The researchers showed for the first time that the galaxies were formed by means of jets of matter, while the collisions between them had only a small effect on their development - contrary to what is commonly thought

A group of researchers led by Prof. Avishai Dekel from the Rakah Institute of Physics at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem showed with the help of advanced computer simulations thatThe galaxies were formed in the early universe Through powerful jets of matter, while the collisions between the galaxies had only a slight effect on the development of the galaxies, contrary to what is commonly thought. The results of the research will be published tomorrow in the prestigious journal Nature.
Galaxies are the building blocks of the universe. Each one contains about one hundred billion stars as bright as our sun and spans about fifty thousand light years (the distance that light travels in one year). Each galaxy lies in the center of a large and ten times more massive sphere than the collection of luminous stars, which is mainly made of dark matter (a substance that does not emit light and whose quality is unknown), and which can be identified through the gravitational force it exerts on the stars visible in telescopes.
There are two main types of galaxies: spiral and elliptical. The spiral galaxies (like our "Milky Way" galaxy) are rotating disks, rich in hydrogen gas which gradually turns into new stars, at the rate of a few stars per year. The young stars give the spiral galaxies a blue hue (Image 1). In contrast, elliptical galaxies have a spherical structure, and are gas-free and therefore contain mainly old stars with a red hue (Image 2). Trying to understand how the two types of galaxies were formed is the biggest challenge in the field of universe research today. The formation of galaxies is the first step in the cosmological process that eventually led to the formation of life.

The accepted model of galaxy formation was based on the fall of gas from all sides to the centers of galaxies and collisions between galaxies. It was assumed that disks of hydrogen gas formed first and formed stars in their content at a slow rate. When two disks collided, they merged and became a ball of stars. According to this model, the colliding gas clouds create a flash of new stars at an increased rate of a hundred stars per year or more.
The researchers decided to re-examine this model following astronomical observations with innovative telescopes, which provide a very deep look into the universe and thus enable the study of the galaxies as they were more than ten billion years ago (about three billion years after the big bang in which the universe was created according to modern cosmology). The large galaxies, as they appear in these ancient times, formed stars at a very high rate, but they do not appear as mergers. Contrary to what was expected, these galaxies are large rotating disks and contain large clumps within which the stars were formed. These revolutionary observations were made by German and American astronomers who are partners of the Israeli research group. Following the discovery, the question arose as to how these galaxies formed stars so quickly and in such a large quantity at such an early stage, not through massive mergers, as suggested by the conventional model.
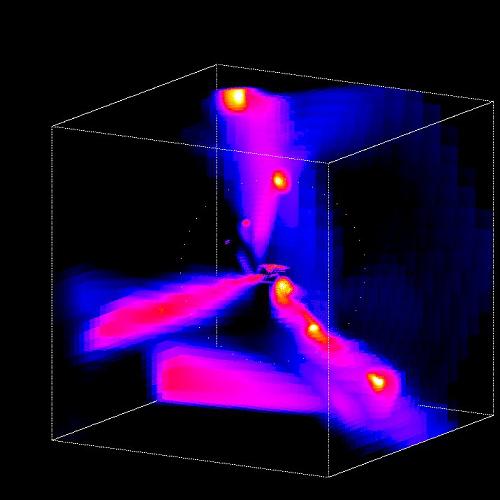
According to Prof. Avishi Dekel from the Hebrew University, "We have developed a new theoretical model that explains the observations that were incomprehensible until now. The theoretical calculations are backed up by an unprecedented quality computer simulation of the evolution of the universe, carried out using a supercomputer by French research partners. The size and precision of this unique imaging allowed for the first time a detailed study of the process by which matter accumulates in galaxies, a process that enabled their growth and the formation of stars in them."
According to the new simulation, most galaxies are built by continuous jets of cold gas rather than by galaxy collisions. On average three jets build each galaxy. The gas jets follow the cosmic web-like structure of the matter in the universe (Cosmic Web), webs along which the dark matter also flows to the galaxies. As seen for the first time in the computer simulation (image 3), the streams of cold gas penetrate through the dark matter sphere containing hot gas to the center of the sphere where they form a rotating disk. The dense gas in the disk, under the influence of its own gravitational forces, breaks up into large clumps where the gas becomes stars very efficiently. Prof. Deckel and his group showed that the rate of star formation according to the theoretical model of the jets indeed corresponds to the fast rate measured by telescopes. "Contrary to the model that was accepted until now, collisions between galaxies play only a secondary role in the formation of galaxies" says Prof. Dekel. the early
"In collaboration with my colleague, Prof. Ram Sri, we developed a physical theory that explains the formation of giant clumps in the disk and also predicts the early formation of elliptical galaxies, as a result of clumps migrating to the center of the disk and coalescing there into a spherical structure," adds Prof. Dekel. Using new computer simulations, more advanced than anything that was accepted until now, Prof. Dekel and his colleagues proved that the theoretical model they developed explains the complex processes that occurred during the formation of the galaxies in the early universe. "This is the main way for galaxies to form," says Dekel. The research contributes to a new understanding of how the structures in the universe are formed - those objects that ultimately led to the formation of life.
Researchers from the Hebrew University discovered a cosmic thread of dark matter near the Milky Way

21 תגובות
To the rebels:
The example you gave reflects correct and accurate logic, but I don't understand what it has to do with the expansion of the universe that we are discussing here. The small is always huge compared to the smaller one and the giant is the smallest compared to the bigger one. Right! But the point is that you have even scratched the surface of the ways and theories that the universe is what it is today.
to the rebels
All your explanations are beautiful, but unfortunately it's not about our universe!
All suns revolve around the center of the galaxy and not one around itself, and moons were not formed by volcanic activity
So for a start it is advisable to read a good book on the subject. Then we will be happy to answer your questions and respond to your comments
sleep well
Sabdarmish Yehuda
Why complicate the creation of the universe?
After all, our sun has a sun if (1) our sun revolves around it
Hence the mother sun also has a mother sun(2) that mother sun(1) revolves around,
In fact, as we go deeper into the center of the galaxy, there will be a mother sun, until we reach the center of the galaxy
And we will find the main sun that erases our entire galaxy and this sun we call a black hole.
And of course our galaxy has a mother sun that holds our galaxy and all the other galaxies in its orbit.
It will not be simpler if we think in the direction that the sun created us and all the planets in the solar system.
And the planets created the moons around them and these moons will create moons in the future.
Hence the universe is only expanding and systems and galaxies are expanding.
After all, every star that has volcanic activity has the possibility that during the life of such a star there will be several eruptions that will leave the sphere of the atmosphere and parts of the material that erupted into space can be caught at zero point with the star and here a moon is formed.
As we go deeper into the universe, we will see that it is only one of many universes that exist.
As we go deeper in the direction of increasing the small things, we will find that there is no end, the smallest particle is still huge compared to the smallest particle.
Everyone is looking for how
Isaiah:
I really wasn't trying to challenge you.
I knew what the argument was between us and I knew that was not part of it.
That's why I also knew that my words would be understood as a good example of the importance of diversity.
Michael R. - Oh well. The honor of the simulations is in place. Also the respect of diversity. It seems that the crude and low humor towards a serious study of the Hebrew University was out of place. Even the dignity of evolution is put in its place. I'll just warn you that you're wasting effort in vain when you try to challenge me on this matter - mentioning evolution, even without a real connection to the subject, does not challenge me. After all, it is a mechanism and not a cause, and we - on the existence or non-existence of one primary cause for everything - that is what we argue about frequently.
Isaiah:
This is the type of claim I always find appropriate to respond to.
Who are you to tell others what to do with their money and their time?
In my opinion this research is justified but my opinion is not important either.
Someone is interested in something, finds the resources to investigate it, and someone else comes and criticizes him for not doing something else (which is usually something the complainer doesn't do either!).
In every field of life - diversity is the key to success.
In biological evolution, the diversity of the species guarantees its survival.
The diverse research creates many practical solutions - even in areas that it was not aimed at - and this is beyond the fact that the areas that the research is aimed at also become useful many days.
The simulations are a way to test assumptions and the assumptions can be refuted in many cases.
How do you refute them? - in part by simulation, because if you simulate the process that was supposed to yield a certain result and the result was not obtained - it is a sign that the process is not yielding what they thought it was yielding.
I just wonder how amusements in graphic simulations will advance humanity in any way. Perhaps it is possible to give priority to applied research over gut-wrenching assumptions that cannot be disproved or proven, nor does it matter if they are proven to be true? I didn't just mention a hungry man as a control group. To use the unique style of one of our former finance ministers, I would say something like "Crazies, get off the stars!" Start finding new methods of producing food, water and energy or we will all die long before we know who inflated the galaxies from his huge stomach.
Mickey:
Galaxies are also seen orbiting each other.
The example of the solar system is somewhat appropriate because most of the material that was in the cloud from which the sun was formed did indeed collide with the sun and is a part of it today.
His minority remains in the stars.
The material that remains in the stars is also formed from the collisions of particles of matter moving in the gas cloud.
The only stars left in the area (up to asteroids) are those that "managed" to synchronize their orbits - that is, to be in orbits that do not cross each other (almost - there is an exception at the end of the solar system, but even there the crescents are few).
There are satellite galaxies that surround the Milky Way and among them there are also those that will fall into it most days.
There are also possible scenarios in which a large galaxy passes close to another large galaxy without the two colliding.
This whole thing still doesn't seem logical to me: if we choose the possibility that it is indeed the force of gravity as the cause of the attraction in question between the galaxies, then if we assume that it is indeed such huge ranges and that each galaxy can be treated as a body in itself, with its own spatial curvature, which is equal to the total spatial curvature of The bodies that create it, i.e. the principle of superposition, and then I ask the question why then we don't see galaxies orbiting each other like solar systems, why collide/merge? After all, according to the common assumption every galaxy has a speed (acceleration?) they don't stand still in place and attracted to each other.
Mickey:
A. Ben-Ner's response seems correct to me and I would only like to add that if you had taken the idea that after your question one step further you would have wondered that we are not blown off the earth and that the earth is not falling apart.
Everything here is a question of ranges.
At the distance between us and the Earth as well as at the distances within the galaxy clusters, the force of gravity increases while at greater distances the dark energy increases.
By the way, since the properties of inflation are not well known, it is not known whether the situation I have just described will remain true forever, and there are predictions that inflation will increase to such an extent that it will overcome not only the force of gravity, but also the electromagnetic forces and the other forces that strengthen matter. According to this theory, the responsibility of the universe is expansion to the point of complete dissolution of matter.
To Mickey, one more thing.
15 billion light years is not the "horizon of the universe" but...
"The Horizon of the Visible Universe". Beyond this horizon, it is not impossible that there is a universe that we cannot see. For example, a universe whose speed of moving away from us, as a result of the expansion of space, is greater than the speed of light and therefore, we cannot observe it through the electromagnetic radiation emitted there.
To Mickey
You raised a question that also interested me,
Indeed, apparently, there is a contradiction here between the expansion of the universe and the collisions between neighboring galaxies.
However, in my opinion, the solution to the problem lies in understanding the magnitudes of the universe. The universe is probably really huge.
So huge, that the size of a single galaxy compared to the size of the entire universe, is no bigger (and probably much, much, much, smaller) than, for example, the size of a single hydrogen atom in relation to the size of our galaxy, as a whole, and thus, the distances between the galaxies . In other words, on a cosmological scale, the distances between galaxies are extremely small. On a cosmological scale, the galaxies are extremely dense, therefore, there is a gravitational interaction between neighboring galaxies, stronger (much) than the inflationary force of the universe, which is now called dark energy. in the published article
On this website only about two weeks ago it was stated that the dark energy prevents galaxy clusters from developing and growing.
As far as I know, a typical size of a cluster of galaxies is
About 10^10 light years while the typical size of a galaxy is about 4^10 light years and a typical distance between neighboring galaxies is about 5^10 light years.
That is, the ranges of distances where the gravitational interaction weakens to the strength of dark energy
are 100,000 times greater than the distances between
The colliding galaxies. This, in my understanding, is the explanation of the matter
The collisions between the galaxies.
Can someone explain to me:
Why can galaxies collide, doesn't this contradict the theory that galaxies move away from each other? (Like the explanation with the balloon that inflates and on it there are points that move away from each other)
How can it be that when you look at the horizon of the universe, that is, about 15 billion years back in time, there are still galaxies that look exactly like the ones closest to us?
Isaiah the servant of God.
From your words it seems that that swelling was God's voice calling you out of the burning bush.
Unfortunately for you, there was no one with you to guide you as to the meaning of the sounds you heard and the smells you smelled.
Isaiah, indeed from your previous comments it seems that you have a full stomach for science that refuses to follow the footsteps of the great scientists before Galileo in the field of astrophysics and before Darwin in the field of biology who believed in good faith that the role of science is to discover the secrets of creation.
Like there used to be a quiz on Channel 7 that before the question presented: Among the wonders of creation - what is the speed of sound...
It was not stated in the article what is the decisive factor in the type of galaxy that is formed - spiral or elliptical. Can someone please explain the process that leads to the nature of the galaxy that is created??
Thank you and good day
A simulation I conducted while listening to the sounds emanating from my stomach after a hearty meal (the stomach of a hungry Somali served as a control group for me), shows that there is a certain possibility that, contrary to what is commonly thought, the world was created by a massive swelling that occurred about 15 billion years ago. The echo and aroma of this swelling is still occasionally visible above the pages of pseudoscientific magazines.
Shlomo, indeed yes the stars were formed earlier than they thought until now, which probably indicates the age of the universe as approximately 6000 years old.
Also, the process of creating the stars lasts about a whole day.
Sataaam
: )
Does this mean that the stars were formed much faster than previously thought?
to the point
Your love, my love!
Good night
Sabdarmish Yehuda
I liked the opening "contrary to popular belief"...