A chain of 14 galaxies arranged in a straight line aroused the suspicion of researchers at Tel Aviv University who decided to investigate them in depth from the observatory at Mitzpe Ramon * Adi Tzitrin, this is his master's thesis and the supervisor Dr. Noah Brosh concluded that these are galaxies formed as a result of a concentration of dark matter
Research recently completed at Tel Aviv University's Weiss Observatory suggests that matter accumulates from space on dark matter concentrations and forms galaxies. As part of the research, nearby galaxies were studied in detail, and the results show the mechanisms of galaxy formation throughout the universe. This research is the master's thesis of Adi Tzitrin in the Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics, written under the guidance of Dr. Noah Brosh, director of the Wise Observatory. The main points of the research will be published in the Royal Astronomical Society's journal in Great Britain.
In a conversation with the science website, Dr. Brosh explains that dark matter can only be discovered through its gravitational force as its effect is measured on its environment. Dark matter makes up about 23% of the universe's content, while luminous matter makes up only a few percent. Although the nature of dark matter is still unknown, calculations show that the universe is dotted with accumulations known as "dark halos". These halos affect their surroundings because the dark matter attracts intergalactic gas that turns into galaxy-forming stars. The currently accepted picture of galaxy formation indicates the accumulation of gas clouds in regions with a stronger gravitational force than the environment. These "sinks" of gravity are created because of dark matter inventions.
Citrine and Brosh's research focused on a group of galaxies located about 15 million light-years from us. This is a close distance, relative to the distance from the Milky Way (our galaxy) of most galaxies. Nearby galaxies appear larger and brighter than distant galaxies, just as nearby objects appear clearer than distant ones. The galaxies were first measured as part of a sky survey in the field of radio radiation carried out at the Arecibo Observatory in Puerto Rico. Dr. Brosh is one of the managers of this survey, known as ALFALFA, in which radio transmission at a wavelength of 21 cm of cosmic hydrogen atoms was measured. The sources of radio radiation are often identified with galaxies that also emit visible light. The transmission is located in the XNUMXD space because of the simultaneous measurement of the source's speed relative to us - the expansion of the universe means that the distance is directly proportional to the speed for distant objects.
The ALFALFA survey found 14 galaxies in a small region of the nearby universe, which are about the same distance from us and whose images in visible light suggest their young age. The researchers' interest was focused on these galaxies because they are arranged in the sky on a straight line, while the entire region is characterized by a significantly lower than average galaxy density. The research described here added to the visible light information a measurement of the amount of light emitted by very young stars, only a few million years old, from each of the galaxies. Together with measurements in other colors, the research enables the reconstruction of the history of star formation in each galaxy.
"Many of these galaxies were known before, but until the radio observation in Arecibo they did not know that they are in a similar relationship in space, that is, in the same area and moving away from us at the same speed. I am one of the research directors in Puerto Rico and in this context I saw one of the first data received and immediately noticed that it was a strange phenomenon - that the galaxies are arranged in the sky and more or less at the same distance from us and then we decided to check what their star formation properties are. We came to the conclusion that the 14 galaxies we studied could be formed on the basis of dark matter. There are several reasons for this, first, the galaxies do not touch each other, and apparently they are even quite far from each other, but they are arranged along a straight line, and they all look like young galaxies - that is, those that were formed a long time after the formation of the universe (some of them are apparently less than 5 years old billion years and the others at most 10 billion years old), and they had star formation in the last tens of millions of years." says Dr. Brosh.
Are these galaxies part of our local cluster?
"These galaxies are close but not within the local group, they are about 15 million light years away. The local cluster extends to about 2 million persec or 6 million light years.”
This phenomenon, of synchronized star formation in several neighboring galaxies, is known in astronomy but is often attributed to the influence of one galaxy on its companion following a collision or by the action of "tidal force"; These spur a burst of star formation. But most of the 14 galaxies studied show no signs of a strong interaction.
Theoretical calculations by Hebrew University researchers led by Prof. Avishai Dekal, of the development of the largest structure in the universe, indicate the existence of conditions in which the intergalactic gas can accumulate on small dark halos without heating to a temperature of millions of degrees. "Cold" intergalactic gas can effectively transform into stars. Other theoretical calculations have shown that in the process of the formation of the large structures in the universe, galaxy clusters are formed (concentrations of hundreds and thousands of galaxies in a volume that is about 10 million light-years in diameter), galaxies in the field where their density is lower than in the clusters, and also "cosmic spaces" that are almost devoid of galaxies. In these huge spaces there are a small number of small dark halos, which are sometimes arranged along a "filament". A filament of dark matter can act as a focus of gravity and pull intergalactic gas from the environment to it.
The galaxies studied by Citrine and Brosh are arranged on a straight line that is at least one and a half million light-years long within a region defined as "cosmic space". All of them are of the young and dwarf type, with the largest of them being only about ten percent of our Milky Way and most of them being much smaller than that. Almost all of them are creating stars in the current period. The galaxies are a collection of dark halos that are arranged along a cosmic thread of dark matter, with the current star formation probably caused by the absorption of intergalactic gas by the cosmic thread. The remaining proximity of this galaxy array to us, only about 15 million light years, allows for research that will further focus the history of star formation in each of the galaxies and clarify the connection between the nature of dark matter and the nature of the galaxies we see today.
What is so strange about the massive creation of stars, after all, new stars are created all the time for milk?
Dr. Noah Brosh: "When you see massive star formation events in two nearby galaxies, it happens because they influence each other, that is, one galaxy tears pieces from the other due to the force of gravity and these pieces fall on one of the galaxies, and if there is gas in them, this gas can become For stars, however, there is no known mechanism that explains why many galaxies - more than ten galaxies that do not touch each other, produce stars at the same time. The Milky Way is an old and orderly galaxy and the formation of the stars in it can be easily explained. However, not all galaxies in the Local Group form stars. In general, the local cluster is also a rather amorphous collection of galaxies and they are not arranged in a single line.
So why determine that they consist of dark matter and not normal matter?
The explanation we propose is that these galaxies we see were formed as a result of the accretion of dark matter. The dark matter attracts gas from the environment. This gas condenses until it can form stars and when the stars light up we see the galaxies.
Was the telescope at Mitzpe Ramon sufficient for this task?
"The optical observations were made from Mitzpe Ramon and from them we were able to learn about the properties of star formation in these galaxies. We would be happy if we had a bigger telescope because then we could do more detailed work such as finding the abundance of heavy elements in these galaxies (carbon, oxygen) and thereby locating their age. For this, a large eight-meter telescope is required."
In recent years there has been an increase in the astronomy community, And Prof. Hagi Netzer even said this explicitly, a request to join one of the large telescope projects, what happened to this request?
Dr. Brosh: "If it was possible for us, we would join. We would like to join the Southern European Observatory located in Chile. Not only do they have 4 8-meter telescopes that work together, but they are also planning a telescope whose diameter is close to 50 meters, but we will settle for a smaller telescope between 8 and 10 meters that can supply us for 10-15 years. There is no progress on the issue. This requires a visionary who can implement budgets for this and who can see that the State of Israel will benefit, not only for the small community of astrophysicists but also for industry in Israel, the advancement of science in general, etc. Cypress summarizes.
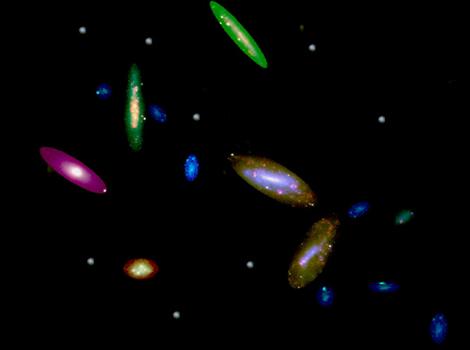
Illustration: The image shows the 14 galaxies studied at the Wise Observatory. The image of each galaxy was composed of three digital photographs taken through different filters. The colors are "blue", "red", and the special color that emits ionized hydrogen gas. The five faintest galaxies are shown synthetically for the visualization. The celestial region where the galaxies are visible spans about 6 degrees in the sky while the apparent size of each galaxy is only about one minute of angle, so the images of the galaxies are greatly enlarged to highlight details within the image. The relative sizes of the galaxies are approximately preserved, but their distances from each other are reduced while maintaining their mutual position. Also, the color ratios between the galaxies were changed to get a good visualization. The background on which the galaxy figures are composed is artificial. It should be noted that the galaxies are arranged along a line stretching from the lower-right part of the image to its upper-left part. The star formation regions in each galaxy stand out as glowing points in reddish hues.
Related news on the knowledge site

20 תגובות
To Michael
Of course I asked myself these questions
1. The mass of that body cannot be calculated, but this does not contradict the theory.
2. It is possible to calculate its speed in an indirect and approximate way, but I cannot go into it in this framework.
3. These clusters do not continue to form further along the trajectory of the body when it leaves the bingalactic cloud.
This is the simplest theory, therefore it is better than more complex theories, this does not mean that it is correct.
A. Ben-Ner:
There is always another question and this is because there are many stages on the way between complete lack of understanding and complete understanding.
Among these stages there are, by the way, also stages in which incorrect hypotheses are raised.
To submit that the young galaxies are arranged along a line, it is because the dark matter is arranged along the same line, is just like saying that if the galaxies were arranged in globular clusters, then it was because the dark matter was arranged in globular clusters. And there are globular galaxy clusters. So what does this mean about the concentration of dark matter in these clusters? The question is how or why the theory explains the phenomenon of dark matter filaments.
Joel:
Your words are unfounded and the explanation does not completely fit the logic.
The fact that there are many clusters arranged along a straight line is a known fact, as you mentioned.
But have you ever tried to calculate what the mass and speed of that body you are talking about should be in order for galaxy clusters to export (the rest of you can also reach tens of millions of light years)?
Have you tried to answer the question why these clusters do not continue to form further along the body's path?
Asaf:
No
Is "dark matter" the modern phlogiston?
The reason they are arranged on the same line is that a super massive body passed through the bingalactic cloud about 10 billion years ago at high speed and caused it to collapse into several points
This phenomenon is apparently very common. It is enough to take a normal picture of young galaxy clusters to see that the galaxies are arranged in straight lines.
point:
I thought before I responded and responded what I thought.
If I misinterpreted your comment, I am happy for your intention and apologize for my misunderstanding.
So what do you say Michael, shall we accept the joke of a point?
Well, come on, let it be.
So good day everyone
And let's win some medal
Sabdarmish Yehuda
come on. I was joking a little too...maybe think before you react
Michael
I have no words. If they were to give out medals on comments on the Internet, you would get at least bronze or silver!
(the gold of course for me)
Have a good day to you and everyone
Sabdarmish Yehuda
point:
Here I agree with Yehuda.
What, he's not allowed to joke either?
I personally have arguments with him and during the relevant discussion we sometimes slip into unpleasant expressions, but there is a big difference between that and just an attack.
And by the way - I actually like his jokes.
Anyone have any idea what's driving this poor point?
Or maybe he just woke up on the left side?
Or is he not guilty at all and that's how he is?
Does anyone know him and can testify to his wonderful personality?
Good day to all commenters, (even the poor ones)
Sabdarmish Yehuda
Yehuda, shut your mouth as long as you do not understand and are unable to calculate those "theoretical calculations".
Dear Sharon
I can't let you down, so here I am responding.
Good night
Sabdarmish Yehuda
Now, in order for the article on dark matter to be perfect, Yehuda Sabdarmish's response is missing.
To my father, I was glad to hear that your site knows how to talk. 🙂
I did not understand from the researcher's explanation why it is unlikely that young galaxies of roughly the same age would start producing stars at the same time.
Could it be that these galaxies are arranged along a cosmic string?