The unique mucus of the Mikisana fish has been researched as a basis for the development of strong and flexible materials * those fibers may in the future replace the synthetic fibers currently based on petroleum. It will also be possible to combine the fibers in the construction of safety helmets or replace the woven material with protective vests. The fibers can be used to strengthen car parts without adding weight and even as a substitute for the gel found in disposable diapers, adhesive for plasters and more / by: Rinat Barko-Filosof
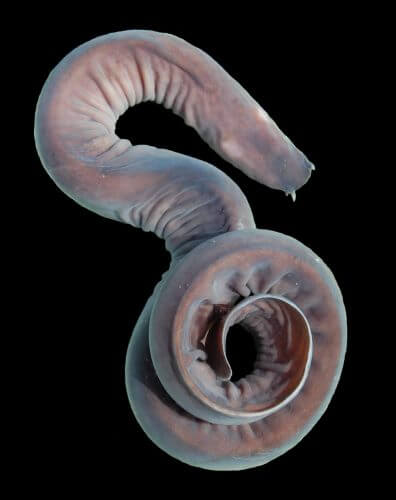
A whole tank of Mixina fish (Myxine), an eel-like fish that lives in the depths, will be able to offer, one day, an innovative type of strong and flexible material, a material that can be used to strengthen the structure of protective vests and even to strengthen strong light weight vehicle parts and more.
The myxina is a jawless, spineless fish that seems like an unlikely source for such advanced material, but it can secrete mucus made up of strong, flexible fibers. At least, that's the great hope of Douglas Fudge, a biologist at the University of Guelph in Canada. Fudge keeps 50-100 of these fish in cool seawater tanks in order to extract the mucus from them.
This viscous fluid is an outstanding defense mechanism. The fish may release only 90 milligrams of a milky, concentrated, "pre-mucous" substance from glands in its skin, even in cold water when attacked by predators. This substance mixes with the sea water and produces almost a liter of viscous substance, which forms a viscous and cohesive network. Scientists believe that this substance blocks the gill openings of the attacked fish and thus they loosen their grip on the Myxina fish.
Mucus has many possible biomimetic applications:
Those fibers may in the future replace the synthetic fibers currently based on petroleum. It will also be possible to combine the fibers in the construction of safety helmets or replace the woven material with protective vests. The fibers can be used to strengthen car parts without adding weight and even as a replacement for the gel found in disposable diapers, glue for plasters and more.

2 תגובות
The following video is recommended: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JrY-gVteHkQ
The fish is jawless but not spineless. If it does not have a spine or is not stringy and not a fish.