The leader of the research Prof. Galia Blum from the Hebrew University: "The research we carried out has tremendous potential to help in the future in the early and accurate diagnosis of cancer diseases"

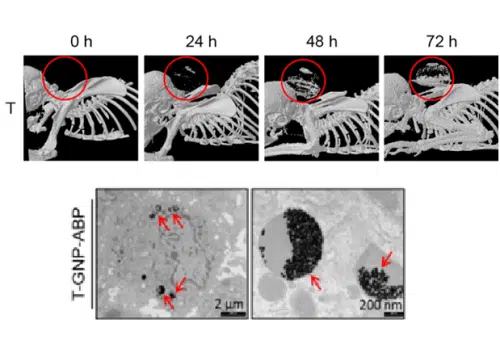
Researchers from the Hebrew University have developed non-radioactive contrast agents that enable the identification of cancerous tumors and inflammatory processes with the help of a CT device in a more efficient way. The leader of the research Prof. Galia Blum from the School of Pharmacy in the Faculty of Medicine at the university and other researchers have developed a family of substances that contain gold particles with tiny sizes of 10-100 nanometers, which are able to penetrate into the cancer cells and optimally bind to cellular enzymes that are highly active in cancer tumors and inflammatory diseases without harming the cells themselves.
Due to the low sensitivity of CT devices today, we need a significant accumulation of contrast agents in cancer cells for their detection and identification in the body. During the research, an experiment was carried out on mice with cancer, into which tiny particles of gold with sizes of 10-100 nanometers, developed by the researchers from the Hebrew University, were injected. The results of the study showed that there was a very impressive accumulation of these particles around the tumors, with over 10% of their cancerous tissue stained with gold particles. In doing so, an inverse relationship was found between the size of the particles and their ability to accumulate in tumors.
According to the researchers, these new materials open a medical door that will help in more accurate diagnosis of cancer and other diseases in which it is necessary to identify inflammatory processes, such as arterial calcification. Prof. Blum stated that "the research we carried out has tremendous potential to help in the future in the early and accurate diagnosis of cancer, and to increase the chances of recovery from the disease. These materials, which the standard CT devices are able to detect, will be able to contribute to hospitals that lack advanced equipment to detect cancer in the human body."
The study was recently published in the "Journal of the American Chemical Society" in which the method of preparation of the materials, their characterization and their use in animals is described. The research work was done with the support of a research grant from the European Union, as part of Daria Tsvirkon's doctoral thesis, and in collaboration with Prof. Rachela Popovtzer from Bar Ilan University.

One response
Please when will he arrive at the hospitals?