Recent models predict a weaker solar cycle, meaning that space debris will stay longer in space and endanger satellites in orbit around the Earth
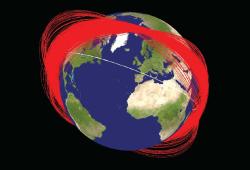
If the current solar flare, which should reach its peak during 2012, is as weak as scientists predict, thousands of fragments of the Chinese Fengyun-1C satellite will remain in space longer than expected. This means that many satellites will remain vulnerable to damage from stray space debris in the coming years.
Usually solar storms damage the electronics of the satellites and shorten their lifespan. But solar storms also have a positive effect as they clear low-Earth orbit of space debris by heating the upper atmosphere, an action that causes the small pieces to fall and burn up in the atmosphere.
According to a simulation performed by the space debris tracking program of the American space agency, if the solar cycle is indeed weak, hundreds of pieces larger than 10 centimeters remaining from the Chinese satellite will remain in orbit until 2019.
space debris

The Chinese experiment to intercept satellites, during which an old Chinese weather satellite was intercepted, created a trail of space debris that includes 40,000 pieces of 1 to 10 centimeters in size and another 2,300 pieces larger than 10 centimeters, with 400 of them being constantly monitored by the Space Surveillance Network Network) of the United States.
Space debris is in orbit, just like other satellites, but over time the Earth's gravity causes these objects to fall into the atmosphere. The problem is that the process can take decades, during which time satellites are in constant danger of collision. In 2007, for example, NASA's Terra satellite had to perform evasive maneuvers in order to avoid an object that approached an intimidating distance of 19 meters!
The solar activity of the sun
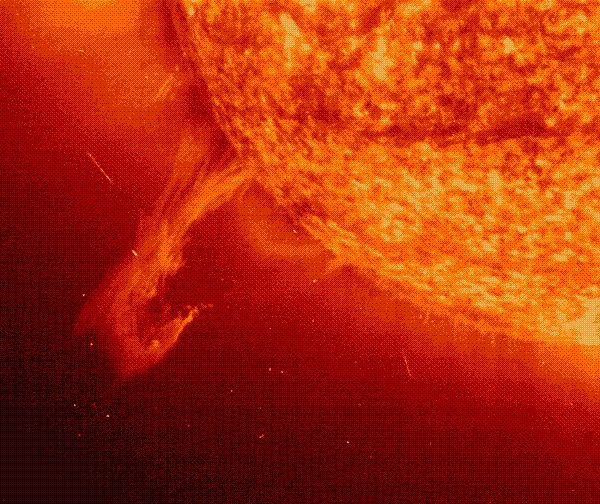
Our sun operates in cycles of 11 years while the rest of each cycle has a peak of activity combined with solar storms. The current cycle will not peak until 2012, but according to computer models based on previous observations, the current cycle will be relatively weak. However, new models based on solar magnetic activity predict a cycle with strong activity.
The difficulty in predicting the "weather in space" creates great uncertainty in industries affected by the behavior of the sun. Since our knowledge and models in this field are in their infancy, there is much speculation - the increase in solar activity in the coming months and the increase in sunspots should determine which model is more accurate and what this means about the activity of the satellites in orbit.

2 תגובות
What about the waste we produce?
Strong and weak sun both. Both articles and ramblings.