Among Saturn's moons, after Titan Enceladus has become the most geologically intriguing moon. The more photographs arrived, the more and more the interest in him grew
soil temperature
Hexini also carried out temperature measurements of the ground, particularly in the South Pole in the "tiger stripes" area, and temperature differences between different areas and changes over time were found. The measurements reported here are in chronological order.
1. Measurements on 14.7.2005. Thermal radiation at wavelengths between 9-16.5 microns was measured from a distance of 84,000 km. The temperature at the equator is 193 C ° -. The temperature at the South Pole is 15° higher than expected. The spectral measurements raised the possibility that small areas at the pole are warmer -163 °C. The evaporation of the relatively warm water ice probably created the water cloud that was discovered over the South Pole by other instruments of the spacecraft. It is difficult to explain this by the subsequent heating from the sunlight heating the ground. The estimate is that there must be an internal source of heat within the moon itself (21).
2. In another measurement, a temperature of -163 °C was measured around the South Pole. In the rest of the moon the temperature was -198°C (22).
3. The temperature range in the "tiger strips" area was 202°C - 187°C. As you move away from this area, the temperature drops. It should be taken into account that the range of uncertainty is increasing as you move away from the "tiger strips" the measurements raised the possibility that in narrow strips hundreds of meters wide along the "tiger strips" the temperature reached 128-4 °C. (Source 23)
High temperatures above the "tiger stripes" C °183- C °201 -. Here, too, the uncertainty range of the measurement increases as you move away from the hottest area. Regarding other areas, the assessment was that in narrow strips hundreds of meters wide along the "tiger strips, the temperature reached -128°C (24).
5. Comparing temperatures between the July 2005 observation and the November 2006 observation, it became clear that the temperature differences are very small, which indicates that the South Pole region continued to be active and that most of the heat came from "the tiger stripes themselves" (25).
6. Measurements on 12.3.2008 in Damascus Sulcus. A temperature of -93 °C was measured. In other areas the temperature was below -201°C (26).
heat sources
Among the researchers, there were those who compared the underground ocean of Enceladus to Lake Vostok trapped 3.6 km under the ice sheet of Antarctica. This lake is deep inside the moon or near the surface (27). The obvious question is what causes the water to heat up and break out. Clearly something is going on underground. Since the geysers burst out through the "tiger strips" the obvious conclusion is that in these canyons there are exits to the water. On the other hand, no ice geysers or ice-emitting volcanoes were observed. The lack of ammonia and the emission of volumes of water vapor raise the possibility of pure water volcanism (4).
According to one explanation, the origin of the internal heat is in the geometry of the moon's orbit around Saturn. An eccentric orbit and its distance from Saturn changes as a function of its position in the orbit around Saturn. Due to the changing distances, tidal waves are created that cause the moon to shrink and stretch. The resulting internal friction creates heat, a process that is estimated to only exist when there is an ocean separating the moon's ice crust from its siliceous core. Without this lubrication, the moon would be too rigid to stretch and contract. It turned out that the heat emitted by the moon is faster than its formation. If the eccentricity of the orbit in the past was like today, the moon would have completely frozen and the heat waves would have stopped. Since all the signs indicate the presence of an ocean, the possibility was raised that this ocean contains a large amount of salts and ammonia that lower the freezing point. It is possible that the ocean itself creates heat waves by beating Back and forth similar to what ocean tides do on Earth. In that case, the moon would not be able to generate this heat for a long time to create an oceanic presence nowadays. It must therefore be taken into account that the moon used to be in a more eccentric orbit. According to one of the proposed models, if the eccentricity of the orbit was 3 times greater than the current orbit, the heat tides would be sufficient to maintain an ocean over time (28).
Another source of heat is the resonance of Enceladus with another moon of Saturn, Dion. The time for one revolution of Dion around Saturn is equal to two revolutions of Enceladus. This resonance causes an eccentric orbit of Enceladus leading to another and continuous "squeezing" by Saturn's gravity (29).
Internal structure
In order to explain the meaning of the geysers on such a small planet, a model was built that tries to answer this question. According to this model, shortly after the formation of the moon, a rapid decay of radioactive materials occurred within it, which resulted in a rapid and long-term warming of the moon's interior that continues to this day. Support for this model was found in the fact that these geysers contain molecules that require high heating. According to this model, Enceladus began as a mixture of ice and rock that contained rapidly decaying radioactive isotopes of aluminum and iron. This decomposition lasted about 7 million years and was accompanied by the release of large amounts of heat. The result was the crystallization of the rock near the core covered by an ice shell. The residual material of the slowly decaying radioactive material continued to heat and melt the moon's interior for a billion years in parallel with Saturn's tidal forces.
This model could explain why Enceladus can produce chemicals inside the geysers. These are the small amounts of nitrogen, methane, CO2, propane and acetylene. The surprise was the presence of nitrogen. It is estimated that the nitrogen is a product of the decomposition of ammonia inside the moon, at the place where the hot core and the surrounding liquid water meet. Thermal decomposition of ammonia requires a temperature of 577 °C, depending on whether catalysts such as clay minerals are present. The problem with the model of the radioactive decay and tidal forces of Saturn is that they cannot explain such high temperatures, the ammonia compounds can explain the phenomenon of geysers (0 3). Some of the researchers raised the possibility that Enceladus has a core of molten rock at a temperature of 1100°C (31).
tectonics
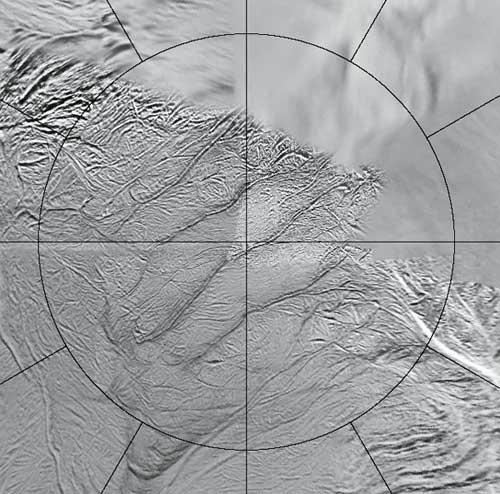
Massive evidence of the power of tectonics began to emerge from the moment high-resolution photographs were broadcast to Israel. Photo 10351PIA shows the ancient and crushed ground of Enceladus. In this photo, long grooves and a large number of parallel and young cracks crossing craters are visible. The craters are 2 km in diameter and hundreds of meters (32) deep. Photo 10352PIA is from a younger area in the "tiger strips". In these strips there are deep grooves and two ridges around them. The strips themselves have almost no relief. The height of the ridges is 75-200 meters and the depth of the grooves between them is 150-300 meters. Ridges along the polar region have undergone deformation and are 1 km high (33).
The set of high-resolution photographs shows that Enceladus' ice sheet is expanding, similar in terms of its tectonics to terrestrial tectonics, but with a number of unique differences. Expansion on Enceladus is in one direction.
The process is not understood, but it is possible to notice branching and mountain building similar to what happens on Earth, which raises the possibility of underground heat and convection currents. Relying on the new maps of the South Pole, a historical map of the "tiger strips" was built in a computerized process. Each time it is found that the remaining segments connect together like a puzzle.
The close-up photographs also raised the possibility that the condensation from the geyser eruptions creates a kind of plugs of ice that clog old exit openings and cause the formation of new openings. This opening and closing shows that the geysers change from month to month and year to year. The cracks not only open and close, but they also migrate up and down along the cracks over time.
Over time the particles return to the ground and form a continuous layer of ice along the cracks. The combination of water vapor, organic matter, and heat released from the South Pole raises the possibility of a potential habitat under the South Pole (34). The tectonics including the structure of the relief found are similar to an oceanic submarine land zone in the East Pacific Ocean, a place called East Pacific Rise W °104 N ° 9.5 (35, 36, 37).
Sources
21.PIA06432: Enceladus temperature map
http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA06432
22. Klotz IM-"Saturn moon spews fountains" 1.12.2005
http://dsc.discovery.com/news/briefs/20051128/enceladus_spa-5print.html
23.PIA07793: Searching for warmth
http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA07793
24. PIA07794: Searching for warmth
http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA07794
25.PIA09037: Enceladus keeps the home fires burning
http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA09037
26.PIA10361: Jets spots tiger stripes
http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA10361
27. "A look at Enceladus' plume" 7.2.2008
http://saturn.jp.nasa, gov/ multimedia images/image-details.cfm?ID=2944
28.Schriber M.-"Ocean on Enceladus may be short lived" 23.6.2008
http://www.saturndaily.com/reports/ Ocean_ On_ Enceladus _May _ Be_ Short_ Llived_999.html
29. "Hot spots on Enceladus cause plumes" 18.12.2007
http://www.saturndaily.com/reports/ Hot_ Spots_ On_ Enceladus_ Causes_ Plumes_999.html
30. "A hot start might explain geysers on Enceladus" 12.3.2007
http://www.spaceflightnow.com/news/n703/12enceladus/
31. Black R.-"Saturn moon best bet for life"
http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/sci/tech/4895358/stm
32.PIA10351: Ancient cratered terrain on Enceladus – A complex deformation history
http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA10351
33.PIA10352: Tiger stripes on Enceladus – Fracture zones and plumes sources
http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA10352
34."Saturn dynamic moon Enceladus shows more signs of activity" 16.12.2008
http://www.saturndaily.com/reports/ Saturn_ Dynamic_ Moon_ Enceladus_ Shows_ More_ Signs_ Of_ Activity_999.html
35.PIA11138: Spreading ridge transforms on Enceladus
http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA111138
36.PIA11139: Enceladus offset spreading center
http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA11139
37.PIA11140: Ancient terrain on Enceladus
http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA11140

3 תגובות
Yes, yes many interesting excavations, but results, when will they say "life has been found", when eh?? Hopefully in another 10 years, now it's another one of the articles of science and Nasa
The article is very interesting but it should be stopped and made sure that it is displayed correctly on the browsers. This material is hard to understand anyway, so its presentation is very important.
Interestingly, if there is water there and if there are warm and deep areas there - there is a good chance that there is also life there that reminds us of life here. Maybe not in the hot center and probably not in the frozen outer layers - but somewhere in between, there must be good places that allow water to be liquid. It's fun to hear that the future doesn't end with Mars.