada is a Lesage model in one dimension of length. Instead of particles in all directions and at all speeds, we concentrate only on those particles that move along a given straight line, in both directions and at all speeds. We will concentrate on speeds up to 500 m/s.
We can compare it to a freeway with 100 lanes, 50 in each direction, north and south. The car moves at speeds of 10 m/s, 20 m/s, …. up to 500 m/s. For the purpose of the discussion, we concentrate the cars with the same speed in one and only route. Therefore, in route number 1, all the cars will be with a speed of 10 m/s, then 20 m/s until route 50 where there are cars at a speed of 500 m/s. The same in the opposite direction.
1. If we draw an imaginary line across the freeway, the total momentum of the cars crossing the line appears to be 0 because the cars from both directions offset each other.
2. If instead of a line we use an entity, for example an electric force field, or for the sake of illustration a sail or a special plasticine that the cars can pass through without distorting it, it seems that we also got 0 momentum on the plasticine.
3. Let's assume according to what we concluded before, that the plasticine is only sensitive to speeds of up to 100 m/s. Cars passing the plasticine at a speed relative to it higher than 100 m/s are transparent to the plasticine and it is transparent to them. Below this relative speed, the cars will exert a force on the plasticine.
4. Let's see what happens when we put the plasticine across the freeway:
All cars with a speed of 110 m/s and above, in both directions, are transparent for the
5. The cars with a speed of 100 m/s or less exert a force on the pulse, but offset each other. The total force applied to the pulse is equal to 0 and it remains in place. (The same thing happens to any sail in still air. The fast air molecules offset each other).
6. What will happen if we put a leveler or a second sail moving at a speed of 10 m/s to the north relative to the highway?
The cars on route number 1 heading north, which relative to level A were moving at a speed of 10 m/s, will have a speed of 0 relative to level B. Those in route 2 who moved at a speed of 20 m/s relative to A will move at a speed of 10 m/s relative to B, etc. All the cars in all the routes in the north direction will be seen by Level B as traveling at a speed 10 m/s lower than they are seen by Level A. On the other hand, the cars traveling south will be seen by B as traveling at a speed 10 m/s higher than what Level A would measure.
However, note that since every car with a speed of 100 m/s or higher in any direction is actually transparent to the plasticine, the sum of the forces on level B is also 0. Hence, it will remain at the same speed of 10 m/s towards the north. If we return to the sail, even at a speed of 10 m/s it will not feel any wind, and by the same logic also at a speed of 200 m/s, or 350 m/s, and it doesn't matter which direction. At whatever speed we put the sail or sail relative to the freeway, they will remain at that, when for them they are in the "stagnant air" system.
We'll take a break to digest ideas and questions, we'll discuss later."
This is Meir Amiram's response to the idea:
"Israel,
I follow. I understood how you overcame the Feynman argument. of genius.
But I don't like LS.'
I believe that my argument works logically although of course that does not mean that this is what happens in reality.
Good night everyone.
Shema Israel,
Yoda already has a patent for the "I didn't get it" trick, you can't use it either!
So now we have 2 versions of Pushing Gravity, and 2 versions of people who don't understand the faults in them.
Come on...
for miracles
Show me an observation of the theory of relativity that is valid and proven even over vast distances and that contradicts the simple universe and I will be happy and invited to a meal at my expense.
waiting
Yehuda
Yehuda
General relativity attributes gravity to the effect of mass on space. Your explanation claims that space has no properties.
We know observationally that the theory of relativity is also valid for vast distances, up to the edge of the observable universe.
Israel
I know exactly what a ballistic concussion is. You can't draw too much from an analogy, certainly not in our case.
In order for there to be no friction, two things must exist. One is that there is a barrier to the speed at which momentum travels. Why is there such a barrier? Is it fixed for every material and in every situation?
The second is that you need an infinite number of particles at each speed. It's not something physical, and even if there is a solution to the first thing - in my understanding, it rules out the idea.
for miracles
Time passes differently because of an explanation of relativity. The simple universe does not rule out the theory of relativity at small distances, the Mickelson Morley experiment is acceptable to the simple universe and does not contradict it, and the respect of the theory of relativity is assumed in its place.
I already explained to Shmolik in response 123.
good week
Yehuda
Miracles
What contradiction are you talking about? I'm saying that today in the laboratory with existing means you can build a system that will yield almost everything I described, that is, almost perfect frictionless gravitation and possibly inertia as well.
Did you read the entry on the ballistic pendulum?
N.C. Sorry, I thought that if you wrote:
The solution is that only particles in a certain speed range react with a body.
So if I move away from (or move closer to) a massive body I will experience less gravitation (compared to a state of rest relative to the massive body). This is because there are particles that did not react with the massive body and also reacted with me, therefore the massive body did not block everything that it promised to block.
You meant less gravity, now I understand that you mean new friction.
But maybe someone else understands better and can explain to me what other friction you are talking about.
Nissim, Yehuda, do you perhaps understand what N.C. means?
Happy holiday.
Israel
Albenzo explained what the problem is here, and you ignore what he wrote.
That's why I asked you earlier about the physical properties of the particles. Every feature I can think of entails a contradiction. If they don't have any physical properties then how do they affect normal matter?
Israel,
I already answered your question.. this is the last time I'm answering: you solved the friction problem but you introduced another "friction" in the back door that may be just as bad.. after all I demonstrated that if something moves faster than the "maximum reaction speed" it will not experience gravity at all , not experiencing gravity at all is not exactly something negligible, is it 🙂
To overcome the friction you introduced, the "maximum reaction speed" should be several orders of magnitude greater than the speed of light (because otherwise light would not experience gravity), and then you return to the problem written in Wikipedia about push gravity in the speed of gravity section..
In short, I prefer the original push gravity theory because..
A. It is simpler
B. You don't need infinite particles at all possible speeds
third. There is friction in both, but at least in the first one there is. Rael understands the friction..
And finally, here are 5 push-gravity particles moving at a speed of 100 km/h from right to left. Kdva is represented as X.
Before: ssssss X
And here is a drawing of them after they crossed the road that one of them stopped.
After a minute: X sssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssss
After 2 minutes: X ssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssss
An entertaining activity for Rosh Hashanah: paint the hole in cheerful colors, send it to the system and write how fast it moves. Among the solvers, an apple and honey will be drawn.
Yoda thanks, from Mitzvah to Mitzvah our strength will prevail.
Miracles
If you mean the average speed relative to the mass - the net - then it is 0, just as the average speed of air molecules at rest relative to the body is 0.
But unlike air, even when the mass changes speed, the speed of the influencing particles is still 0, while in air the average speed of the molecules relative to the body is the speed of the body relative to the air (wind speed).
Do you see another option?
Yehuda
You didn't explain to me why time passes faster in a gravitational field, and slower (relatively) at high speed.
Israel
Is your claim that at any speed V, the average speed of the "influencing" particles is V?
Dear Israel
I received your request. I will try to promote it with the telescope of the observatory in Givatayim.
Good week
Yehuda
to Albenzo
First of all, thank you for your comment.
There is a significant difference between my formula with the addition of the natural number as explained in my previous response to Shmulik, and which was obtained by deduction from the development of the idea of pushing gravity, and Newton's formula which was obtained by induction and, as David Yum said, is true where it is measured. The two formulas are very similar to each other unless we go far away,
You said correctly, and I quote, that the theory of relativity is a model - a set of assumptions regarding the behavior of gravity. This model entails a set of equations, which in the weak field approximation give the Newtonian formula I know. Now the "fatal" question is asked: is it possible that there may be a slightly different model of the theory of relativity - a set of assumptions regarding the behavior of gravity. Launching a set of equations, which in the weak field approximation give my simple universe formula which is almost identical to Newtonian??
To me, in my poor intuition, it seems so, but, I would like to hear your learned opinion.
Thanks again, and thank you for your patience.
good week!. Sincerely appreciated
Sabdarmish Yehuda
http://yekumpashut.freevar.com/
Not changing stars, changing (not changed!).
Yehuda
Can you telescope and video rapidly changing stars such as CY Aqr?
or the ALGOL defects that occur every two days or so, the times are listed in:
https://freestarcharts.com/algol-eclipse-dates-times-september-2017
I have access to telescopes online but they are all in the southern hemisphere. I always get a message that Algol is under the horizon.
Thanks
Yehuda,
You do not understand. I've explained it to you before, I'll try to explain it again.
Relativity is not a formula. You act as if the theory of relativity is a formula and if your invented formula (in a moment I will explain what is meant by "invented") is similar, then it will explain the same phenomena as the theory of relativity. This is simply not true at all.
The theory of relativity is a model - a set of assumptions regarding the behavior of gravity. This model entails a set of equations, which in the weak field approximation give the familiar Newtonian formula. Relativistic phenomena such as the difference in the flow of time in different gravitational fields are not explained by the formula, but by the model. If you come up with a different formula (that is, not deriving it from a model but simply deciding that it describes gravity) that is not the same as the field equations of general relativity, then they are not consistent with the model. It does not matter if the difference is only in large distances, or short, if it is exponential or polynomial, if it is black or white. Once your force equation is different, it means it is not derived from the relativistic model (because if it was derived from the relativistic model, it would not be different). Therefore, all phenomena explained by relativity are *not* explained by your formula. If somehow miraculously some of the phenomena (or all) are actually explained by your formula, then you have the burden of proof to show how this happens. In other words, you have to show how time flows differently at different heights above Earth, and you cannot say that it is because your invented formula is similar to the equation of forces derived from relations at this distance, simply because it is not the equation of forces that causes the phenomenon, but the role that time plays in the pseudo-Riemannian cloth ( which is exactly the basis of the model of relativity).
Shmulik
You asked: "How is it possible on the one hand to accept the theory of relativity and on the other hand not to accept its approximation that produces Newton?"
Answer: not accurate. At small distances up to a few thousand astronomical units I do get, and not only that but also my formula is like Newton's and it is an approximation of the theory of relativity! What is meant: - that at small distances my formula converges to Newton's formula. Unfortunately, it is not possible to copy formulas in comments, but I will still try to explain:-
The gravitation formula of the simple universe is Newton's gravitation formula multiplied by the term (e^(-r/a) where e is the natural number, r is the distance between the masses creating the gravitation, a is the mean free path of the two pushing gravitational particles (the collision between them reduces the formation Therefore, at distances r very small relative to a, the term (e^(-r/a) tends to 1 and its multiplication in Newton's formula obtains Newton's formula, on the other hand, at distances r very large relative to a, the term (e^(- r/a) tends to zero and likewise its product in Newton's gravitation formula also tends to zero.
Since there is no difference between Newton and the simple universe at small distances, then there is also an identity with relativity. At large distances the point is different because there is actually no gravitation according to the simple universe and therefore no compatibility with Newton or relativity. Let's not forget that Newton also has no match with the data measured in the field of the movement of galaxies unless we add dark matter and energy like a king. The rotation problem is solved by the simple universe with the pressure differences found in it due to its essence as a gas.
I hope I understood. If you can't access my blog, maybe there will be more understanding.
good week
Sabdarmish Yehuda
http://yekumpashut.freevar.com/
N.C.
I could not understand why the "holes" move at the speed you mentioned. What moves are the particles, and these can move at speeds much higher than the speeds of the meshes (unless you mean that the holes are a superposition of the speed of the particles + the meshes).
But I don't see the relevance, suppose we really get less gravity because of the effect you described. As long as we haven't quantified it, we can't know how much it really affects.
Example: If the gravitational force between the earth and the moon is a trillion newtons when they are at rest relative to each other, but it decreases by 10 newtons when they are in motion as in reality, then the effect is negligible.
What is important and what I talked about is that no matter how fast the nets move, they will not encounter the "wind" of Lasage particles which is Feynman friction. And this is in contrast to a network moving in the air for example, since you will encounter the wind from the air.
getting?
Israel,
Let's keep it simple and focus on the freeway example... I'd appreciate it if you could answer the questions below.
1. I stand next to your freeway, and look at holes that were "created" when cars pass through filter A. I watch the potholes progress along the highway. So the fastest hole I will see is a hole at a speed of 100 km/h (this is the maximum speed of particles that react with the filter).
Do you agree with this sentence? Yes or No? If not, please explain.
2. If the answer is yes, let's say I see filter B moving on the highway at a speed of 120 km/h (in the same direction as the holes). Do you agree that from my point of view, no hole created in sieve A can get it? (It sounds trivial to me, but I'm just making sure..) Yes or no?
3. If you agree to section 2, you must agree that, from my point of view, as someone standing on the side of the highway, filter B will not experience gravity from direction A. Yes or No?
If not, please explain how something that does not meet the holes of sieve A manages to experience the gravity of sieve A
Thank you and sorry and good evening
N.C.
Did you look at the link I provided on the ballistic pendulum?
Israel,
The holes created in sieve 1 do not reach sieve number 2 if it moves too fast, what you wrote about "new holes being created" is not relevant.
Yehuda,
How is it possible on the one hand to accept the theory of relativity and on the other hand not to accept its approximation that produces Newton? There are no choices here. As Weinberg said, Newton's gravitation formula inevitably emerges from an approximation of relativity. So how do you accept relativity without accepting Newton? How does it fit?
waiting
How come I'm not surprised?
Maybe you should look at the link before we continue:
http://study.eitan.ac.il/sites/index.php?portlet_id=110529&page_id=36&page_mode=printable
Miracles
What is "this speed"? And what did I ignore?
N.C
True, but then the filter will block new balls that it did not block at the previous speed and you will have a new hole where there was none before,
Israel
You are ignoring the problem again 🙂 You want that at any speed, the average speed of the particles will be equal to this speed - right? Albanzo explained why it didn't work.
You can adapt the model of the particles to reality by more and more additions, as Yehuda does, but why is this similar? to the idea of simulacra. Plato described two types of statues. The first is a copy of reality, like an exact statue of a person in all dimensions. The second is like the Greeks built big statues, or like the Taj Mahal: higher parts are distorted so that from the viewing point they look the right size. The Pushing Gravity, with the additions to solve the friction, are like the big sculptures - a distortion of a model to fit reality.
Flamonymous
Such questions are addressed to Yoda, this is his field of interest. I am only interested in ancient pottery from the Neolithic period.
Israel,
You didn't understand the problem I'm describing.. Imagine for a moment the "holes" in your freeway, these are the spaces between the cars created by the first filter. These holes move on the freeway between 0 speed and maximum speed - for example 100 km/h. That's how you defined it, if the car is too fast then it won't block, and then there simply won't be any holes at a speed higher than 100 km/h.
The holes are the interesting part, because they cause gravitation... those who do not encounter them do not experience gravitation.
That means you have countless holes with a speed of 0 to 100 and even a hole with a higher speed. These holes move in the direction of the second filter. But then, if the second sieve is moving away from the first at a speed of 120 km/h, then no hole can get it, right? (Actually, if you think about it carefully, she will "get" holes, meaning she will probably experience gravity in the wrong direction..)
Even if the speed of the sieve is only 5 km/h there is a problem with 5% of the holes (those at a speed of 0 to 5 km/h).
Pending response I don't understand why maybe because I used a holy word?, or maybe cosmology? We will wait patiently
To anonymous
Question: What are large distances in cosmology?, Answer: Gravitation to a large distance is for distances that are much more than the solar system where the distances are several tens of astronomical units which is less than a thousand light years, a light year and more are medium distances and these are the distances to the stars closest to the sun. The closest Proxima Centauri is 4 light-years away, just over a quarter of a million AU. The greatest distances in cosmology are in galaxies with a radius of tens of thousands of light years, and their distance is millions of light years. If at large distances one tries to use Newton's gravitation formulas then a lot of matter is missing in the galaxies. And so it is claimed that there is a lot of additional dark matter hiding in the galaxy.
And here we move to the question of Shmulik who insists on the correctness of adding dark mass. so true
When you add dark mass then everything works out. But people forget that the formulas are not important because if the data measured in the field and if the data do not match what is predicted by the formulas, the formulas should be thrown away! No formula is so sacred that we will change the measured data. Newton's gravitation formula proves itself well at small distances. A small falsification of it appears in the precession of the planet Mercury, which is corrected by the relativistic correction of the theory of relativity. But at large distances another possibility must be looked for since eighty years we do not find the dark mass.
Dear Valnisim, I say that apparently you did not read my previous response, so I say again:-
I explain the dependence of time on gravity with the help of... the theory of relativity. I have no objection to the theory of relativity, and regarding your second question you ask "Since when does not finding something prove that it does not exist?"
I never claimed that, but some claim that, for example, they claim that the Michelson Morley experiment proves that there is no ether because light does not use ether.
And dear Israel, I have access to telescopes with tracking, I would be happy to help, just keep in mind that some of the members of the association are still in the US, and some continue to Serbia for a meteor conference.
Shabbat Shalom
Yehuda
Yoda our brother
Do you have free access to perhaps powerful telescopes, preferably with go to, so that they can be aimed without problem to specific space coordinates?
Miracles
The response to the mass increase was released, did you see?
Let's start with the fact that I have no intention of advocating the Lesage model, as I have stated several times. My interest is more the relativity.
The issue of particles moving at infinite speeds is not critical to Lasage gravitation, because if, as I showed in the example of the ballistic pendulum, above a certain speed it no longer reacts to the particles. Therefore it is possible to be satisfied with high speeds for particles that are not infinite.
The infinite speeds are only critical when trying to integrate the concept to include non-locality.
I don't see why the distribution must be uniform to have Lasage gravitation, but it is said to be. So what?
Look at the Autostrada model, which is a Lasage in one dimension. Do you see that you will get gravitation there? Do you see that the movement of the nets does not change their position relative to the weighting of the cars and therefore there will be no friction but there will still be gravitation? Do you see that only during a speed change will there be a balanced force on the nets and therefore you will get inertia (I am still not sure about this, but it is not that fundamental).
And the most important thing for me: do you see that a wave advancing in such an open model always advances at a certain speed relative to each measurer, and it doesn't matter what the speed of the measurer is?
Yehuda
How do you explain the dependence of time on gravity?
Since when does not finding something prove that it doesn't exist?
Israel
How do you overcome the problem raised by Albenzo? To mention - follows from your explanation that there are an infinite number of particles in all beings, everywhere.
N.C
You write:
So if I move away from (or move closer to) a massive body I will experience less gravitation (compared to a state of rest relative to the massive body). This is because there are particles that did not react with the massive body and also reacted with me, therefore the massive body did not block everything that it promised to block.
I assume that when you write "moving away from (or approaching)" you mean "in relative motion".
Let's take the example of the freeway: cars travel in both directions at all speeds.
You put a huge filter on the freeway, and it blocks some of the cars. At a certain distance from it you put another filter and it also blocks some of the cars. According to Lesage there will be an attraction between the two filters, accept?
Let's introduce the Tikun Israel. One of the filters is in motion relative to the other. It now blocks cars at speeds it didn't block before, but others that were blocked before manage to pass because they don't respond to the filter. getting?
We will see what the effect is on the second filter.
For her there is no change in the situation. There are still more cars hitting it on one side than the other, so an equal force will be exerted on it in the direction of the first sieve, right?
Yehuda,
You did not answer me. Sean Carroll says that the reason (at least one) that physicists think that dark matter exists is that by adding it to the calculations, there is no need to change the theory and the result obtained from the calculations completely agrees with the results of the experiments
He says that exactly the opposite happens when trying to fix the gravity formulas. your reply?
In Steven Weinberg's lecture (very nice that it took me some time to find it again) he describes that while for Newton the dependence on 1 divided by the square of the distance is arbitrary since the square was placed because it suited the results (and actually relative to the accuracy of the measurements that existed in Newton's time, it was equally possible place 2.01 and get the same result), Einstein's equations are not gameable. Everything stems from the basic idea of space being curved as a result of the presence of mass, the equations that stem from the basic idea are rigid. Any attempt to play with them will lead to nonsense and invalidate the basic idea of the theory. From Einstein's equation for slowly moving bodies, Newton's square appeared to him, but it must be a square and not 2.01 (Albanzo wrote this before if I'm not mistaken. Albanzo, you're in good company)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x9Jqgxh6D2s
The silent section starts at minute 18:20 and concretely from 22:20 until about 27:00
That is, if you accept the theory of relativity, you must agree that it is not possible to change Newton (or argue mathematically with Weinberg) what's more, Shawn Carroll told you that attempts were made to change Newton and this led to a contradiction with experimental results, so what probably remains is dark matter because it Mass addition without changing the basic idea
Judah, Israel
What is meant by the sentence: gravitation to a great distance?
Nissim Israel and others
I will start by saying that my theory explains gravitation at small distances of a few astronomical units. It has no contradictions (almost) with the theory of relativity at small distances and accepts everything deduced by the theory of relativity. At this point, I accept the Michelson-Morley experiment and all of its conclusions except for two important ones that I don't think stem from the experiment, namely that the speed of light was the same in the past as it is today, and the second thing is that the site does not exist. The light does not use a dot site. He also doesn't use me, Nisim, Israel, Albanzo and in general the knowledge site. Nevertheless it does not affect our existence or non-existence. Likewise on the website. The GPS can continue to operate because of... the theory of relativity, as above also with the planet Mercury and its precession, everything is there because of the theory of relativity. Therefore there is no room for the question of how I explain something that is explained by the theory of relativity. I explain it with the help of the theory of relativity.
The theory of relativity with the GPS, etc., the North Korean precession and the atomic bombs work and are well proven at distances of less than a thousand light years (the solar system)
But my theory has a problem with gravitation over large distances, but so does Newton and relativity. Don't tell me that adding mass and dark energy to the data is not a problem. Therefore, since the theory of relativity talks about gravitation in the entire universe (based on what?, has anyone measured there?) even for the great distances of billions of light years, so I have disagreements with it in this case. For me, at large distances it works differently, almost without gravity.
I hope the question will no longer be asked: How does my theory explain relativity at small distances?
But, don't think that I like the theory of relativity, I like Galileo, I don't like the relativistic connection of velocities and other conclusions. But it works and I connect with the theory of attribution even without "love" but I would love to gnaw at it.
That's why I was very happy about the nice and interesting idea of our friend Israel that we might "bite" in the theory of relativity and I'm preparing for the upcoming holiday to think about the possibilities that open up on the subject.
And by the way my theory can already explain the precession of the planet Hema without attribution. Anyone who wants to enter the blog
Shabbat Shalom
Please respond gently
Yehuda
http://yekumpashut.freevar.com/
It's a bit difficult here with the waits that don't get released, let's hope it goes away.
The pattern of the bullet through the country is not complete and accurate, as I showed in the original article. It was only brought up to illustrate the main idea of projectiles passing through the ballistic pendulum, which is a perfect example. which do not need to be particles to Sage. They can be charged particles through a magnetic field (which eliminates the Kelvin friction that Nissim pointed out) or simply radiation. All will fall under the poshing category.
Is pushing true? I don't know (but neither do you!). Is it particularly important? Leoda is safe.
I'm interested in relativity, and the mechanism I proposed can perhaps explain the invertibility of the speed of light and not through a postulate.
It's hard to enter personal details every time, does anyone know a trick to make the computer save them?
Good night everyone (will pass?).
Israel, to your question:
https://www.hayadan.org.il/how-much-does-the-kilogram-weigh-0909179/comment-page-3/#comment-721352
Israel to your question..
https://www.hayadan.org.il/how-much-does-the-kilogram-weigh-0909179/comment-page-3/#comment-721352
Yehuda,
He said that according to the background radiation, the predictions involving dark matter were accurate, while the modification of the gvitation formula failed against the observations. clear and smooth. That is, there is very strong evidence here for Newton's correctness outside the short distances of the solar system. You no longer claim that the law of gravity needs to be changed because it has not been tested far enough?
Yehuda, I just saw your comment.
The Turkish head works correctly. If you read the first link I provided to the article from five years ago with Yuval and R.H., then the conclusions you drew appear in them.
Happy holiday.
N.C
Happy New Year, and may we be the head and not the tail. All the best and stay fit.
Why did I spoil Lesage's Gravity? What will prevent it from existing in the format I proposed?
A joke with all those waiting, they don't let a word out of their mouths.
Is there really a need for this, my father? How many inappropriate comments did WordPress catch this month?
From the waiting list:
Reuven Nir in "Attraction" explains that a rapidly rotating mass according to Lesage is like a rotating net that will block more particles and therefore mass increases.
I did not understand why Newtonian gravity is incorrect. Newton never explained the origin of gravity, that's what Lesage tried to do.
They are muted for some reason, a mass increase.
Mass increase: according to Reuven Nir, a rotating disk blocks more particles, just like a rotating sieve. Therefore, according to Lesage, more blocked particles means a higher mass.
My job is not to defend the Lesage theory, our Yoda does that, and devoutly.
My job is to solve the friction problem. The bonus: also the problem of the source of inertia (only by acceleration you will get force on a body) and the reason for the invertibility of the speed of light. And maybe also the possibility of non-locality.
Is this what is really happening? Apparently not. The advantage: this can be tested experimentally, which is now really just a matter of improving existing technology.
Israel
I understood what you are saying. But, you use Newtonian gravity to prove that Newtonian gravity is incorrect.
And what happens if the theory of relativity? Why does mass increase with speed?
Miracles
A projectile passing through a tunnel in Israel below the escape velocity will capture in simple harmonic motion and transfer to it a momentum proportional to its speed relative to Israel.
The amazing thing is that beyond the escape velocity even by a clear fraction of speed, it will not transfer momentum at all. Newtonian mechanics.
If we apply the principle to Lesage particles, you can think in one dimension of a two-way highway on which cars travel in both directions at many different speeds, but you, as a sail spread across the highway, only reacts to a narrow range of speeds. Therefore the balanced force acting on you is zero, like the force acting on any air-filled body at rest.
If you are at a different speed, the balanced force acting on you will still be zero, because certain high-speed cars will disappear from your perspective ("beyond the escape speed") and new ones that you did not feel will appear in their place.
Therefore, unlike the air that exerts a force (wind) on you, if you are in motion relative to it, no matter how fast you move relative to the freeway, the force acting on you will be equal to zero.
Israel
First of all, Happy holiday.
In your response to me you simply repeated what you said earlier about the friction. But I didn't say that what you wrote about the friction is wrong, but that in your attempt to fix the friction you spoiled something else - now your improved gravity pushing is not doing what it is supposed to do - produce gravity.
Think you're a plumber, and you came to fix a leaky faucet at a customer's, and you did fix the problem! But now the faucet is closed - no water comes out of it at all even if you open it... and then when you are told about it, you say: "It's not accurate, you can see that the faucet is not leaking." Really beautiful..
In any case, I recommend drinking a lot of water and if you have time, refer to what I did write, if not, that's fine too... and have a good year.
to Shmulik
I went to the link you directed me to. Sean Carroll explained known things and also mentioned the wimp who is being searched for without success. And he also does not rule out the possibility that something in gravity is not right. So he didn't tell me much.
Yehuda
Yehuda,
Sean Carroll in four minutes explains why he thinks dark mass exists.
https://m.youtube.com/watch?v=hHMSvSqCDKc
Watch about four minutes from 02:06:44
Israel
The amount of momentum transferred is the integral of the force over time. In the case of the projectile in the tail, at a certain speed the force will no longer increase because shearing will take place. Above this speed the amount of momentum will really decrease significantly. It will not reset at any speed.
Regarding the projectile through a tunnel. I think it has nothing to do with speed, but time. Imagine a very distant projectile passing through the hole. At first, he was attracted to Earth. The momentum of the projectile increases and so does the Earth's. After the transition the situation is reversed and at the end the bullet will stop. That is, a pendulum will be produced.
Miracles
I showed that I believe that a body whose speed is above the escape velocity, will not transfer any momentum to the earth if it passes through a tunnel in it.
The same goes for bodies passing through a ballistic pendulum, but suffice it to say that they transfer less momentum above a certain speed.
And why go far? Which projectile would you rather hit your phantom tail: the one that travels at half the speed of sound or the one that travels at half the speed of light? Who will do more damage to the plane?
Yehuda
150 years ago they saw anomie in the orbit of the planet Mercury. Don't you think that today we wouldn't see an anomaly in satellite orbits several hundreds of kilometers high? Don't be naive 🙂 Read a bit about Cassini's discoveries and see what resolution of information we have reached in the study of Saturn. As I wrote - the lack of friction contradicts your theory.
How do you explain time variation in speed and gravity? How do you explain the photoelectric effect? The teachings you dismiss explain these things. We need much more than the excuse "but they didn't find the dark matter!!!" To reject such successful teachings.
Regarding charges - a neutron is not made up of a proton and an electron. A proton and a neutron are made up of 3 quarks each, and an electron is a lepton type particle. Quarks have charges of +2/3 and -1/3 of an electron. Why exactly these numbers?
Error: a western satellite lives less than an eastern one.
for miracles
Satellites fall from time to time, don't forget that they have fuel that occasionally corrects their course, I believe that the ones flown to the east will last less.
Regarding the theory of gravitation that "requires" the production of mass and dark energies, where are these your super successful theories? Newton does not explain anything and mine also explains the movement of galaxies without mass additions.
And regarding the theory of relativity and the Michaelson Morley experiment, it is acceptable to me with all its relativistic conclusions for short distances. It doesn't seem to me that there are relativistic proofs for large distances that wouldn't require you to invent crazy things. But keep believing in dark mass and dark energy. Don't worry about miracles, when they find that an eastern satellite lives less than a western one, there will already be someone from NASA who will say that it is not due to excessive friction, these engines are hot (or cold) or that they transmitted more (or rather less) from there and that is the reason. They will not give up so quickly on Newton.
Regarding proton and electron, I don't know what electric charge means so that I can explain it. But I'll try anyway - I have a feeling that we took something from a proton and the result is a proton and an electron, so they must be equal. If I had 30 students in my class and I took out one child, I would have 29 left and one out. The one is exactly 30 minus 29. But you know,
Israel
Getting ready to read the link you sent us to. Sounds interesting.
That's it, come the Shabbat meal.
So please please respond gently. I know people don't like me bashing Newton and Einstein.
Good day and happy new year! And please respond gently
Yehuda
http://yekumpashut.freevar.com/
Israel
In order for a particle not to transfer any momentum, its speed must be infinite (assuming continuity). On the other hand, a particle with infinite speed will not transfer momentum to any body, so it can be ignored.
We are back to the beginning...
I have to fly to work. I am not claiming that the Lesage model is correct. He suffers from many problems, of which the second friction (Kelvin) brought up by Nissim is only one of them.
I only claim that the main problem (Feynman friction) can be solved using the idea I put forward. But first one must understand the principle of the ballistic pendulum, and why bodies passing through it will stop transferring momentum to it above a certain speed.
You can also read at:
https://www.hayadan.org.il/astronomers-reach-new-frontiers-of-dark-matter-130112/comment-page-11/#comment-326491
Yehuda
Satellites have been orbiting above us in both directions for decades (I think more than 30 years). I find it hard to believe that your friction phenomenon would not have been discovered during this period. Think about the fact that 150 years ago they knew that there was a deviation in the declination of the planet Mercury, the size of the deviation is less than half a second per year!
Yehuda
You need a good reason for a new theory, especially if it dismisses existing theories that are very successful. The theory of relativity predicted many observations that verified them, it is a simple theory, and it explains phenomena that your theory, for example, does not explain. Two simple examples are the time dependence on velocity and the time dependence on gravity.
Quantum theory is more complicated, but it predicts experimental outputs with an accuracy of 12 digits. She predicted many particles that were discovered, and again - explains observations that your Torah cannot.
There are things much simpler than dark matter that cannot be explained. For example - why are the charges of the electron and the proton exactly the same in absolute value? So do you think this is a good reason for disqualification?
Albenzo - Am I right about the chargers?
Albanzo, Israel, Nissim and others.
A, I don't understand why the absolute need for an infinite number of particles? After all, if we assume we take a finite amount of particles that 99.999999 percent of the particles will move between a speed of 0 and two V, we can still say with a very high degree of accuracy that the average speed is V and draw conclusions very close to reality. We don't demand zero friction, we demand friction that will keep our precious planet going for just another billion years or years.
B. A fundamental question. If we are talking about a new theory or a new idea like the one that Israel brings us, is using an existing theory (relativity, or quantum) a must?, just a question.
Happy New Year Albanzo and let's hope the black cats are over.
Happy New Year to everyone too
Yehuda
http://yekumpashut.freevar.com/
Happy New Year.
Dear Israel
It's fun in the comments that you suddenly wait after encountering something you hadn't thought of before, and immediately my Turkish head starts drawing "flying" conclusions.
So I have two things for you:
A. Won't there be a Boltzmannian distribution also regarding gravitational pushing particles at different speeds? That is, let's say the average of the speed will be a million kilometers per second regarding 999,000 or 1,009,000 there will be slightly fewer particles, so there will be a change in the gravitation that is created in both of the above cases?
And let's assume that gravity is created only by the particles moving at 900,000 km per second, and everything else passes without us feeling it, so if the planet moves at ten km per second, depending on the direction of movement, the number of particles in the Gaussian curve at this speed will be less than that in one case, and more From this in the second case then the gravitation will increase or decrease depending on the rotation around the sun of course. interesting!
B. The second thing is even more important:- we constantly talk about the same speed towards the bodies and it doesn't matter how fast they move, doesn't this remind you of the theory of relativity. Maybe after all Galileo controls space with the help of Israel Shapira's correction?, maybe that's why the speed of light is the same in every direction and not because of what our friend Albert said? Did she understand how the Turkish head works at different speeds?
So please please respond gently. I know people don't like me offending Newton's tender soul and even more Albert's relative one.
Good day and happy new year!
Yehuda
http://yekumpashut.freevar.com/
P.S. Meanwhile, I saw a new guy coming to the neighborhood. Happy New Year Albanzo!
Israel,
Something to think about. You don't have to answer if you don't feel like it, just now this is the first time I've seen your explanation for the claim (which I've heard you claim before) that the friction problem can be solved with mechanical gravity. I see a problem in your solution that makes it completely irrelevant, but I have no intention of getting into arguments, so I'll just explain what the problem is as I see it and you can do with it as you wish.
A mere distribution of particles with different velocities between infinity and minus infinity will not solve the problem. The distribution must be uniform. On a mathematical level, this is obtained from the fact that adding speed to the body in the gravitational field will shift the distribution, and to get that gravity the distribution must be invariant to displacements (in momentum of course). On an intuitive level, this can be understood from the fact that in order for gravity not to change as a result of the body's speed (=no friction is created), then exactly for every additional particle that the body collects in the direction of its speed, there must be a particle that stops contributing to the mechanical gravity (becoming "transparent" to it as you define it). Again, this requires a uniform distribution of speeds. It is easy to do an experiment with a Gaussian distribution and see that at high speeds there will simply be far fewer particles whose relative speed to the body is in the relevant range and therefore gravity will be weaker.
But the uniform distribution has a critical problem, which is that the total number of particles in it is infinite. Not a very large number, not "a lot" - to prevent friction in the way you suggest, you need exactly an infinite number of particles sitting at all speeds in every direction. If you take a finite number - no matter how large - the integral over its distribution must converge, and therefore it must fade to 0 at the edges, and in particular it will feel friction (because the distribution will not be invariant to displacements, and always asymptotically there will be more particles "behind" it than "in front" , exactly what creates the friction).
Classically, this is nonsense. Classically there is no such thing as an infinite number of particles. This is not a valid physical model, and certainly not a mechanical model (which claims to explain a phenomenon through kinematic interactions). For that matter, it's a pool trick that only works when there are exactly infinite balls on the table. Take out even one - and the trick no longer works.
Quantum has a lot to talk about. It is not trivial, but quantum there are mechanisms of creation and destruction of particles that can make the concept more physical. But of course if the particles are quanta you run into two new problems. First, the classical mechanical considerations are no longer valid. The whole idea of mechanical gravity is that there is a particle traveling in orbit, and if there is something between you and the particle that hides you, the particle will not hurt you. Therefore, in practice you will feel negative pressure from this direction and will be attracted to the concealing body. But there is no quantum for an orbital particle. And even if you look at particles that started their lives at infinity and want to reach you (on a non-specific route), of course you have to consider tunneling, and in general the paper is short of explaining how much the mechanical model needs to change from end to end in order to be consistent with quantum mechanics. I will remind you that quantum models of gravity are some of the most difficult problems we have encountered in physics. This claim in itself is not an argument against the idea, but only a reminder of how many thousands of problems arise when trying to reconcile the two friends together, problems that you will have to account for if you claim that the particles of mechanical gravity are quanta.
The second problem is not exactly a problem as it would be: why? I will remind you that gravitons are also particles that create the force of gravity mechanically (by transferring momentum between two bodies). The difference is that they are not an ether, but particles that can be found in a bound state in space (like matter), or emitted spontaneously from bodies that perform gravitational interactions. In other words, a quantum analog to mechanical gravity has already existed for a good few decades. If the particles in your model are quanta, it is not clear to me what the model offers that does not exist in the existing models that include gravitons (apart from the fact that your model is much "younger" and untested compared to these models that have been studied for decades and have made significant theoretical advances).
N.C.
Kind, but not accurate.
Don't forget that these are an infinite number of particles that move at all speeds from minus infinity to infinity, but react to the body only at certain speeds (like the Earth with the tunnel to which only projectiles 1-11 transfer momentum from an infinite number of projectiles at speeds from minus infinity to infinity, everything else is "transparent").
Now what will happen if the car has a different speed? It will respond to 11 other projectiles and all the rest will be transparent.
Therefore, no matter how fast the bullet moves, it is in the same situation in relation to all the projectiles.
And in the Lasage system, no matter how fast a planet moves, it is at 0 speed relative to all the Lasage particles, just as a sheet is at 0 speed relative to air at rest, even though the air molecules are at a high speed relative to the sheet, and none are actually at 0 speed relative to it.
And just as a sheet at rest relative to the air has no Feynman friction with the air but only if it is moving, so the planets also have no friction with Lasage particles: no matter what the speed of the planet is, it is at 0 speed relative to all the particles.
Yoda happy holiday, let's hope that the only bombs we encounter will be bombs for the back.
Dear Israel
I saw your response to the miracles about an atomic bomb structure that we have in the North Koran neighborhood in Herzliya, the Holy City, and we can really learn from them about Le Sage particles - Pushing Gravity - a simple universe. and draw conclusions about the beloved gravitation and the results can be interesting for the fate of the simple universe and the universe in general.
I didn't think of it that way. Indeed, food for thought!
Happy New Year Israel my friend
Yehuda
http://yekumpashut.freevar.com/
for miracles
Let us make a rough calculation of the friction of the satellites for and against the rotation of the Earth
In general, the satellite is flown at a speed of eight kilometers per second. The speed of the earth is 40,000 km in 24 hours, which is 0.46 km per second, so the friction differences between the two cases will be like 8.46 to 7.54, which is about 12 percent, and since the friction is according to the square of the speed, it is about the order of a quarter. It's not much, but it's "tolerable", that is, if a normal satellite lasts 100 years, the Israeli one will last about 75 years. By the way, the reason they send spacecraft towards the east is to take advantage of the 0.46 km per second in sending the rocket into space.
Good day miracles
Yehuda
Yehuda
Because of constraints, the satellites that Israel launches actually rotate in the opposite direction to the Earth's rotation. According to what you describe, it should have greatly increased the friction. I don't think that's the case.
Miracles
The rotation of the sun around an axis is due to the direction of rotation of the primordial cloud from which the solar system was formed. The sun and planets have the same general direction of rotation. If you move around like everyone else, your chances of survival are greater than if you move differently. This is what I also said about the satellites.
Good night
Yehuda
Yehuda
So you are saying that the rotation of the sun on its axis is what eliminates friction?
Miracles, again, Happy holiday to you too!
Let's see what you wrote: my response - in brackets (). Let's start:
"The wind is driven by an external source, the sun" (correct).
"Your particles are like gas in an open space" (it is true that its particles are highly permeable)
"And there is no wind in them," (incorrect, there are pressure differences and wind in them)
"That is - their average speed is 0" (that's right, usually on average).
"You repeatedly say that the particles move in the direction of the movement of the planet" (that's right, the particles move the planet and themselves in the direction of the planet),
"But I showed you that it doesn't go well with a situation where two satellites orbit a star and pass through the same point" (not true because the particles have a high permeability, but the satellites will eventually fall to at least one of them, the one that moves against the direction of the planet's self-rotation).
"And in any case - no planet moves in a "fixed" orbit (fixed is a matter of definition relative to what?, it's complicated).
"The Earth orbits the Sun, the Sun orbits the center of the Milky Way, and the Milky Way does not stand still either (relative to the cosmic background radiation)" (correct)
. "In other words, the planets pass through "new" particles." (Right)
To sum up miracles, so what is the conclusion? Check if you understand the principle of creating gravity by pushing gravity. Almost everyone agrees that gravitation is created. There is a claim that it won't last long because of the friction, and here we disagree
Please respond gently
Happy New Year!
Yehuda
http://yekumpashut.freevar.com/
Yehuda
First - Happy holiday!
The wind is driven by an external source, the sun. Your particles are like gas in open space and have no wind, that is - their average mass is 0. You repeatedly say that the particles move in the direction of the planet's movement, but I showed you that this does not add up to a situation where two satellites orbit a star and pass through the same point.
And in any case - no planet moves in a "fixed" orbit. The Earth orbits the Sun, the Sun orbits the center of the Milky Way, and the Milky Way does not stand still either (relative to the cosmic background radiation). That is, the planets pass through "new" particles.
for miracles
I will be brief in analyzing your response
You said: "The wind pushes the boat in the sea and in this process the wind loses its strength" end of quote
So what? Meanwhile, the wind that lost its strength passed and a new wind arrived, fresh and with full force that continues to sail the ship. This is exactly what happens with the gravity pushing particles that hit bodies and pass through them at the speed of light (apparently) and immediately new, fresh particles continue to arrive in full force.
Dear Nissim, with all the appreciation for your words, there is no point in continuing the argument between the two of us, I see that everyone is fortifying their position and is confident in it. We are before Rosh Hashanah, so let's say goodbye here, and if you visit Herzliya during the holiday, I would be happy to meet with you and discuss Pushing Gravity, and maybe we will come to some conclusions
May you, to all science respondents and to all the people of Israel, have a happy and blessed New Year
All the best!
Yehuda
Yehuda
The wind pushes the boat in the sea and in this process the wind loses its strength. Without the sun's energy there would be no wind, because of friction.
The connection between wind rotation and planetary rotation is very loose. Wind rotates due to a combination of linear motion and rotational motion of the Earth, which creates the so-called Coriolis force. Hurricanes gain energy in the sea because the sea makes the air warm and moist, and because the sea is flat and facilitates air movement.
There is an interesting phenomenon in aviation called "wind dialing" - the higher you climb, the direction of the wind moves clockwise, and this is because of the decrease in friction with the ground.
Planets rotate because they were formed from particles that came from afar, and have initial kinetic energy, meaning they have a non-radial velocity component. If you take a lot of particles and perform an integration, you will end up with a system that is a spinning disk, because at the end there is rotational momentum which is a vector (a bit of a lame explanation, I know).
True, there is a little friction in space, ask NASA what happened to Skylab at the time because of this friction.
But, the friction resulting from your particles is much greater and will therefore cause a much faster orbital decay.
Still, your calculation is wrong and does not describe anything physical. As long as the planet is in motion there will be friction and equilibrium will never be created. On the contrary - the closer the planet gets to the sun, the stronger the gravity, the faster the (longitudinal) rotation will increase and therefore the friction.
In my opinion, it is possible to declare "checkmate", no?
Yesh.R.A.L's solution to friction is nice, but it will spoil gravitation.
The solution is that only particles in a certain speed range react with a body.
So if I move away from (or move closer to) a massive body I will experience less gravitation (compared to a state of rest relative to the massive body). This is because there are particles that did not react with the massive body and also reacted with me, therefore the massive body did not block everything that it promised to block.
Miracles
Interesting response.
I will start from the end of your response - the example of the sailboat does not completely match the beam in the solar system, but, just as a sailboat moves in the sea despite the "friction" with the wind and waves, so too will the planet move despite the friction. The source of the energy is the source of the gravitational pushing particles, whose source of energy is possibly/probably the big bang and they have the required energy.
This should be enough for the rotational movement and there is no need to explain what will happen if the friction still works. Because there is no friction
But you raised an interesting question regarding both the Newtonian explanation and the simple universe explanation: why do the planets rotate at all and why in the same direction?. What gives them this push and in my humble opinion the one who gives them the push is the rotation of the galaxy itself otherwise the planets are supposed to fall into the sun. A similar thing happens with the winds on the Earth whose rotation is what gives the rotational movement to the winds (tornadoes and hurricanes) and as long as they move in the open sea their speed is maintained and even increases despite the great friction with the sea itself. This is the situation in the gravitational pushing explanation.
Take into account that friction is created (albeit to a lesser extent) also in motion according to Newton, also according to Newton there is friction in motion in space because the "empty" space is not completely empty (gas atoms, meteors, asteroids, the solar wind, cosmic rays, neutrons and so on) , which will cause the planets to be in a loose equilibrium and the little friction will eventually cause them to fall into the sun if there is no repair mechanism for this.
But according to the calculation I made, even a small fall towards the sun will create a greater gravitation since we are in a more inner orbit and therefore with the help of the galaxy and possibly the sun, it will be translated into a sufficient rotational movement.
But... you are right, the problem of the direction of the effect of the friction is a bit "disturbing", but also for the Newtonian explanation.
But again, as our beloved prime minister says: "There is no friction because there was never any friction, but even if there is friction it can be solved (maybe)" in my opinion with the help of the sun and the galaxy but... maybe I'm wrong.
A place for thought. But that's no reason to stop believing in the simple universe,
Please respond gently. It's just science.
Yehuda
http://yekumpashut.freevar.com/
Yehuda
Your calculation at the end of the article is wrong. The centripetal force is radial while the frictional force is longitudinal. The friction is not eliminated by reducing the radius and eventually the planet will fall into the sun.
What does it have to do with a sailboat at sea? There is an external energy source there that causes the wind (they call it "sun").
for miracles
The particles pass them almost without colliding with the bodies they pass through. They behave like the neutrino particles that can cross the whole earth without being aware that they have passed through it but almost. Some of them are braked, so it doesn't matter where the satellites are moving, they will all hit particles, and almost as much you will treat the gravity pushing particles as tiny gas particles with very high permeability. Google or Wikipedia about Pushing Gravity, Le Sage. Or on my blog it is well explained
Good night
Yehuda
http://yekumpashut.freevar.com/
For years I was convinced that my house was 312 square meters.
Now I understand that the probability that my house is 312 square meters tends to zero.
I don't weigh 72 kilos either.
And my height is 176 cm.
The ground was dropped for no more.
Yehuda
If the explanation for the lack of friction is the movement of the "ether" on the same track, then how can there be a point in space where there are two tracks?
for miracles
Why won't satellites cross or move in opposite directions? After all, that's how we sent them into space. Note that all the moons in the solar system move in the same direction, apparently those that arrived from a different direction did not last, the question is whether the satellites will keep their movement in space for billions of years. Note that in one direction of their rotation the friction increases, but in the other direction they will actually benefit from a "tailwind"
Regarding the second question about infinite movement in a straight line, then it is that in the direction from the sun outwards the bodies will have a deceleration, and even a certain deviation from the straight line. I tried to calculate it and couldn't, lack of math. Slowing down will be according to the speed of the bodies. That's why I think a spacecraft should be sent to check the phenomenon.
Anyone volunteer to do the calculation?
Please respond gently. It's just science.
Yehuda
http://yekumpashut.freevar.com/
waiting
Miracles
The friction you are talking about is a different friction than the Feynman friction caused by the movement of the planets, and it will exist even if the planets are at rest. This is the friction that Lord Calvin spoke of in his essay on Lesage.
To see why this is not relevant, think of a tunnel that runs between the North and South Poles (no atmosphere) and is reached by projectiles at speeds of 1-20 km/s. Who will transfer the most momentum to the earth, and will there be a loss of energy due to friction?
The answer to the second question is negative, and to the second: projectile No. 11 (escape velocity). 12-20 bullets, and any bullet with a higher speed will not transfer momentum, and from the point of view of the country they are "transparent".
Alternatively, think of a block of plasticine hanging from a string on a tree and you shoot projectiles at it at different speeds. Who will move the block the most?
As before, you will see that above a certain speed the bullets transfer less momentum, and above a certain speed they stop transferring momentum at all.
Even fast neutrino particles pass thousands of suns without effort and friction, and without leaving a mark on the sun or slowing down.
And we have already mentioned the slow neutrons that explode the uranium while the fast ones pass through it without a problem.
This is a natural principle, there is no reason why it should not work in the case of Lasage particles, and it solves the Feynman friction problem.
Yigal
A cancer cell has almost the same genetic load as the rest of the body's cells. This is how the immune system "knows" not to attack the body's cells, and therefore also cancer cells.
Yehuda
Your answer does not explain how two satellites can cross a point in space in different directions. Nor does it explain how a body can move through space for unlimited distances in a straight line.
Israel
If you don't get friction you won't get gravity either. And not a mass.
And as soon as a very fast particle hits a neutron for example, the neutron will receive a large amount of energy, therefore Brownian motion.
Nissim, my father, Yariv, Judah, Israel
Speaking of cancer, sorry, unrelated:
Question, how does it happen that a cancer cell "knows" how to trick the body's immune system (to block the interface sites of antibodies so that it cannot be marked for elimination???? It's just a stupid cell that went crazy and multiplies a lot.
what is? A bacterium or virus that goes through trillions of mutations until one of them manages to trick the T cells.
for miracles
The link you sent me to about ten or twenty comments ago talks about cleaning the correct kg, so they cleaned it too much and you need to add a few micrograms to it, I don't understand what it is for our eyes. This shows the difficulties in determining the kg that may absorb dirt, etc., etc.
And regarding the friction as Israel explained to you (thanks for the help my friend) there is no doubt that particle activity would have created gravitation and therefore also the rotation. But gravitation would act on all the bodies found in the solar system and also... on the particles themselves, therefore they too would have a rotational moment around the sun, and therefore their average movement would be like that of the planet in their area, so there would be no friction. Richard Feynman brought an example of the friction of a person moving against the rain, surely more raindrops will hit his face, but the example is not good because if we assume that the person is also blown by the wind, he would move at the speed of the drops and would get equally wet from the front and back. Israel gives an example that should be studied in depth, what would happen if only a certain speed of the particles had an effect and the rest did not. Honestly, I didn't think about that. There will be something to do at the weekend.
In short, the friction problem that flawed the pushing gravity theory is not fatal to the theory, so I continue with it. Waiting for the winning proof that will take away my belief in the simple universe
Please respond gently, SA is just science
Yehuda
Let's assume for simplicity that the particles are little chocolate teddy bears, and the stars and planets are huge networks that transport most of the particles but not all of them.
Will you get a gravity laser when the plates are at rest? Positive. Feynman also says this.
Will you encounter friction in the original Lesage model? Also positive and this is what Feynman says.
Would you get gravitation in an open system where the particles move at all speeds from minus infinity to infinity but react to the grids only at certain speeds but not beyond them? Positive.
Will there be friction? Negative. At any speed of the net, the average of the velocities at which the relevant particles hit the nets is 0, like air around a sheet whose particles hit it at all speeds and balance which ones.
Israel
I ask about the properties of the particles because it is important. especially their density in space. I would expect to see Brownian motion of small particles.
Israel
That's a lot of hand waving. A particle collision law is not a bullet colliding with a piece of jelly. In my understanding, a good analogy for particles is billiard balls.
Please Eraf, how do I know? And what does it matter? All the details appear in the entry on the Lesage model on Wikipedia. My job is just to solve the friction problem, and if you read the explanation about the ballistic pendulum that shows that fast particles transfer less momentum than slow ones (like slow neutrons that explode the uranium nucleus while the fast ones pass through it without a problem), then in my opinion the explanation does solve the friction problem.
And also the constancy of the speed of light in all reference systems..
And also the source of inertia..
And also the possibility of non-locality..
Israel
Answer my question and you should understand.
Regarding the particles at all speeds - I don't understand what their properties are. Do they have mass? size? What is their density?
Miracles
1. What happened that made the probability that Maxwell's model is wrong to 1.
2. Friction see:
https://www.hayadan.org.il/astronomers-reach-new-frontiers-of-dark-matter-130112/comment-page-6/#comment-324924
Israel
How do you solve the friction?
Israel
What is the probability that yesterday was Monday? One, or seven?
Miracles
What happened that made the probability 1?
The friction does not refute, it has a logical solution.
Israel
Yehuda wanted a refuting experiment. The friction refutes…. Light would not come from the edge of the universe, the galaxies would shrink and so on.
Miracles
What happened?
Yehuda
I have asked you several times how your theory overcomes the friction problem. So far you have not received an answer except "that's how it is!!"
Sabdarmish Yehuda
Read here:
https://www.livescience.com/26017-kilogram-gained-weight.html
for miracles
Apologies, in the meantime the "proof" has arrived
Well you bring up the case we are talking about in the article of the KG losing weight. So first of all you were wrong and it is not about the kilogram losing its mass but its weight. The mass remains constant.
The explanation is this. According to the simple universe, and the particle theory of Pushing Gravity and La Sage, those who determine the weight are the two particles of Pushing Gravity. If the universe is expanding, the gravitational pushing particles fill a larger space, therefore less gravitational pushing particles will affect the mass per unit of time, therefore they will determine a smaller weight as time passes. It's easy to do the math because Hubble's constant is more or less known. I did the math and it turned out that each kilogram will lose a value of a little less than half a microgram per kilogram per year on Earth. So much for the theory. What is really happening in the field, there is a loss of weight exactly like this, but it is determined that it is due to a relative to another kg. I don't know how to treat this, but if there is no weight loss, why change the definition? I suggest conducting an experiment and taking any mass and weighing it on sensitive pressure balances, and seeing if it loses about 0.45 micrograms per kg per year. Remember. Normal scales that use weights will not help because the weights also lose their weight only sensitive pressure scales will.
If the weight changes after a year, you lost. If the weight does not change. This would be a severe blow to the theory because it is impossible for the weight not to decrease. And so you will receive a beautiful gift from me as promised and with joy.
Please respond gently
Yehuda
http://yekumpashut.freevar.com/
for miracles
where is the proof As usual, just talking.
Yehuda
You claimed that the standard kilogram should lose mass over time and that turned out to be wrong.
Israel
The probability of an event that has already happened is 1. I just tossed a coin - I got a 'tree'. I know I got a tree, so the probability is 1.
If I haven't looked at the coin yet, the probability that in the future I will see a 'tree' is 0.5. But, it speaks of the future.
Yehuda
friction.
You wanted conclusive proof, you got it.
Yehuda
friction.
You wanted conclusive proof, you got it.
For miracles and others
Part II'
I was once happy (yes, I was happy!) when I found out that the friction of gravitational pushing would prevent the planets from moving for millions of years, and then (unfortunately) I had the idea that there is no friction because the gravitational pushing particles also revolve around the sun. There is no reason not to. But there will be friction moving away from the sun like Pioneer. My theory explains the Pioneer anomaly. Those who do not accept the pushing gravity found another explanation for the heat emitted by its atomic engines. so be it. I think it would be wise to send a tiny probe that would do just that. check if there is an unexplained jerk in the movement away from the sun.
Albanzo showed me the possibility that in the axle experiment they would find out if there is friction in the movement of the particles with the two particles pushing gravity. So here, the math there is beyond my understanding but also beyond the understanding of many. You need to meet with a scientist there and ask if there is a disturbance in the movement of protons.
My theory also does not believe in singular points, you want to believe your right. To remind you, the laws of physics have never been measured near singular points, and everything that has been determined about their behavior is just an unfounded hypothesis, based on laws that have not been proven there and have only been measured at large distances
In short... I was tired, I gave a lot of possibilities to prove the refutation of the simple universe, unfortunately the experiments are a bit expensive.
So maybe all the many naysayers are right. I only work with evidence. show me
Yehuda
Miracles and others
I have a theory and I don't care if someone sees that it contradicts the data in the field, I would be happy and it would take away the headache I get from all kinds of smart people (no disrespect)
I didn't say the scientists are stupid, that's what you're saying. Everyone thinks the best according to the knowledge available at the time and therefore Ptolemy also deserves a prize for his epics and for me he must be a genius even though I know he was completely wrong. My theory explains the universe without dark matter and dark energy. You insist on using it, you will be perfumed. You want to use gravity in the whole universe?, based on what? After all, Newton determined what he determined by induction, and the formula absolutely does not have to behave even at distances that were not measured. Any attempt to use it at large distances leads to the necessity of saying that "we did not measure well and there is more matter in the universe" my theory does not "fundamentally" contradict the theory of relativity and at short distances it is completely compatible with the theory of relativity but it is not compatible with the theory of relativity at the great distances of the universe because She also does not believe in the existence of gravitation even at distances of a few light years. Beyond that, at large distances the pressure difference works well.
I have never admitted that I have no mathematical knowledge. I have sufficient mathematical knowledge for my needs (usually).
Aristotle did not think like La Sage nor did I live in his time. You just confused your head.
And in general, note that I constantly have to apologize for all the scum you and others throw at me. So it got tired. Show me conclusive proof that my theory doesn't work and I'll give you a fun gift as a thank you. Don't repeat tweets that everyone is tweeting on repeat. There are other things you wrote, we'll leave it for after dinner.
Please respond gently. It's just science
Yehuda
Yehuda
Don't care about your theory? How good to start the morning with a joke 🙂
And after that you show here how much you don't understand people. You don't understand that every scientist, like every other person, longs to find fault with everyone and be the hero of the day. Instead, you live in a world where all scientists are slaves to some revered master who forbids them to contradict his words.
You are told that scientists have found an explanation for the Pioneer anomaly. Instead of accepting it as it is, you call them idiots and liars (in slightly more subtle words perhaps but very clearly).
They explain to you that there is a lot of evidence for dark matter, evidence that your theory cannot explain.
They explain to you that your theory fundamentally contradicts the theory of relativity, and this is negligible on your part.
They tell you that the issue of friction completely disqualifies your theory, and you quibble that it actually strengthens your theory.
You admit that you do not have any mathematical knowledge (like me), but you are not able to understand that it is a basic tool in understanding physics. You think the universe is "simple". The last one who thought like that was Aristotle... I wonder why?
Miracles
I don't care about my theory and contrary to your opinion. Only measurements determine for me, show me one measurement that I ignored?? Those who ignore the measurements are the scientists who decided to change the data measured in the galaxies to fit the formula with the help of illusory matter and energy. And if I show that there is friction in Pioneer's movement, then they tell me stories about Pioneer warming up to the exact extent and direction required. But here, I am not the only one who claims that the speed of light changes, there are several others, and there will be many others.
Israel
You asked if I get a chance to watch variable stars (Cephoids in the sky) through the telescope, the answer is no. But in the next observation I will ask the member of the association to show me. Usually their cycle time is days, so in one night it will not be possible to look at their change. Why is it interesting to the above-mentioned cupids?
Good Day
Yehuda
That the probability is 1 is definitely a matter of opinion. Mine is different. The fact that light is not a wave is also a matter of opinion.
Relativity accepts the conclusions of Maxwell's theory, but rejects the static ether model, and rightly so. It is related to the Jewish theory in that both Lesage and Maxwell speak of a hydrodynamic model of particles. But while Lesage's theory is mainly qualitative, Maxwell gives a precise quantitative description backed by equations for the phenomena.
Israel
The probability is 1. This is not a matter of opinion.
I don't understand why Weichen is different. Light is not a wave. His equations are wave equations, but that is not reality.
In any case, there is a close connection between an electric field and a magnetic field, and the connection is the theory of relativity. Therefore it is not surprising that the speed of light appeared there.
How is all of this related to Jewish law? The Torah that is not suitable for observations. You said that too.
How is it different from Weichen? Why not?
Gegel Heichen and Gegel Maxwell. See how many results you get for each. If Hoychen was wrong it is a marginal mistake, if Maxwell was wrong it is a colossal mistake.
Note also that Maxwell did not come to explain existing observations like Ptolemy and Weychen. Maxwell built his model and discovered - to his surprise - that it links the constants of electricity and magnetism to the speed of light.
The probability that such a complex and accurate model will by chance yield the speed of light is extremely low in my opinion.
Israel
Differentiate between model and reality. McBwell's model is great, and his equations are still used today.
The problem is the projection made from the model to reality.
How is it different from Hoychen's wave theory? An excellent model that is still used today by every optician, every optometrist and every photographer.
Yoda
Do you get to look through the telescope at changing stars?
Miracles
I have a feeling you haven't looked at the model yet.
Take a look and compare to Newton's general light model, Lasage theory or even the theory of relativity. We'll talk after you take a look.
Israel
Newton had a wonderful model of light particles and Hoychan had a wonderful model of light waves. Ptolemy's epicycles and deferents were also amazing.
Greek mythology and the Torah were also wonderful in their time, because they described what they thought was reality.
They are much better, in my opinion, than the model of Yehuda Yedidino, because in their time there were no observations that disproved the models.
Miracles
So Maxwell's theory with its dozens of illustrations and hundreds of equations is wrong.. Schwinn.
And the derivation of the speed of light (Equation 136) is just a lucky coincidence... so be it.
Do you remember Mr. Nachshon from the tracker? He had a method of guessing the results of the lottery: he would count the bumps, multiply by the length of the walls and put the neighbors inside. He always succeeded.
And what about Maxwell's equations? Are they also the result of the blind case? Or maybe just magic?
Did you look at the model? Have you seen how complex and precise it is? Really this Maxwell magician..
Yehuda
Would you please direct me to where I said I think there is no change in the speed of light?
And let's say that there is a change over time in the speed of light - what does this have to do with your theory? After all, you are the last one who believes that observations confirm a theory...
Israel
Are there any cases where a wrong theory gave correct results?
Israel Shapira
Thanks for the help. Valnisim says that since there is no firm decision, I took the possibility that there is a change in the speed of light as a function of time (date), while you prefer the possibility that there is no change. I showed a way how this can be tested in the LIGO facility. And it really doesn't matter if you are smarter and I understand or don't understand physics. There is a figure and you have to decide what is right.
Have a good day
Yehuda
Miracles
Maxwell's site model
https://en.wikisource.org/wiki/On_Physical_Lines_of_Force
From it he deduced the speed of light from the constants of electricity and magnetism, very reminiscent of the Lasage model or alternatively the simple universe, and also in which it is a hydrodynamic universe (liquid or gas), and also in which there are molecules, pressure differences, eddies, currents, zebras..
So the conclusions of the model - the speed of light, Maxwell's equations - are correct, but the model itself is wrong?
?
??
??! ??
Yehuda
You wrote that wave speed is relative to temperature. I explained to you that this is true for longitudinal waves, and if you want, I can explain to you why. But you are not interested in understanding physics, but in advancing your theory despite physics 🙂
If you ever studied physics, you would know that the transverse movement of light waves is exactly what determines the speed of light (again, Maxwell's equations). If I remember correctly, in Berkeley's physics book, the speed of light is calculated as a result of the progress of a transverse electric wave, and the counter EMF created due to the induced magnetic field (also perpendicular to the direction of motion).
Light passes through gas, also through diamond. What does this have to do with it? The medium of light is not the gas molecules.
I didn't cancel any speed changes. On the contrary, I said that I don't see an ad hoc reason that it can't happen (I wrote earlier, because the speed of light depends on two properties of space (mio-0 and epsilon-0).
Say - your particles do not move in space?
Miracles
Light has many properties, but is it really the length or width that binds the speed of the wave? They determine if it will change its speed at different temperatures? at different times?? What is there in longitudinal waves that changes their speed at different temperatures and this something is not in transverse waves?
Secondly, forgive my ignorance, but doesn't light also move in a gas battle? In short, you decide to cancel the option of changing speed, and I decide to accept the option of changing. What will be determined is an experiment that will test for several hours at the LIGO facility the speed of light should show a change of a few angstroms per second for a distance of about 1600 km measured by lasers in LIGO, the more accurate calculation on my website. If anyone has contacts at the LIGO facility I would appreciate it.
Third thing - you said that my space has no properties at all. Unfortunately you are wrong and my space, as soon as it was defined as a gas, has all the properties of a gas, therefore it will have temperatures, pressures, pressure differences, therefore of course winds and a sign of sympathy with Hurricane Irma in Florida, so also in my universe there are also hurricanes, for example Hurricane Andromeda which rotates next to Hurricane Bil The milk, and for that you don't need gravitation or invented dark mass and energy, just a little pressure difference, and everything rotates, but that's for another time. And if you're angry about what I wrote, remember that it's already one after midnight, so please hold back, smile, and respond gently, it's just science.
Anyway, I'm going to sleep!
Sabdarmish Yehuda
http://yekumpashut.freevar.com/
Yehuda
Wave speed in gas is relative to the temperature of the gas, that's right. But... that's when it comes to longitudinal waves only. Light, to remind you, is a transverse wave.
Yehuda - there are no transverse waves in gas...
Yehuda
At all - in your theory, space has no properties at all...
Miracles
Wave speed is proportional to the root of the absolute temperature of the gas in which it moves. I know that the speed of light is something special, and it is also difficult for scientists to accept that the empty space of the universe is actually gas, (in the simple universe theory this follows from the essence of the particle theory) but until it is proven otherwise I assume that light also has this property, meaning that the speed of light is proportional to the root The background temperature of the universe therefore if the background temperature decreases then the speed of light will also decrease. I can know how much the universe is expanding because I know the Hubble constant, therefore the universe cools accordingly, the speed of light will also decrease. I did the calculation and got that the speed of light decreases by XNUMX km per second per year.
On the other hand, at a time when the universe was, for example, 380000 years old, the temperature of the universe was about 3000 degrees Kelvin, that is, a little more than 1000 times the background temperature of the universe today, therefore the speed of light was approximately 33 times the speed of light today, that is, it was around ten million kilometers per second. At such a speed it might not have been necessary to define an inflationary expansion for the universe as stated in the link I gave in my previous response.
And regarding what you wrote miracles about the words of our friend Maxwell, I wonder if there is a corresponding relationship between the magnetic permeability, the dielectric coefficient, and the background temperature of the universe. If there is a connection, it might prevent arguments between me and Maxwell.
Please respond gently
Sabdarmish Yehuda
http://yekumpashut.freevar.com/
Yehuda
According to Maxwell, the speed of light depends on two properties of space - the magnetic permeability and the dielectric coefficient. If they depend on time then the speed of light will change.
But - what does this have to do with your theory?
For miracles and others
Thank you for your kind response
Below is an excerpt from the attached link: Note that I am not alone in my opinions.
"Researchers from the University of Waterloo in Canada and Imperial College London offer a slightly different theory. According to them, the speed of light is indeed constant in all reference systems at any given moment, but it changes in time and was higher in the past. The theory they propose may solve an existing problem in cosmology and explain the early stages of the evolution of the universe." End quote
Here is the link:
https://davidson.weizmann.ac.il/online/askexpert/%D7%94%D7%90%D7%9D-%D7%9E%D7%94%D7%99%D7%A8%D7%95%D7%AA-%D7%94%D7%90%D7%95%D7%A8-%D7%A7%D7%91%D7%95%D7%A2%D7%94
You see I'm not alone and the Nobel Prize will probably be given to others.
Yehuda
Where is your Nobel Prize? I suggest that you write to the Nobel Prize Committee and demand that all previously given physics prizes be canceled!!!
No offense, but your response is just poor - you think you are smarter than physicists who have been working in the field for decades.
You have a delusional theory that explains nothing and contradicts all existing theories. Really embarrassing….
Again, no offense. I generally say my opinion.
Lorem Ipsum
Today we know the source of the discrepancy in the mass of the standard kilogram. It turns out to be hydrocarbons, and they also know how to clean them.
Oh, how naive the surveyors are who use constants which unfortunately are not constant
The speed of light is not constant and changes by about XNUMX cm per second per year, and no Mikkelson Morley experiment can contradict this because the above experiment was done at one point in time somewhere at the end of the nineteenth century. He never pretended to measure the speed of light at different times and compare them. It is impossible based on one measurement to decide that the speed is constant at all times!
The kg itself changes because the gravitational constant changes due to the expansion of the universe, and the same mass will weigh differently at different times.
So you can engrave the kg with super quantum-mythric-plankian methods and with the approval of the rabbinate and the Bedz, but it will not help, and as soon as you reach a final result, your kg will begin to lose its weight, slowly but surely, a little less than half a microgram per year. That's what there is!
And it's true, I know that everyone will attack me, so I really don't care, but I will still ask:-
Please respond gently
Thanks
It is not clear to me by what they will determine the mass of the new kilogram. According to the original weight, with 50 micrograms less? Or maybe according to a certain weighting of the mass of "witnesses"? And what are the consequences anyway?
my father
I think the solution of a liter of water is technically problematic. You have to make sure that the water is completely pure, and this is difficult: the water dissolves everything in the environment, from the air to any container you put the water in.
In addition, water has a surface tension that makes it very difficult to measure the volume.
There was a similar idea - to use a mass of carbon atoms. Instead of determining a volume, do something simpler - determine a certain number of atoms. In my understanding, this method is limited by the accuracy in counting the atoms in a certain body (a pure iron ball with a diameter of 93 mm).
Another method, the one that is probably more practical, is based on Planck's constant. This constant links mass, distance and time, so as soon as you know the size of the constant - you know how to define a unit of mass. And it turns out that there are a number of different experiments that provide the size of the constant with a very high accuracy.
In the past, the kilogram was defined by a fundamental constant in the universe: 1000 cc of water (at temperature and pressure...)
For practical reasons, it was decided to change the definition to relate it to a piece of metal kept in...
Now you see how wrong it was, so why not go back to the original definition?
After all, the standard length is already fixed by a fundamental constant in the universe, (the length of a wave of a laser beam that is produced from a specific isotope of a specific substance...) therefore also the volume, and therefore also 1000 cc of water... so what could be simpler and more correct than that as many of the measurements as possible Will they refer to the same fundamental constant in the universe?
Severing the connection between the mole and the weight is also a problematic thing, because in practice a quantity of substance is weighed to know how many moles it contains, and there is no practical possibility to count the molecules.
And if the weight is attributed to water that is attributed to the length, then it will always be possible to check the correctness of the accuracy of Mol based on the standard of wavelength of...