Hayadan > The Hebrew University > Page 2
The Hebrew University
- The Hebrew University
- March 19, 2023
- No comments
A team of researchers from the Hebrew University has developed a device that is able to easily and quickly measure the properties and thickness of surfaces 35 times smaller than the diameter of a human hair. The method is expected to significantly optimize the production of solar cells, flat screens and a variety of futuristic technologies
- The Hebrew University
- March 17, 2023
- 3 תגובות
Researchers at the Hebrew University and the University of Kentucky believe that a specific type of protein, which has not been studied before, substantially increases the molecular complexity in the brain and improves its function. "Such a discovery may have implications for the study of neurological diseases such as schizophrenia, epilepsy and autism"
- The Voice of Science website - the Israel National Science Foundation
- October 29, 2022
Volatile molecules may characterize diseases such as tooth decay and gum disease
- Avi Blizovsky
- August 29, 2022
- No comments
The first selected experiment led by Professor Sarah Eyal from the Hebrew University and in collaboration with Space Pharma and is designed to test the stability of drugs in space over time, in orbit around the moon
- The Hebrew University
- August 6, 2022
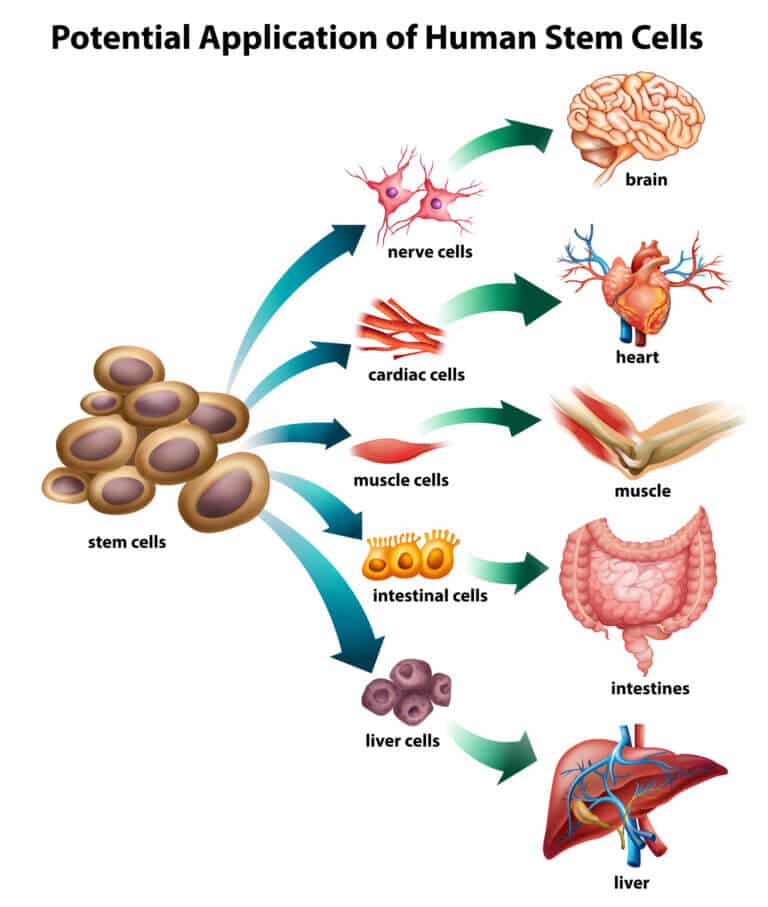
By creating artificial embryonic and placental stem cells and comparing them, the researchers from the Hebrew University identified about 14,000 sites in the genome that control the development of all the organs of the fetus
- The Hebrew University
- July 26, 2022
A study by the Hebrew University found that the tobacco companies offer benefits and gifts to store owners to market their product in a prominent location and in a more beautiful display, and teach them how to circumvent the legislation that prohibits the advertising and display of the products
- The Hebrew University
- July 5, 2022
University researchers have identified a new type of organelle that has not been discovered in gametes before. According to them, a failure in its function causes infertility because it is responsible for the organization of the chromosomes in the sex cells: "The discovery advances us towards finding medical solutions"
- The Hebrew University
- July 1, 2022
As soon as the disease develops, significant damage has already occurred that cannot be cured, but the development of a unique genetic strain allowed the university researchers to stop the pain and erosion. The findings can predict the disease after joint trauma and start critical medical treatment
- The Hebrew University
- June 29, 2022
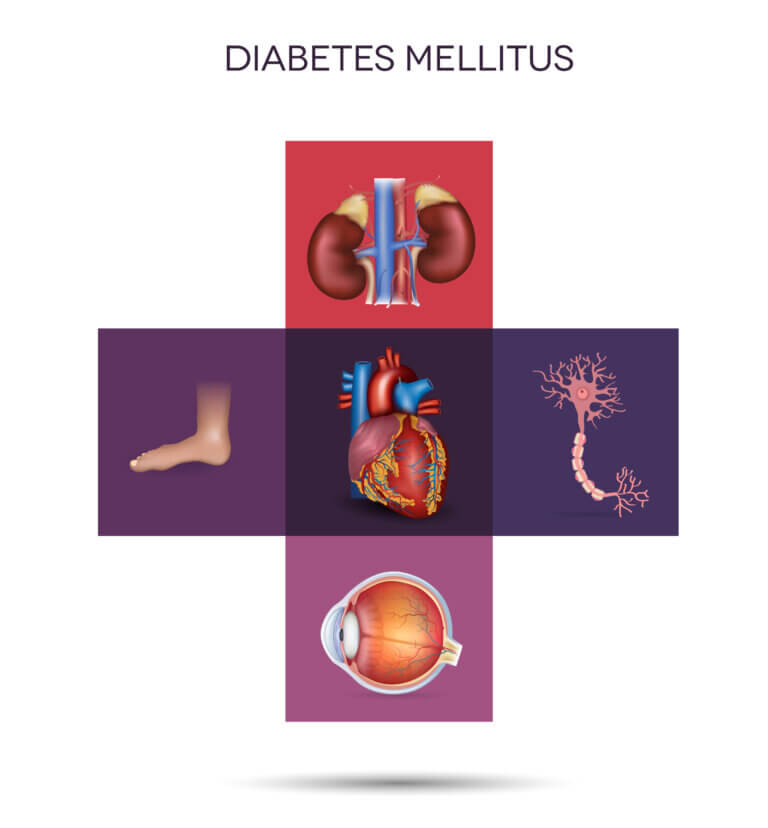
In this disease, the body produces substances similar to those found in cannabis, which damage the kidney * University researchers have found a way to improve the medical treatment of diabetic kidney disease, which affects approximately 30% of diabetics in the world. The new method that is adapted to each patient can prevent the damage, and even the development of the disease
- The Hebrew University
- June 28, 2022
University researchers have discovered a breakthrough magnetic phenomenon that will improve technological production. The researchers: "The discovery could change the next generation of nanoelectronic devices with reduced power consumption and faster capabilities"
- The Hebrew University
- June 27, 2022
Using XNUMXD printers and ink based on natural materials, university researchers are able to print wood and plan its shape while drying. "The development will revolutionize the design and construction of buildings that change themselves," shares one of the researchers
- Tel Aviv University
- June 16, 2022
An analysis of charcoal remains collected as part of an excavation at the Tel Tsaf polyglot site in the Jordan Valley determines that these are the remains of olive trees. Since the Jordan Valley is outside the olive's natural habitat, this means that the local residents planted the tree on purpose about 7,000 years ago
- The Voice of Science website - the Israel National Science Foundation
- April 15, 2022
- One response
Between rain and flood, between time and terrain, between yesterday and tomorrow
- The Voice of Science website - the Israel National Science Foundation
- April 14, 2022
- No comments
Microscopic oases on plant leaves allow bacteria to survive during the day
- The Voice of Science website - the Israel National Science Foundation
- April 12, 2022
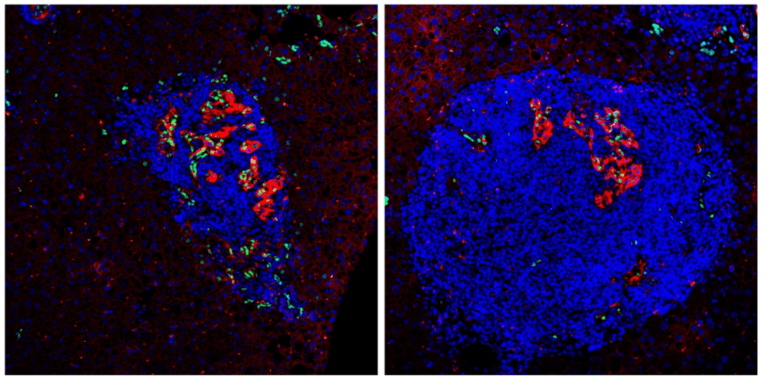
Pools of immune system cells taken from patients and mice with liver cancer and melanoma, partly composed of tired immune cells
- Avi Blizovsky
- March 29, 2022
- No comments
The award is given for his pioneering work in the field of two-dimensional nanomaterials built from defined and oriented monoatomic layers. His groundbreaking contributions include the creation and understanding of two-dimensional topological and magnetic structures, and the discovery of superconductivity and coordinated states in bilayer graphene oriented at a magic angle * Two years ago he won the Wolf Prize for Physics
- The Hebrew University
- March 19, 2022
Researchers from the Hebrew University found that nitrogen pollution caused by human activities has a direct effect on the decline in the variety of species in about a hundred sites in the world, including Beit Govrin: "Not enough efforts have been made in Israel to gauge the severity of the problem"
- The Hebrew University
- March 9, 2022
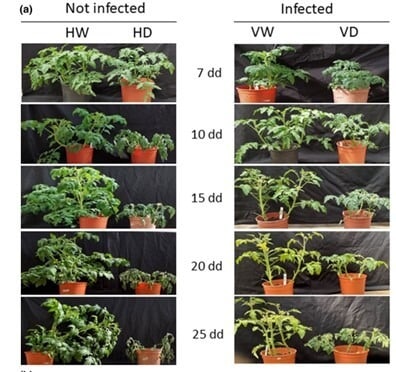
Although we are mostly familiar with viruses that harm us, it turns out that some of them are actually good and beneficial, both for humans and plants. A virus discovered in Israel in the XNUMXs helps tomatoes grow in a harsher climate
- The Hebrew University
- February 24, 2022
The study modeled over 1000 test sites and found that in 25% of them there is contamination from drugs that harms the water quality. "Even the most efficient purification plants are not able to eliminate the pollutants before they reach the rivers. The pollution is only going to get worse because the use of medicinal solutions for every disease is increasing"
- The Hebrew University
- February 24, 2022
A combination of personality characteristics such as reliance on self-intuition, belief in conspiracy theories, "need for chaos" and lack of intellectual modesty, along with an unusual state of persistent social mistrust, leads to people simultaneously rejecting any existing, well-founded and reliable information and embracing new, completely unfounded information , just because it is an alternative
- The Hebrew University
- February 23, 2022
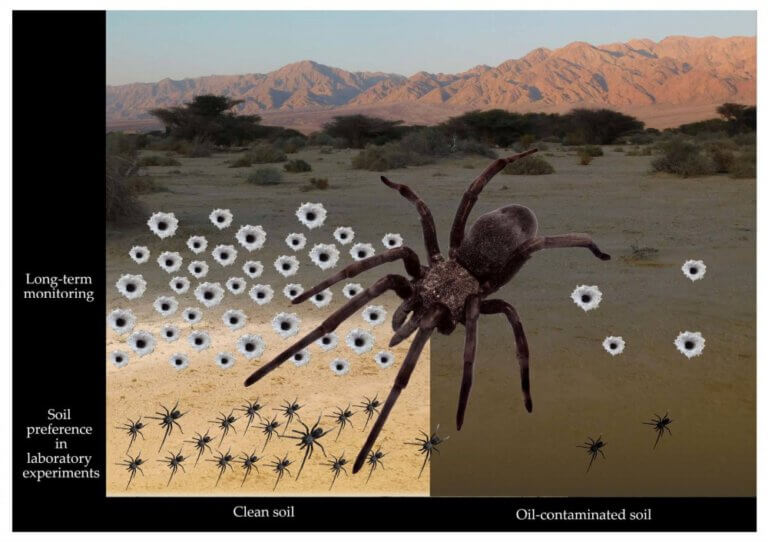
The spider, which was discovered for the first time in the Arava region, prefers soils free of oil pollution and thus constitutes a biological marker
- The Hebrew University
- February 21, 2022
Prof. Zvi Peleg: "The constant increase in demand and the suitability of the sesame for growing under high temperatures associated with climate change, led to an attempt to return it to agriculture in Israel. Finding the connection between the timing of flowering and the components of the crop, could help in the future to adapt this crop to deal with climate change, and together with other developments in our laboratory , to transform the cultivation of sesame from a traditional-local cultivation to a modern and global cultivation''.
- Avi Blizovsky
- February 14, 2022
Two of the grant winners are from the Hebrew University and the others from Bar Ilan University
- The Hebrew University
- February 11, 2022
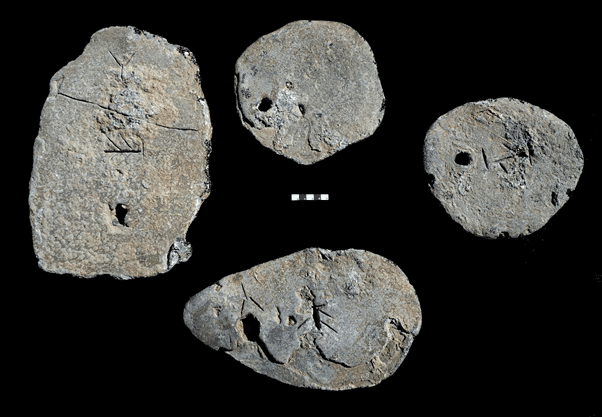
The cargo, which contains metal ingots and stone anchors dating back to about 3500 years ago, proves that there were significant trade relations between Cyprus and distant Sardinia
- The Hebrew University
- February 4, 2022
A new study reveals that an increase in the frequency of storms, along with a decrease in evaporation about 20 years ago, were likely significant factors that enabled the transition to permanent settlements and an agricultural society