This is what Claire Biot (Biot), vice president of life sciences industries, Dassault Systèmes says in an interview with the Hedaan website following the Science in the Age of Experience events that took place over the past month in the digital space

The COVID-19 pandemic has placed the issue of health at the center. This is what Claire Biot (Biot), vice president of life sciences industries, Dassault Systèmes says in an interview with the Hedaan website following the Science in the Age of Experience events that took place over the past month in the digital space.
"Since the outbreak of the epidemic, we have helped the ecosystem of health services in three ways throughout their innovation cycle to find treatments and of course vaccines, and we have also developed a method that makes it possible to reduce the risk of spreading the virus through the air conditioning systems in hospitals.

"We are committed to helping find a treatment or vaccine for Corona. I will give two examples - the first is in Israel, where we work together with the Miguel Research Center. Using Biovia solutions, we enable them to perform molecular modeling of viral proteins to identify vaccine candidates that will prevent the replication of the virus and therefore also the spread of the disease. Miguel previously worked on developing vaccines for the corona strains that affect poultry. They used Biovia's solution to build a molecular model and process a lot of data from different sources to filter molecules that would be the basis of the vaccine candidate. They also use our solutions in laboratory management. Every time they do an experiment, they collect the data in the electronic laboratory and are able to cross-reference data effectively."
How to avoid contracting corona through the air conditioning systems in the hospitals?
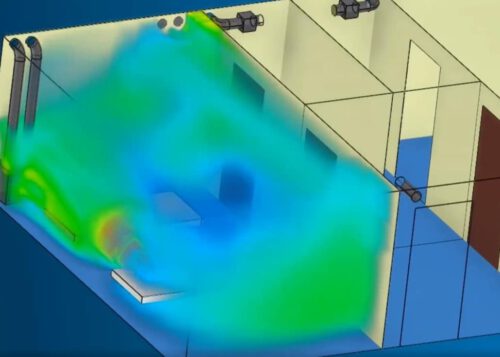
An example of the last process I mentioned - the help to prevent the spread of the corona virus through the ventilation systems of the hospitals. We used our simulation capabilities to address this issue in many hospitals in different countries. For example, we were involved in the rapid construction of a hospital in Wuhan and a hospital in Marseille following the concerns of one of the employees, whose grandmother was hospitalized there, and worried about the fate of the elderly hospitalized in the hospital under other circumstances. We performed simulations of the air flow in each hospital separately, according to its specific conditions, so that we could, for example, recommend opening certain windows to limit the spread of infection. Then we applied the simulation process to the other hospitals.
"As you may recall, last year Dassault Systèmes acquired Medidata, a global leader in providing end-to-end solutions for managing clinical trials, including operational management of a clinical trial, clinical insights and more. Thanks to this acquisition, we help our customers plan and perform, as quickly as possible, clinical trials. One of the challenges in the clinical trials in the search for cures and vaccines for Corona is that they do not want the participants to come to the hospitals so as not to increase the load, which is the biggest in the world, and because of the inability to separate them from the patients and the fear that they will be infected with Corona there. That is why it is important that the researchers are able to collect data at the patient's home either by reporting the experimenters, or by using wearable sensors and processing the data obtained from them. Researchers who used these solutions have demonstrated in recent months impressive capabilities in large-scale remote data collection, which is the key to the success of clinical trials."
Management of clinical trials
"Corona vaccine developers are required to register at least 40 thousand experimenters for each company (Pfizer and Biotech, Moderna, AstraZeneca and the University of Oxford), and in normal times such a process takes two to three years. Our solutions helped the developers to recruit 30 thousand experimenters in only three months, during which they are required to stay at home and report the results with the help of the devices."
"Another example: at the beginning of the epidemic there was a shortage of ventilators. We opened the system to engineers from all the pharmaceutical and medical device companies so that they could collaborate in designing components to build the ventilators, and develop the ability to infuse four patients with one machine at once. There are also engineers who have developed and shared monitoring systems."
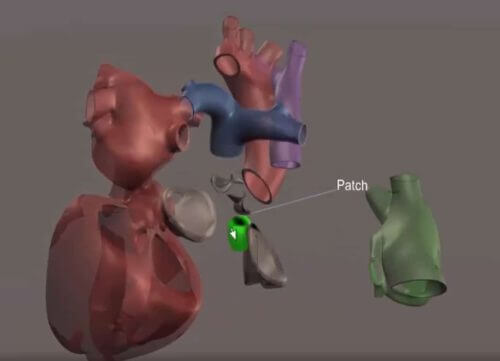
What is the virtual twin of the human body that you talked about at many conferences?
Dassault Système was established around the simulation capability in the aviation industry, and then we also expanded into the automotive field. We build a virtual twin of an airplane or a car and conduct experiments on it instead of building a prototype. In the same way we build a virtual twin of the human body to understand how drugs will affect heart patients, or what surgery is required for the particular patient, or in general to build models of diseases and find ways to cure them. Our oldest project is the living heart project, a model that most accurately simulates the geometry of the heart, the pumping process, the electrical behavior of the heart and more. All the physical parameters have been reproduced in this model and now drug or medical equipment developers can imagine and plan the development of a new medical device, and perform crash tests and other tests of their invention before testing it in humans. Many companies, as well as academic institutions, use this model to design their new medical devices."
What is the next organ you want to model?
Most likely these will be the lungs, which is an organ related to the activity of the heart anyway, but in the future we plan to build a virtual twin of the brain. We started development in partnership with several hospitals, when we develop a model of the disease of falling - epilepsy. We want to understand how fibers in the brain connect with each other, and what effect damage to one part of the brain has on other parts. We try to help surgeons identify the smallest intervention area and treat it, to avoid side effects.
"In the next step we want to help humanity also in the field of preventive medicine and contribute to a healthy increase in life expectancy. Today's systems are not focused on the individual patient. Our customers today are life science companies or technology companies, but our vision is that we will not only continue to serve companies like Pfizer and help them bring innovation more effectively, but we also want to serve the wider ecosystem. We aim to build the platform for excellence in medical care where we will utilize the knowledge accumulated by the doctors to help them identify the best medicine needed by each patient."
"Through the experience of the virtual twin of the human body, Medidata knows how to build modeling and simulation of the patient's data and perform advanced analysis of the data obtained from them in order to realize these aspirations," concludes Biot.
More of the topic in Hayadan:
