Researchers have created a new map of the Milky Way that shows that almost a third of the stars have significantly changed their orbits and are in an inner or outer orbit around the center of the galaxy where they were formed.
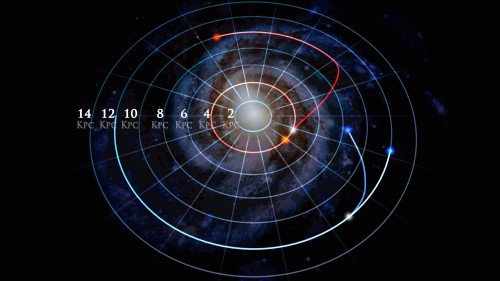
Scientists working with the Sloan SDSS Digital Sky Survey have created a map of the Milky Way that shows that many stars have significantly changed their orbits since their formation.
The discovery, published on July 29 in the Astrophysical Journal, provides new insights into the way stars were formed and how they moved within the galaxy.
"In the modern world, many people have moved to a place far from their birthplace, sometimes half a world away," says Michael Hayden, a doctoral student in astronomy at the University of New Mexico who was the lead researcher on the project. "We have now found that a similar thing is also happening with the stars in our galaxy - about thirty percent of the stars in the Milky Way have traveled a long way from where they were born.
In order to build the map, the scientists used the APOGEE (Apache Point Observatory Galactic Evolution Explorer) spectrograph, which is installed in a 2.5 meter diameter telescope and is used in the survey to observe one hundred thousand stars over a period of four years.
"The key was to create the map and decipher it by looking at the chemical composition of each star. From the composition we can learn about kinship and the history of stars." Hayden says. The chemical information coming from the spectra shows the amount of light the star emits at different wavelengths and provides information about elements and compounds in the stars' atmospheres. Astronomers can tell what a star is made of by reading the spectrum lines.
"The spectrum of the stars shows us that the chemical composition of our galaxy is constantly changing," says John Holtzman, another astronomer from the University of New Mexico and a member of the research team. "Stars create heavy elements in their cores and when they die these heavy elements return to the gas cloud that creates the next stars."
Due to this process, "chemical enrichment" is created, with each generation of stars containing a greater proportion of heavy elements compared to the previous generation. In some regions of space, the star formation activity is higher than in other regions, therefore more generations of stars are formed there. This means that the proportion of heavy elements in stars varies according to their place of origin in the galaxy.
The astronomers then determined in which regions of the galaxy each star was born according to the amount of heavy elements in it. Hayden and his colleagues used the apogee data to map the relative abundance of 15 different elements including carbon, chromium and iron in stars throughout the galaxy. They discovered to their surprise that up to 30% of the stars contain a composition indicating that they were formed in regions of the galaxy far from their current location.
When the researchers examined the distribution pattern of the elements in detail, they discovered that it is possible to explain a considerable proportion of the data using a model in which stars carry out radial migration, meaning they move closer to or further away from the center of the galaxy over time. Such movement in and out is called "migration" and it is apparently created due to irregularities in the galactic disk such as the famous spiral arms of the Milky Way. Evidence of stellar migration has previously been seen in stars close to the Sun, but the new study provides the first evidence that stellar migration occurs throughout the galaxy.
For information on the University of New Mexico website
More of the topic in Hayadan:

14 תגובות
Maybe this is the way we've all been waiting for interstellar travel
may be…
You didn't ask any hard questions. As usual - you slandered scientists without understanding what you are talking about
Is there any information about the origin of the solar system? Where in the galaxy was it created? And from whom and where are its members in the cluster in which it was created? Where are the remains of the cluster? Is it even possible to classify the population of stars in the Milky Way into their source galaxies (from which the Milky Way was formed)?
Indeed, this is exactly the place to hold a crash course in physics on the history of the universe for someone who will reboot his brain as soon as he closes the browser window and restores it to factory settings.
Clarification: The manufacturer is none other than the "teacher" in "Haydar".
Nissim, Sabri Marnan, Ariel,
I ask the hard questions here
When I am convinced that "science" has no answers...
The questions are intended to show the hypocrisy of those who speak in the name of science.
inability to answer these questions,
He is proof of the failure of the big bang theory.
Nissim, Sabri Marnan, Ariel,
I ask the hard questions here
When I am convinced that "science" has no answers...
The questions are intended to show the hypocrisy of those who speak in the name of science.
inability to answer these questions,
He is proof of the failure of the big bang theory.
to remind,
The theory was born at the beginning of the last century,
In order to give an answer to what was then known about space.
Since then, amazing discoveries have been made about the size and complexity of space.
I thought they would abandon this theory,
After it was discovered that galaxies increase their escape velocity from each other,
Contrary to all the predictions of the big bang theory...
Maybe ..
They ask a question in physics. There are several options:
1) Ask a physicist who understands the subject.
2) If you have background on the subject, you can search for the answer yourself - Google or in the library.
3) You can say "I don't know the answer".
4) And you can shout "Conspiracy! ", or "Aliens! " or God! ". But - then you show that you are stupid...
So what is your answer to your question?
Perhaps, Google "how galaxies are formed", you will find that there are excellent explanations, videos and even beautiful scientific simulations based on real data collected and the results agree well with the observations.
Maybe Google is your best friend in case you don't know something, so stop complaining to people that you don't understand something and start reading.
Maybe, how about reading a bit on Google?
https://www.google.co.il/search?site=&source=hp&ei=S5zQVf2fEMqzaYiWgtgF&q=איך+נוצרות+גלקסיות&oq=איך+נוצרות+ג
Sabri Maranan
Finally there is a physicist here who can explain to us
In what physical process was the great "Virgo Cluster" formed?
Or any other galaxy cluster…
(By the way, we still don't even know how one single galaxy was formed).
What exactly is not clear to you? The integration
Between the galaxies in the cluster is caused by something called "gravitational force" you learn about it in the physics major.
A question I asked followers of the Big Bang theory...
We are part of a cluster of galaxies called the "Virgo Cluster"
https://he.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D7%A6%D7%91%D7%99%D7%A8-%D7%A2%D7%9C_%D7%94%D7%91%D7%AA%D7%95%D7%9C%D7%94
The size (diameter?) of the cluster is more than a hundred million light years!!!!!!!!!!!!!
It is an incredible distance, within which there is integration
Among the galaxies in the cluster!!!
How is the "scientific" theory of the Big Bang able to explain this fact?