The Israeli labor market is moving from a traditional economy to a modern information technology and service economy. As a result, some professions in the economy are at risk of automation, meaning that the workers employed in them may be replaced by machines or computers. A new study by the Taub Center conducted by Prof. Claude Bar Rabi and Kirill Scherberman reveals that in recent years there has been a decrease in the share of workers in high-risk professions, but among Arabs and immigrants the decrease is smaller than among non-Olim Jews. The study also found that the return to education has increased since 2003, especially among women.

From the research findings:
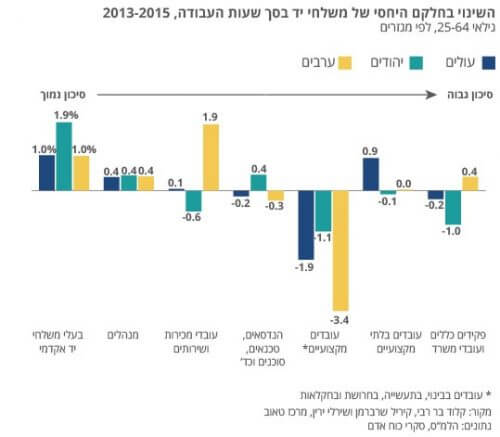
- Between 2013 and 2015, there was an increase in the relative share of workers in manual trades at low risk of automation, and a decrease in the share of manual trades at high risk. The decrease among women was greater than among men.
- In the Arab sector, there was an increase in the share of workers in relatively low-risk professions, mainly sales and service workers. On the other hand, among immigrants, the percentage of those employed in non-professional trades (defined as high risk) among those aged 54-45 has increased, which may be due to absorption difficulties.
- The hourly wage gap between those with 18 years of schooling and those with 12 years of schooling was about 35 percent among men and about 40 percent among women in 2014 - an increase compared to 2003. The smallest wage gap between the different levels of education is among immigrants.
- In the Arab sector, the skills of the workers are relatively low: the proportion of those with high skills in reading and mathematics stood at
Only one percent, compared to 13-10 percent among Jews (according to the adult skills survey of PIAAC).
In recent years, there has been a lively discussion about professions that are at high risk of disappearing from the labor market as a result of modernization processes, which are manifested in the transition from a traditional economy, where industry and production are the engine of the economy, to an information technology and service economy, where knowledge-intensive industries and services are the main engines of growth.
A new study by Prof. Claude Bar Rabi and Kirill Scherberman from the Taub Center adds a new layer to the subject, and examines the trends in the risk of automation in the market between 2013 and 2015. The study examines the changes in the relative share of different manual dispatchers in the economy as a whole, and presents the changes according to the rating of the automation risk of the manual dispatchers. The changes were examined both in the general sector, and in the division into men and women and into different sectors (non-immigrant Jews, Arabs and immigrants who arrived in Israel since 1990).
The study found that the relative share of workers in low-risk occupations increased, while the share of workers in high-risk occupations decreased. The changes among women were greater than among men, mainly because there was an increase in the share of workers in the "academic occupations" category, and among women the average level of education is higher. At the same time, the share of clerical manual workers in the economy as a whole has decreased, and the percentage of women employed in these professions is particularly high.
Alongside this, Bar Rabi and Sherberman found a significant decrease in the share of women employed in the clerical category - a process that may indicate that certain administrative jobs have already undergone automation and computerization (evidence of this is the closing of bank branches, outsourcing of secretarial services and the use of computer software for office management).
The increase in the share of low-risk jobs, which probably stems from a growing demand for professions that require high skill, affects the average salary.
More Arabs work as sales and service workers; Immigrants employed as unprofessional workers are exposed to a high risk of automation
The findings of the Taub Center's research show that in the Arab sector there has been a decrease in the share of workers in industry and production (who are considered to have a high risk of automation) and a relatively large increase in the share of sales and service workers and those in clerical professions, who are at a lower risk. A possible explanation for this is that the process of automation of manufacturing, industrial and construction jobs led to low-skilled workers being forced to move to service and sales jobs. There was a small change (an increase of one percent) in the share of Arabs working in academic occupations. However, the change is small compared to the Jewish population (an increase of 1.9 percent), and accordingly the change in the average salary among Arabs is also lower.
A possible reason for this is that the skills relevant to the labor market in the Arab sector are relatively low: the percentage of Arabs with high skills in reading and mathematics among Arabs aged 65-16 is only 13 percent, compared to 10-XNUMX percent among Jews (according to PIAAC's international adult skills survey).
Among immigrants there was a greater decrease in the share of professional workers and a smaller increase in the share of workers in academic occupations (relative to Jews who are not immigrants). An unusual increase in the share of those employed in non-professional occupations (such as cleaning and guarding) is evident among men aged 54-45 who immigrated to Israel in 1995-1990. According to the researchers, "the data most likely indicate absorption difficulties among this group of immigrants who have been in Israel for over a decade and have difficulty adapting to changes in the modern labor market."
Women who immigrated to Israel from 2008 onwards are employed as unprofessional workers at high rates in almost all age groups, but the changes in the mix of manual workers among them are faster - and from this it can be assumed that their chances of improving their situation and working in more profitable and lower-risk occupations after acclimatization in Israel are higher than for men.
Among the reasons for the difficulty of immigrants to be absorbed in the employment market are language difficulties in Hebrew, and sometimes also in English. The immigrants in general, and the women immigrants in particular, are characterized by a high proportion of those with academic degrees that do not match the local labor market, and therefore compromise on employment in trades that do not require an academic education. Despite this, immigrants are employed at slightly higher rates than non-immigrant Jews.
The increase in disparities based on education contributes to the increase in disparities in income from work, especially among men; Among the immigrants, the gaps widened
The second part of Prof. Bar Rabi and Sherberman's research dealt with the change in the return to education, that is: to what extent a year of formal education improves the average hourly wage of the employee (controlled by other characteristics of the employees such as potential experience, sector and occupation).
The findings show that since 2003 there has been a general increase in the return to education. This increase encourages workers (especially young people) to acquire additional education, thereby improving the quality and skill of the workforce. However, the increase in the return to education also contributes to the increase in the disparity between workers in income from work.
In 2003, the hourly wages of men with 18 years of schooling (equivalent to a master's degree) were about 31 percent higher than the wages of men with 12 years of schooling (equivalent to high school graduation or a matriculation certificate). In 2011, the gap was about 40 percent, due to an increase in the contribution of a year of education to the employee's salary. In 2014, the gap was about 35 percent, i.e. higher than in 2003 but lower than in 2011. The narrowing of the gaps between 2011 and 2014 was mainly due to the increase in wages among men at all levels of education and a decrease in the contribution of a year of education to wages.
Among women, the gap in the correlation between the hourly wage and education in 2003 of those with 18 years of schooling and those with 12 years of schooling was about 27 percent. In 2011 the gap rose to about 37 percent and in 2014 it reached a level of about 41 percent. According to Bar Rabi and Sherberman, the reason for the increase in the gap is changes in the mix of manual workers in which women were employed between 2003 and 2014.
Among Arab men, the wage gap between educated workers and workers with a lower education was similar to the general rate in 2003, but by 2014 there was a decrease in the gap, contrary to the trend among all men. The difference lies in the fact that the increase in the wages of Arab men in these years was more moderate than among all men, therefore the value of a year of education remains lower.
There has also been an increase in the return to education among immigrant men, but the differences are lower than among all men: the wage gap between an immigrant with 18 years of schooling and one with 12 years of schooling was only about 14 percent in 2003, and about 22 percent in 2014. For the differences between the distribution The differences between immigrants and non-immigrant Jews have a large contribution to the disparities between the groups. The relative share of immigrants working in occupations with low and medium wages is high compared to Jews who are not immigrants, as is the proportion of those with academic education employed in these occupations, therefore the return to education among them is smaller.
A different trend was evident among immigrant women. In this group, the return to education decreased between 2003 and 2011, due to an increase in the relative share of women working in occupations with intermediate or low wages (sales and services, clerical and technical professions) and a decrease in the share of women employed as professional and non-professional workers and working in management positions. Conversely, between 2011 and 2014 there was an increase in the return to education among immigrants, as a result of an increase in the share of women employed in academic occupations, a continued increase in the share of employed women in technical occupations and a decrease in clerical occupations.
Among other things, the immigration took place thanks to young women who were minors when they immigrated, whose education and skills are more adapted to the Israeli labor market. The proportion of female academic immigrants employed in occupations with medium and low wages is higher than that of male immigrants, a figure that suggests that their skills are less adapted to the labor market compared to men.
Taub Center researchers point out that "the increase in the return to education, combined with the increase in the labor supply of those with higher education, indicates the continued increase in demand for workers with high skills, and it is likely that the increase in their wages will continue."
The wage gap has increased, especially the gap between Arabs and immigrants and the rest of the population
Since the beginning of the 2013s, a trend of narrowing gaps between high and low wage earners has been observed, but from XNUMX onwards, the widening of the gaps in the labor market is evident. Inequality is also expressed in the wage gap between non-immigrant Jews and Arabs, and between immigrants and non-immigrant Jews. In an examination over time, the gap between Jews and Arabs was found to be quite stable, but the gaps between immigrants and old Jews and the natives of the country have narrowed, due to an improvement in the mix of manual workers in recent years (mainly among female immigrants). Higher employment rates of immigrants also had a contribution to narrowing the gaps.
Bar Rabi and Sherberman point out that "the trends described above contributed to the acceleration of the polarization process in employment and wages, which is accompanied by the increase in inequality in the labor market. However, these trends also reflect positive changes, such as the modernization of the workforce." According to them, "the increase in the wage gap is affected by the entry of people with low skills into the labor market, who in the past probably relied on the welfare system and now contribute to the national product. But the main reason is a constant increase in the share of those with an academic education in the labor supply, due to the entry of younger and more educated workers than before into the labor market."
The Taub Center for Social Policy Research in Israel is an independent and non-partisan research institution that deals with economic and social issues. The center provides policy makers and the public with research and data on some of the most important issues that Israel faces in the fields of education, health, welfare, the labor market and economic policy, in order to influence the decision-making processes in Israel and improve the well-being of all the country's residents.
See more on the subject on the science website:
- No government in the developed countries is prepared for the robot revolution that will eliminate jobs throughout the organizational hierarchy
- Retirees who have been counted have no choice but to work as Uber drivers for a much lower salary
- Welcome to the haggling economy: the implications of artificial intelligence
- About 40% of employment in Israel is in professions that are at high risk of going through a computerization process in the next two decades
