Assaf Rosenthal expands the coverage following the exciting news from the weekend about the disappearance of fish and seafood within fifty years
In an uncharacteristic move, Japan announced that the fishing fleet had been ordered to cut the amount of tuna caught in half. The tuna meat is used to prepare "Sushi/Sashimi" and as such is considered a delicacy in Japan and in Japanese restaurants around the world, which feeds the high demand.
About 10.000 tons of tuna fish were consumed every year in Japan alone, the wild fishing of tuna fish caused severe depletion and therefore quotas were set.
For years, Japan disobeyed the tariffs with various claims, this year it announced that "despite the damage to the economy and despite the demand for fish, it agrees to the tariffs, recognizing that overfishing will harm the industry." The announcement was received with joy by all the green bodies, and despite this they warn that without a further significant reduction in the amount of fishing, there is a real danger to the existence of the species.
Another fish species is the cod, COD. Since 2001, fish researchers have proposed to completely stop cod fishing in the North Sea, understanding the need to restore the cod population, the authorities (European Union) agreed to gradually reduce the fishing quota - from 100.000 tons in 1990 to 50.000 tons in 2000, and later The quota dropped to 23.000 tons in 2006, and despite this, the population is not recovering. It turns out that the problem is with "indirect fishing", a fisherman who targets other types of fish ("sea donkey" "levanin" and others) is not selective and when cod fish also come up in the net they are not returned to the sea (and they are not included in the calculation of the quotas), and thus the damage actually continues in the population despite conservation intentions.
Since the tuna fish like the cod are predatory fish that are high in the food chain - at the top of the pyramid, damage to their population is a fatal damage to the entire marine system, which means that having healthy populations of the predators is important for the system. In order to allow the populations to recover, the experts suggest establishing extensive areas where fishing will be completely prohibited, without extensive marine reserves. The immediate economic damage is clear, the future economic benefit is much higher.
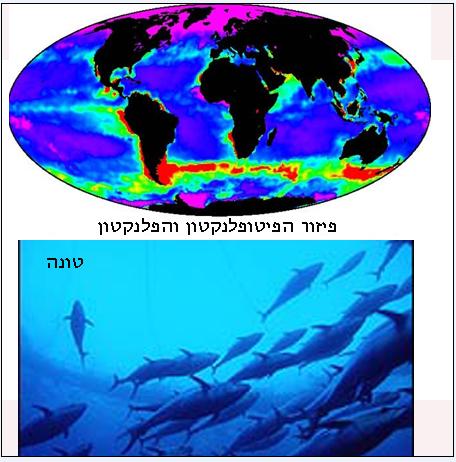
We all hear, in the morning news, how humanity affects the environment and more so the global climate. It turns out that we are not the only ones affected, tests and studies have shown how the movement of plankton (tiny animals) and phytoplankton (tiny plants), as well as the movement of schools of fish, affect the currents of the oceans. The nutritional basis of existence in the oceans are those tiny animals and plants that make up most of the biomass today, their importance to the system has long been known, in calculating the caloric value it turned out that plankton (and phytoplankton) have an energy value that is five times the consumption of the entire human population. Energy production by the tiny creatures that move in huge quantities affects the currents of the oceans, so contrary to what has been accepted until now - that the plankton is completely passive. It turns out that its movement causes the strengthening of the oceanic currents, those currents that move cyclically from north to south (and back), are accelerated by the movement of animals in the sea, shoals of fish, whales, panlactans and phytoplankton, all of which move with the help of the currents and in the process strengthen them.
According to the researchers, the contribution of the movement is equal to the contribution of the winds and the movement of the ebb and flow. The movement brings up cold food-saturated water from the depths to the surface of the sea, meaning it feeds the system. The human impact on the global climate systems - global warming, also affects the wind and current system in the oceans, an effect that... again harms the cycle of food movement and thus in feedback harms the environmental system.
Another and increasing damage appears as "ocean dead zones", large areas in the oceans where there is no life. The concept of "dead zone" in the oceans has long been known. Algae and phytoplankton reproduce and grow at a much higher speed than usual, and reach a density (biomass) hundreds of percent higher than the natural density, not only rapid reproduction but also a fast/short life cycle, at the end of which the plants sink to the bottom of the ocean. The sunset disturbs the gas balance in the upper level, lowering the amount of oxygen in the water. At the bottom, the plants are eaten by bacteria that for their activity "take" oxygen, and thus areas where the algae and phytoplankton culture appears become oxygen-deprived areas where there is no life.
The phenomenon is attributed to pollution... mainly by phosphorous fertilizers that are washed into the sea by rivers, pollution from agricultural areas as a result of over-fertilization, the fertilizers are washed to the depths and later reach streams and rivers that flow into the sea. Untreated sewage also plays a significant role in the discharge of nutrients into the oceans. The forecast is that in 2030 the rivers will flow 15% more "nutrients" into the oceans and thus strengthen and increase the "dead zones".
The "dead zones" are constantly growing: according to a recent UN report, there are about 200 "dead zones", a 34% increase from two years ago. "Dead zones" have been mapped in the Sea of Finland, Poso Lagoon (Ghana), the estuaries of the Pearl and Changyang rivers in China, the mouth of the Mersey River in England, the Aegean Sea (Greece), the Gulf of Paracas in Peru, the mouth of the Mondego River in Portugal, the Montevideo Bay in Uruguay, the Western Ocean The Indian, off the coast of California, off the coast of Florida, the Gulf of Mexico, the size of the areas reaches hundreds of thousands of square kilometers, so that when creatures / fish fall into such an area their fate is one - death by suffocation. In other words, the "dead zones" are a death trap for fish, shellfish and marine mammals, the damage to the environment is clear, at the same time of course also an immediate (negative) effect on the fishing industry, that is, on the economy of everyone connected to fishing!
Interesting to the interest in the same matter: Icelandic authorities announced the renewal of whale hunting. This is after the Icelanders refrained from hunting for 20 years mainly due to international pressure, of course the announcement was received with great indignation by all the countries of the European Union, as well as many countries in the world, the reaction of the world audience was immediate and painful...One of the most important industries in Iceland is tourism, where "whale tourism" is An important part, many of the tourists who used to dedicate a large part of their visit to Iceland to a whale watching cruise, immediately after the announcement of the resumption of the hunt, travel agents reported a sharp drop in tourist bookings. Now it remains to compare the profits from whaling compared to the losses from tourism, and hope that the "hint" will be understood by Icelanders as well as others.
