Following the closure of European airports for the second time in a year due to the eruption of a volcano in Iceland, we bring again the scientific explanation of the risk posed by the volcanic ash to airplanes and other factors

Volcanic ash consists of tiny, jagged particles of natural glassy rock thrown into the air by a volcanic eruption. The ash can threaten the health of people and animals, is a danger to passenger planes, may cause damage to electronic systems and machines and interfere with electricity production and communications. The wind can carry the ash for many kilometers, affecting more distant areas and many more people than the direct damages of the eruptions. Even after the emission of ash from the volcano ends, the wind and human activity can cause the ash to fall for months and even years and cause long-term health and economic damages.
The case of St. Helens as an example
On the morning of May 18, 1980, many residents of eastern Washington State noticed that it was getting dark and threatening clouds were coming from the west. Most believed that the clouds were part of a system of large thunderstorms common in late spring. However, what they didn't know was that at 08:32 the St. Helens volcano erupted and shot a huge jet of gas and volcanic ash over 20,000 meters into the air.
As the cloud swept over them, a shower of ash began to fall, covering the area in darkness for the rest of the day. Houses, farms and roads were quickly covered in 10 centimeters of dust. The small particles penetrated the machines and all the structures except for the particularly sealed ones. By the end of the day over 500 million tons of ash had fallen over parts of Washington, Idaho and Montana. The ash prevented the possibility of road travel in eastern Washington state due to poor visibility, slippery roads and the impact of the dust on cars, an impact that was felt by about ten thousand people in isolated areas and small communities. Calcutta suffered a loss of over a billion dollars due to the eruption of the St. Helens volcano in 1980 - most of it due to the ash. If a volcanic eruption were to occur in the USA today, the damage would be much greater due to the increase in population and economic activity since the XNUMXs in the western USA. Much more widespread use of computers and electronics and a sharp increase in the amount of flights, especially over the North Atlantic Ocean, have made more people and more property vulnerable to the impact of volcanic ash. Knowing the characteristics of volcanic ash and being prepared for it when the volcano shows signs of restlessness can reduce the economic damage and health consequences of the ash.
What is volcanic ash?
Jagged particles of rocks, minerals, and volcanic glass made of sand and silt 2 millimeters or less in diameter that are ejected from volcanoes are called volcanic ash. The smallest of these particles can be 0.001 millimeters wide). Unlike the shavings created from cutting wood, leaves or paper, the volcanic ash is hard, does not dissolve in water, is jagged and causes erosion, and it also serves as a good electrical conductor when wet.
Volcanic eruptions occur when gases are absorbed by molten rock (magma) and together they escape from the volcano into the air, when it is a wet area, the water also adds to the celebration and turns into steam. The escaping forces cause the rocks to tear, and the lava erupts into the air where it hardens and crystallizes into particles of volcanic rocks and glass. The intensity of the eruption is such that the ash and gas particles create a huge eruption column, sometimes over 10 kilometers high. Fragments and rocks larger than 5 centimeters are ejected and fall in the immediate vicinity, at a distance of a few kilometers from the site of the eruption, but the finer particles are carried by the wind in a visible form as an eruption cloud. As the cloud moves with the wind from the volcano, the heavier ash falls and the cloud is made up of thinner ash layers. The ash cloud can travel thousands of kilometers and even circle the earth.
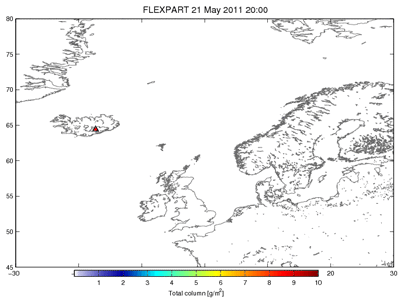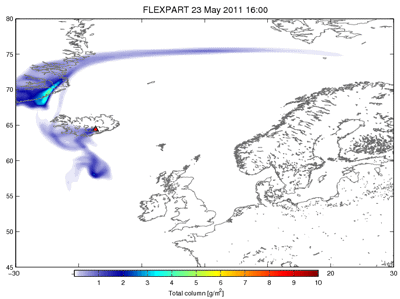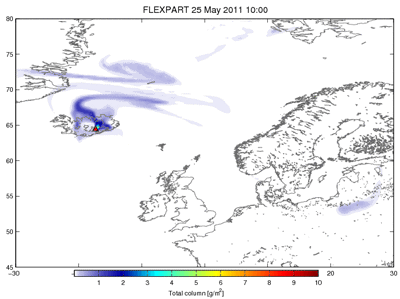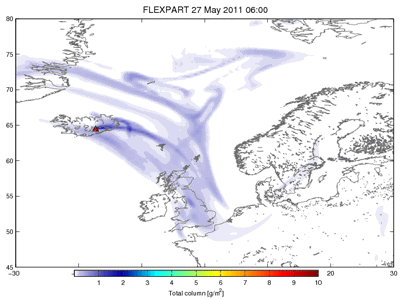
Some consequences of the volcanic ash
When the volcanic ash accumulates on buildings its weight can cause the roofs to collapse, killing or injuring their occupants. A dry layer of ash 10 centimeters thick can weigh up to 100 kilos per square meter, and wet ash can weigh as much as double. The intensity of the damage depends on the shape of the roof - flat roofs tend to collapse faster than sloped roofs.
Because the ash is electrically conductive, it can short circuits and disable electronic components, especially high voltage circuits and transformers. Power outages are common in areas affected by the ash, and therefore it is recommended to install electrical backup systems in sensitive facilities such as hospitals.
It turns out that even the media - including the cellular one - may suffer damage - when the ash affects in several ways - starting with shorting out end equipment and transmission antennas, the lightning created as a result of electrical voltage discharge also damages and the radio waves are scattered or swallowed by the hot and charged particles.
Damage to car and aircraft engines
Volcanic ash can cause internal combustion engines to break down due to the clogging of air filters leading to damage to moving parts of vehicle engines and machines, including the relays and gears. Jet engines may stop working after flying through the cloud containing even thin ash. Roads, highways and airport runways can become dangerous and unusable due to their slickness and near-zero visibility. Driving a car at a speed of over 8 km/h on roads in an area covered in ash means a real danger of a car accident.
The ash can also clog cooling air conditioning filters for computers based on air flow, which will cause the computers to heat up. Agriculture may also be affected by the fall of volcanic ash, the damage to grain varies according to the thickness of the ash layer, the type of plants and their age, and the timing of the rain that follows. Farm animals, especially grass-fed animals, may suffer health damage, including dehydration, starvation and poisoning.
Like any flow of particles from other sources such as wind bringing dust from the desert (as happened to us last week), forest fires and air pollution, the volcanic ash may cause health problems especially for children, the elderly and people suffering from heart disease or respiratory diseases such as asthma, chronic bronchitis and emphysema ( emphysema). Therefore it is recommended to listen to forecasters who convey this information to the public. The science of meteorology makes it possible to get a forecast hours and even days before the arrival of the cloud and thus the victims can minimize the damages. The US Geological Survey constantly monitors over 40 active volcanoes in the US.

9 תגובות
L1 - Batya:
The interesting part is that it goes both ways.. In fact ash and reed is a very fertile soil and on small islands in the oceans especially islands formed by reefs .. an islet of land suitable for agriculture and even for plants.. In such islands most of the good soil for agriculture comes from ash and reed that is carried many kilometers above the sea and reaches them.
Those who sometimes watch National Geographic's "Aviation in Investigation" program will surely watch in the future - or have watched in the past - the episode dedicated to the flight Arya described.
About thirty years ago, all four engines of a Boeing 747 shut down as a result of flying in a volcanic ash cloud.
"On June 24, 1982, a British Airways jumbo (Boeing 747) flight 009, with 248 passengers and 15 crew members on board, was flying in the Indonesian region on its way to landing in Australia. He entered into a cloud of volcanic ash originating from the eruption of the Galangong volcano, located about 180 km southeast of Jakarta. The pilots, who did not yet know that they were flying in a volcanic cloud, noticed strange phenomena. Strange flashes of light suddenly appeared on the front window and the cockpit was filled with smoke, which was accompanied by a pungent sulfur smell.
The pilots tried to find out from the control unit if they knew about any unusual phenomena that planes encountered in the area. The answer was negative, because even the Bekrs had no idea about the presence of the volcanic cloud. Passengers who peeked through the windows said, afterwards, that they saw the engines engulfed in flames, as if they were on fire. Within a few minutes, all four engines of the huge plane shut down and it began to spin, while losing altitude.
Despite the extreme emergency the plane was in, Captain Eric Moody broadcast to the passengers, with British coolness and extreme understatement, the following message: "Ladies and gentlemen, this is your captain speaking. We have a little problem. All four engines of the plane stopped working...". In contrast to the calm wording of the message to the passengers, there was a lot of tension in the cockpit. Modi decided to try to reach the Jakarta airport, making repeated attempts to start the stalled engines.
Only after 13 nerve-racking minutes and after the plane had lost more than 22 thousand feet (more than seven kilometers), they managed to start one engine. After a few minutes, the other engines were started (one of them went out again later) and the pilots continued on their way to Jakarta."
http://www.haaretz.co.il/hasite/spages/1164689.html
Thanks for the article, the question really occupied me recently
Machel
Not pretty. 'Bat-ya' not only worries, she must also pray (for God's sake) that it will be good!
So if she prayed to God while he wasn't in Shlapstunda - be good, and there's no need to worry!
Two comments
A]. In the 9th row from the bottom, there is a grain and not a claim
B]. At least in terms of agriculture, it seems that in the long run the volcanic minerals
Fertilize and improve the soil.
forward! Let's take care!
The damage that should worry us the most is the damage to agriculture. It is true that you feel first of all the power outages, traffic disruptions, etc., but when there is nothing to eat - the computers will not help. Agriculture is immediately affected! And even if the rain comes after the ash quite quickly, all the annual crops die, and the fruit trees can only regenerate the following year. Many years of famine have already been recorded in history because of the volcanic ash, and that is what should worry the world, not the state of the planes.