Mars lander Phoenix spotted snow falling from Martian clouds. The spacecraft's ground experiment also provided evidence of past interactions between minerals and liquid water, a process that occurs on Earth.
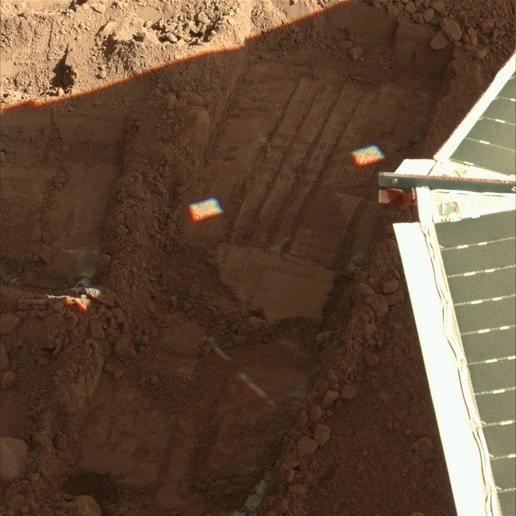

Mars lander Phoenix spotted snow falling from Martian clouds. The spacecraft's ground experiment also provided evidence of past interactions between minerals and liquid water, a process that occurs on Earth. A laser device designed to gather knowledge about the interrelationship between the ground and the atmosphere on Mars discovered snow falling to the ground from clouds 4 kilometers above the landing area. The data showed that the snow evaporated before reaching the ground.
"We've never seen anything like this on Mars," said Jim Whitway of York University in Toronto, lead scientist for the Canadian Meteorological Station on Phoenix. "We will look for signs that the snow may have also reached the ground."
The experiments on Phoenix also yielded clues indicating the existence of calcium carbonate, the main component of the chalk we write with on the blackboard, as well as particles that may be clay. Most of the calcium carbonate and clay on Earth is formed solely in the presence of liquid water. "We're still collecting data and need to do a lot of analysis, but we're making good progress on the big questions we've put forward," said Phoenix lead researcher Peter Smith of the University of Arizona in Tucson.
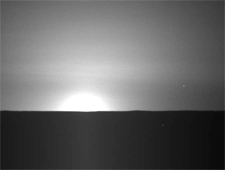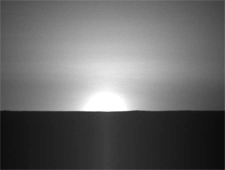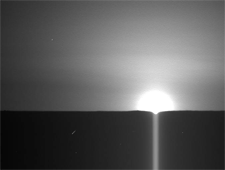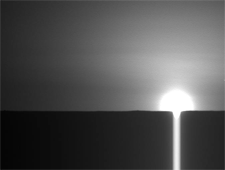
Since landing on May 25, Phoenix has confirmed that the hard surface layer in its northern landing area contains water ice. Determining whether this ice ever melted will help answer the question of whether the environment was once friendly to life, one of the main goals of the mission.
The evidence for the existence of chalk in the soil samples from the excavations carried out by Phoenix's robotic arm comes from two devices - TEGA, which is a device for analyzing the gases coming out of the ground, or in other words the oven, and MECA - the conductivity and electrochemistry analyzer.
"We found chalk," says William Boynton of the University of Arizona, the principal investigator of the TEGA device. "This indicates the possibility of interaction with water in the past." MECA identified carbon compounds emitted from the soil sample when heated, which are typical of calcium carbonate compounds. MECA detected the chalk's response in soil wet chemistry analysis. The measured concentration of calcium was exactly that expected from a solution of calcium carbonate. Both devices also detected the clues to the existence of clay-like material in the soil samples.

The Phoenix lander, which has been operating for the fifth month, is suffering from a decrease in energy production capacity, and this may result in the end of its active life by the end of the year. Before the power goes out, Phoenix crew members hope to operate a microphone on the lander that will try to listen for Martian sounds.
"For nearly three months, the sun did not sink below the horizon in the landing area," says Barry Goldstein, JPL's Phoenix Project Manager. "Now it already disappears below the horizon for four hours every night and the output of the solar collectors decreases from week to week. Before the end of October, there won't be enough energy to move the robotic arm.

10 תגובות
Hmmm good to know. Excuse me but I would love to read more details translated with pictures and videos on any topic related to space! Thank you in advance. May we have a tour of space in the middle of this century at costs that an average citizen can afford.
If you found out that it snowed and snow is made of water, then that's not enough. Hello, there was life there, and maybe now there is a developing bacterium. Km from us lives is great
We are just looking as far as we can
A little foiled, not too much
But he was not caught
Cool:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mars
What is? How are the seasons and the self-rotation of Mars?
In my opinion, the dispersion of sunlight at sunrise on Mars appears much more limited than on Earth.
Probably because of the thin atmosphere.
Phoenix surprises us with new discoveries almost every week. A real pleasure.
Just like in Jerusalem. The snow melted before they reached the ground.
And a tender has already been issued for the establishment of a yeshiva in KK Mars.
Will she go back to work later when the sun rises, or will what happened in the movie pitch black happen to her?
to the editors
I really liked the section if the pictures add a lot to the illustration of the article
Maybe try adding links to relevant movies from YouTube, this will add a lot to articles that seem dry and boring