Dr. Assaf Rosenthal
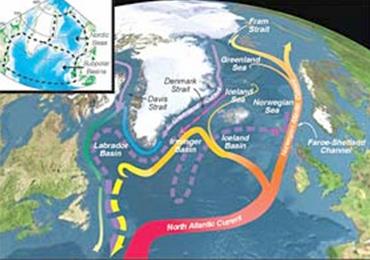
The Gulf Stream and its sections - the upper "moving film" - are marked with a continuous line and the deep currents with a dashed line
Direct link to this page: https://www.hayadan.org.il/rosentalgulfstream.html
Are the arctic lakes shrinking? If so, does this have anything to do with global warming? Permafrost area Permafrost is an area where the temperature is below zero all year round and therefore the ground is frozen.
When the temperature rises - if global warming melts snow and glaciers and therefore the expectation is that lakes in the warming permafrost areas will grow, and not it - it turns out that in areas where the earth warms the ice in the earth melts and allows for "escape", water absorption to the depths, which leads to the shrinking and disappearance of lakes in Alaska and Siberia. The smaller the lakes are, the faster they shrink.
According to measurements using satellite images, about 6% of the lakes in the area have "disappeared". On the other hand, in the area where the permafrost was not damaged, the lakes kept their size and some of them even grew.
The comparison is with the help of satellite images of more than 10.000 lakes, in an area of about 500.000 square kilometers, referring to the situation 30 years ago. It seems that lakes in "permafrost" areas where the ground is frozen grow in area, but in places where the frost layer is thin, or melts, the lakes shrink or disappear completely, a situation that harms the habitats of migratory birds, millions of which spend the summer in the Arctic Circle and raise the next generation. The damage is also to the mammals for which these birds are a source of food, as well as to local (human) hunters.
The change in land cover causes a change in the local weather. The winds are stronger resulting in increased evaporation which accelerates and invigorates the process. And so the answer to the question at the beginning of the passage is positive. Global warming is having a severe impact on the Arctic
Since warming causes more water in the global system, northern rivers flow more water into the arctic sea. Fresh water is lighter and therefore remains in the upper layer and stops the ascent of nutrients from deeper layers. Less food - less fish, and the northern fishermen suffer.
Closer to us it turns out that there is a different effect. The fishermen of the Arabian Sea are producing larger fish harvests than they were used to. How does this relate to warming? The warming causes melting of snow in Southeast Asia and the Himalayas, less snow in the mountains - the ground absorbs more heat in the summer - which causes air pressure differences between the land and the sea - differences that cause stronger monsoon winds.
The winds stir the Arabian Sea and the eddies bring up nutrients from the depths of the sea, substances that feed phytoplankton which is the basis of food in the sea, according to the color differences in the satellite photographs the concentrations of phytoplankton can be identified, and thus it turns out that in the last seven years the concentration of phytoplankton in the Arabian Sea has increased by 350%! More phytoplankton - more food - more fish - and the fishermen are happy. The question is for how long? Because phytoplankton are tiny plants that need oxygen, and the more of it there will be less oxygen in the water, until the weight is violated, then a lack of oxygen will cause the mass death of fish and all animals in the sea, and in the next step, a lack of oxygen encourages the growth of bacteria that emit nitrogen oxide (a greenhouse gas) that captures 300 times More heat than carbon dioxide.
Changes in the water cycle seem small but more than that are not understood. And yet the effects of the changes can be extreme. According to measurements, observations and comparison of data, it turns out that the warming causes an increase in the amount of precipitation in the Arctic region and at the same time a decrease in the amount of precipitation in the equatorial regions, that is, a shift of precipitation from south to north! Less water in the south - more in the north. Such a change endangers the balance of marine currents, the most familiar of which is the Gulf Stream, when the fear is that the Gulf Stream will change its character, flow at different depths in the ocean and at different distances from the continent, a change that will change the "fusion" system of Europe, since the Gulf Stream merges the The climate in Europe, (by changing the name it also merges Africa) eases the cold winter and causes summer rains. The Gulf Stream also serves as a "conveyor belt" that transports nutrients from the depths of the sea to relatively shallow areas, changing or stopping the "conveyor belt" will cause a shortage and disappearance of fish.
Until today, the public - global issue in water was mainly from the point of view of the need to provide water to dry areas and (clean) drinking water to weak populations, a narrow point of view focused on immediate needs. The data obtained from the latest studies show that the changes in the climate cause changes in the way the water "moves" the effect of this "movement" on the global system is enormous and must be taken into account in any environmental discussion.
