The first stars were formed earlier than the scientists thought * as shown by images taken by the WMAP satellite
The universe will continue to expand forever at an ever-increasing rate. This is what NASA scientists are going to say in a statement they will make in the coming days. Scientists base their conclusions on new data provided by the MAP (Microwave Anisotropy Probe) satellite that has been orbiting the Sun beyond the Moon's orbit since it was launched in 2001.
The MAP data also confirm the findings that most of the universe consists of mysterious "dark energy" that causes the expansion of the universe to accelerate.
The atoms, the basic components of matter that emit light - and they make up only a few percent of the universe. "For the universe, stars and planets are a marginal component," an astronomer from this group is quoted as saying by the BBC.
MAP is located at a fixed point in the Earth's orbit around the Sun, a point known as L2 and is one of the Lagrange points - points where objects will remain in place towards the Earth, compared to the orbit around the Sun. L2 is the point of balance of the gravitational forces of the Earth, the Sun and the Moon.
The echo of the big bang
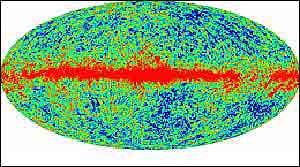
MAP is the first spacecraft placed at the L2 point, which is behind the Moon and follows the Earth and the Moon in their orbit around the Sun. MAP specializes in the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB). The CMB radiation was first discovered in 1965 by Arno Panzias and Robert Wilson from Bell Laboratories in the USA. This radiation was called "the echo of the Big Bang" - the event that created the universe about 15 billion years ago.
The cosmic background radiation was created about 400 thousand years after the big bang. When the universe cooled enough for hydrogen atoms to exist. In 1992, the Kobe satellite (detector of the cosmic background radiation) discovered variations in the background radiation, attributed to the initial structure that created the universe within which the seeds of galaxies appeared in the giant clouds of hot gas that made up the universe at that time.
Astronomers believe that the cosmic background radiation contains a lot of information about the origin of the universe and its fate. Measurements of this radiation will allow cosmologists to determine what the basic parameters of the universe were, for example, whether it will expand forever or collapse, or whether the expansion is speeding up or slowing down.
The MAP satellite scans the entire sky every six months, thus providing a highly accurate map of the cosmic background radiation. The first complete MAP data will confirm previous findings obtained with the Boomerang balloon that flew over Antarctica in 2000.
The balloon showed that dark energy controls the universe, and it causes the expansion of the universe to accelerate. This means that eventually the matter in the universe will be even more dispersed than today, the stars will burn out and the galaxies will evaporate, and everything will become a thin cloud of cold gas forever.
The first stars were formed earlier than scientists thought
by Uriel Brizon
NASA has presented the first data from a satellite that tests the cosmic background radiation

About a week and a half after the disintegration of the space shuttle "Columbia", yesterday the American space agency (NASA) was proud of the achievement. At a press conference it held, the agency presented new discoveries about the structure of the universe and its development, based on findings obtained from the research satellite "MAP" (AnisotropyProbe MAP - Microwave).
NASA scientists were able to determine with an accuracy of 1% - which is considered quite high in this type of research - that the age of the universe is 13.7 billion years. Until now, scientists have estimated that the age of the universe is about 15-14 billion years, but the current findings make it possible to determine its age with greater precision, and strengthen the accepted model in recent years regarding the evolution of the universe and the relationships of its components.
"The big surprise arising from MAP's observations is that the first stars and galaxies formed only about 200 million years after the Big Bang, a significantly short time compared to
The estimates so far," Prof. Avishai Dekel, head of the cosmology group at the Rakah Institute of Physics at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, explains the importance of the findings.
The MAP satellite examined the cosmic background radiation, which fills the entire space and originates from the Big Bang. It was discovered by chance in 1965 by Penzias and Wilson, two scientists of the American telephone company "Bell" who were investigating the source of communication disturbances. The discovery that there is radiation of a uniform nature from every direction in the sky, matched the predictions of astrophysicists who were based on the Big Bang theory, and earned Penzias Wilson the Nobel Prize. In June 2001, a map was launched into space
Collect data on this radiation, and since then it has been orbiting the Sun with the Earth, at a distance of about 1.5 million kilometers from the Earth.
The advantage of studying the cosmic background radiation lies in the fact that it is radiation that is a kind of "photograph" of the universe in its early stages. In the beginning the universe was compressed, very hot and opaque to radiation (like inside a thick fog). Gradually, cooling occurred, and when the universe was about 380 thousand years old, the temperature dropped to about 4,000 degrees Celsius and the universe became transparent to radiation, which began to move freely through it. Today, tiny differences between the radiation intensities observed in different directions in the sky are a source of much information about the structure of the universe and its development.
The study of the cosmic background radiation is the highlight of cosmological research today, but it is mainly possible from space, because of the disturbance created by the Earth's atmosphere. About a decade ago, the COBE (Cosmic Background Explorer) satellite was launched to study the background radiation. Special balloons that cruise at high altitude, at the edge of the atmosphere, also provide data on the background radiation, but MAP's findings are the first of high quality and coverage of the entire sky.
According to Einstein's theory of general relativity, the universe itself may be flat or curved - similar to the surface of a sphere, for example. The degree of curvature of the universe determines whether it is finite or infinite. Therefore one of the most fundamental questions in cosmology is how the universe is curved. Observations conducted in recent years reinforce the assessment that the universe is flat, and MAP's data add further confirmation to this assessment.
Using MAP's results, it is also possible to estimate the contents of the universe: only 4% of the universe is normal matter, which is what the stars, planets and humans are made of. The rest of the universe consists of "dark matter" (23%) - particles whose nature is still unknown; and "dark energy" (73%), which acts as a repulsive force, as opposed to gravity, and causes the expansion of the universe to accelerate. These measurements correspond to the popular opinion among scientists in recent years.
Prof. Dekel concludes: "From the image of the young universe as shown by the satellite map data, the process of the universe's development can be explained: relatively dense regions exerted a greater gravitational force, collapsed in on themselves, and created the galaxies and galaxy clusters we see today. The measured changes in the cosmic background radiation are direct evidence of the initial 'seeds' from which all the objects in the universe 'grew'.

5 תגובות
a question:
Are the galaxies in general or the Milky Way in particular not expanding/contracting?
Thinking logically, I find it hard to believe that all this constantly interacting energy is in a static state.
The dark energy only accelerates the distance of the galaxy clusters. Even without this energy the galaxies would have moved away due to the bang and the bulge.
Nadav, interesting question. As Aryeh Seter answered, the galaxies move away from each other, but the galaxies themselves do not break up.
Why, you must have asked? So the answer to this is: that gravity keeps the galaxies from falling apart, while what increases the distance between the galaxies is dark energy.
The expansion of the universe increases the distances between galaxies. The galaxies themselves do not expand and neither do the solar systems within the galaxies.
If the universe is expanding then how is it that we are always at the same distance from the sun?