In an interview with the Hidan site, Prof. Avi Leib, head of the Department of Astronomy at Harvard University, says that if the discovery of gravitational waves is confirmed by an independent experiment, it is a discovery worthy of a Nobel Prize for the team of researchers led by John Kovacs and adds: The discovery also supports the existence of a multiverse. And therefore also in the understanding of our true place in the universe which is also just one of many species

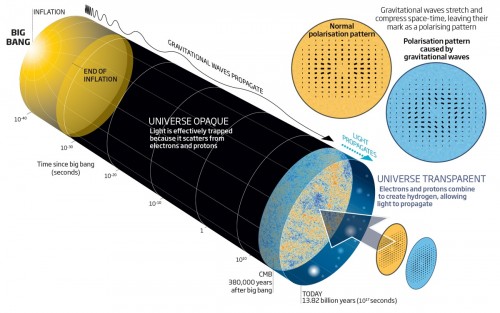
Astronomers from the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics in Massachusetts, the California Institute of Technology (CALTECH) and NASA's JPL Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California claim to have discovered evidence, worthy of a Nobel Prize, for the existence of gravitational waves - ripples in the fabric of space-time. This is the first direct evidence that the universe underwent a brief but massive rapid expansion immediately after the Big Bang.
"We found the smoking gun for the inflation of the universe and we also provided the first evidence for the existence of gravitational waves crossing the sky," says Chao-Lin Kuo of Stanford University, designer of the BICEP2 detector that provided the new data. The researchers used the BICEP2 (Background Imaging of Cosmic Extragalactic Polarization) telescope that scans the sky from the South Pole and detects slight changes in the cosmic background radiation - the radiation that erupted 380 thousand years after the big bang when the universe cooled enough to allow photons to move freely in the universe.
More of the topic in Hayadan:
- What are gravitational waves?
- NASA and the European Space Agency's large detector to prove Einstein's gravitational waves
- An attentive ear to the Big Bang
The cosmic background radiation fills every square centimeter in the visible universe with 400 photons in the microwave field. The glow after the big bang is spread almost uniformly in all directions but small residual changes (at the level of 1 in 100 thousand) in the radiation temperature can show specific patterns. The irregularities are consistent with what would be expected if momentary quantum fluctuations caused the universe to inflate to the size of the universe seen today.
Prof. Avi Leib, head of the astronomy department at Harvard University, director of the Institute for Theory and Computation at the Harvard Smithsonian Center for Astronomy and member of the American National Academy of Sciences and Arts says in a telephone interview with the science website: "We have to start with the caveat that this is one experiment that made observations of a certain frequency of radiation. There is always some chance that they are not coming from the early universe but a struggle in our galaxy that emits these frequencies but researchers have done their best to rule out that possibility. However, it is important that two independent groups approve it. If it really turns out to be true, this is the most important discovery in the last 15 years since we discovered (with the help of the Hubble Space Telescope. AB) that the universe is not only expanding, but that its expansion is accelerating in time.
Back in the 34s, astronomers developed the theory of the inflationary universe according to which in the period immediately after the big bang (actually ten times minus 10 seconds after the big bang) the universe swelled exponentially (by orders of magnitude of 25 times to the power of 10 or XNUMX million trillion trillion). At this inflation these quantum fluctuations were amplified to a cosmic scale. "Not only did inflation help to explain why the universe is so uniform on a large scale, but also how the quantum disturbances were created on a scale of much less than a millimeter, to huge bodies like the Milky Way galaxy." Live explains
"We exist because of these disturbances because the area where the Milky Way was formed was a quantum disturbance. These disturbances can be described by a wave function because as we know in quantum theory everything is probabilistic, and since the universe stretched to enormous dimensions the quantum disturbances stretched and became large objects like the Milky Way galaxy at a later time. The discovery provides a connection between the quantum world that describes small dimensions and the classical world in which we exist. In addition, it also links us to the earliest times, so this is a very significant discovery."
While inflation is a mainstay of Big Bang cosmology, it remains in the theoretical framework. Many astronomers don't 'buy it' because we can't explain what the mechanism is that explains what drives such a massive expansion, let alone stop it. The findings published today (Monday) provide support for inflation.
The trick was to look in the cosmic background radiation for the signature of the inflationary swelling of the universe that would manifest itself in particularly pale patterns of polarized light - some light waves have a preferred plane of oscillation. If the gravitational waves crossed the space-time fabric they were supposed to crush the space-time in one direction (thus heating it) and stretch it in another direction (ie cooling it). The heating will amplify these quantum fluctuations into a detectable signal: the hotter and therefore higher-energy photons will become visible in the cosmic background radiation and leave a slightly polarized signature.
The effect produced two distinct patterns E-modes and B-modes, which differ in the issue of whether they have equality in a pair or individually. In simple terms: E-modes patterns will look the same even when reflected in a mirror while B-modes patterns will not look the same.
E-modes have been observed and studied in the past, but while both modes are the product of gravitational waves from the early universe, the E-modes can be formed through many mechanisms while the B-modes could only be formed through primordial gravitational waves. The discovery of these waves will be proof of the existence of these waves or as astronomers call "smoking gun proof" of the inflationary expansion of the universe that increased the gravitational waves in the early universe.
Team members from the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics analyzed the observational data for over three years in order to rule out errors and unequivocally identify direct evidence of the bulge.
"The research offers new insights into some of the most basic questions: Why do we exist?, How did the universe begin? Prof. Leib says. "The research results don't just provide a smoking gun for inflation, they also tell us when the inflation occurred and how strong it was."
"The experiment also opens a window to energies 10 trillion times higher than those that can be obtained in the laboratory at the LHC in Sarn. The reason we can reach such high energies is because the universe is transparent to gravitational waves and they were created at an early stage in the existence of the universe (10 to the power of 34 seconds). The heat levels were very high, and correspond to the situation where the forces we know - the electromagnetic, the weak force and the strong force come together. (These are three of the four forces of nature. The fourth force is of course gravity AB).
"The energy required to produce the gravitational waves we see is approximately the energy that also caused these high temperatures. The results are consistent with the hypotheses that once the unification was broken there was a phase transition that produced this period of inflation where the universe expanded very rapidly from a point size, to the diameter of the universe almost as we see it today. This is also the reason why the universe is uniform, because it started from a very small area that was stretched, like you stretch a small area in a shirt with an iron and every small unevenness is smoothed out and the area becomes uniform."
"The physics of inflation is beyond the standard model we have been working with until now. In order to understand what happened there it is very important to continue making observations on the regularity of the cosmic background radiation. You can think of it as an experiment that measures things that happen at very high energies." Leib says and adds: "Not only did inflation manage to explain the origin of the cosmic structure - the way in which the cosmic fabric was created from the aftershock after the Big Bang - but it also allows us to speculate wildly. The model appears to produce not just one universe, but a collection of universes, a feature known as multiverse. The collection of data has no end and had no beginning and they keep popping up forever.
"The results of the study published today provide a strong blow to the existence of "eternal inflation" which provides us with a perspective on our desolate place within the universe, in one galaxy out of hundreds of billions of galaxies, but our entire universe may also be just one bubble in a cosmic ocean of other bubbles."
Leib emphasizes that although it is an observation, it is actually an experiment in which the researchers used the free electrons in the universe as a device for measuring gravitational waves. "We use the free electrons that were in the early universe. As the gravitational wave passed through the areas we observe it caused matter to move and we measure this movement, despite this the discovery can definitely be defined as a direct discovery of a gravitational tool and not as one that relies on indirect considerations. So far gravitational waves have not been directly measured. If this discovery is recovered, a Nobel Prize will be awarded to the discoverers."
And who are the discoverers?
Leib: "There are 4 central researchers in the group and many students and postdocs, the main researcher is named John Kovacs, a non-tenured professor in the Department of Astronomy at Harvard, which I head. It is likely that if this turns out to be true, there is a reasonable chance that he will receive tenure and more importantly a Nobel Prize. It's very exciting, especially since I'm the one who brought him to Harvard seven years ago."

74 תגובות
Do you mean gravitational waves for energies at enormous levels? Kobe.
In my opinion:
If we accept the explanation of the inflation of the universe, then we have no choice but to relate to the spaceship two types of speed:
1) The normal speed.
2) The speed resulting from the expansion of the universe.
deer
Thanks!
ב
Read what Zvi wrote...
Let's say that a spaceship leaves Earth for space.
Is it possible to separate the speed of the spacecraft into normal speed and the speed resulting from the inflation of the universe?
B.
The idea is that the galaxies that move away from each other solely as a result of the Hubble expansion do not move (of course it is also possible for galaxies to move in relation to the Hubble expansion as for example Andromeda moves in our direction). The way Shmulik described it is quite correct - there is a GRID, it itself is expanding and as long as you are static in relation to it your speed is 0 in relation to the rest of the universe and yet you are moving further and further away from the other galaxies.
So are there two different definitions of speed here or is it really the expansion of space itself?
Let's start with the fact that it used to be considered speed - when Hubble discovered the expansion of the universe he treated it as a graph of speed as a function of distance - that is, treating the expansion of the universe as speed is not wrong, it just misses too many things. It was only after this discovery that it was discovered that it actually corresponds to Friedman's prediction that the universe must be expanding (or contracting) and if this is indeed the case it is possible to learn more things, such as for example that there are regions in the universe that we cannot see moving away from us at a speed greater than the speed of light.
So whether it is speed or not is a question of definition.
Under the assumption that we believe in the theory of relativity and according to Friedman and the big bang idea, this speed is very strange in that it is apparently possible to move at a speed higher than the speed of light. Also, this is a location-dependent velocity field so you will have to set a velocity for each galaxy because each one has its own velocity (only the Milky Way will be referred to as a velocity of 0). You see, then, you could define this movement as speed, but you would have to put so many limitations and so many "yes buts" on it that in the end it seems that it is simply not wise to define it that way.
On the other hand, you can refer to this speed as it is treated by the Friedman-Robertson-Wecker hammer (search for its code, even in Hebrew about the "Friedman equation"), as a time-dependent "R" factor that determines how far two points are from each other - with this method, everything is much more Simple and intuitive. More than that, you have equations that describe exactly the development of this R as a function of time (by the way, you can develop the first equation in Wikipedia with the exception of the part of the cosmological constant from completely classical considerations, this is a discounted case, although not surprising, which indicates, if you will, that general relativity conserves energy when it Required).
In conclusion, you could say that this is not an expansion of space but a speed dependent on place as he did in the original Hubble, but in this way you would lose so many understandings and complicate the formalism so much that it is not at all clear why he wanted to do this.
On the other hand, if we treat this speed as an expansion of space - everything becomes much clearer.
Two more notes:
Miracles,
There is indeed a preferred system here and in cosmology this is the case - the system of the CMB, or of the galaxies is to some extent a special system. There is no violation of the principle of relativity here since this is not a special system in terms of the laws of nature that govern it (the laws of dynamics are not true only there and in any other system they are corrected), but rather it is a privileged system by virtue of the special history of our universe. In the same way, a Christian can claim that the direction in which the cross indicates that Jesus was crucified is a preferred direction in space - but this is a historical case and it is only your choice to determine that this is an important direction.
the balloon analogy,
The balloon analogy is one of the most useful, cute and confusing analogies in the field.
The most basic creature in general relativity is the matrix. The metric is the distance between two points - stand at the point, now go dx in the direction of x, then go dy in the direction of y and finally dz in the direction of z. Now check how far you are from the point you left. In the ordinary world the trike is simply a Pythagorean theorem. In the world of special relativity, some kind of component relating to the time distance between two points is also added, but the spatial smoothing is still Pythagorean - this is broken in general relativity and there, as a result of the existence of masses, the Pythagorean theorem does not hold.
The discussion of spaces where the Pythagorean theorem does not hold began in the 19th century (mainly by Gauss and Riemann). One of the results is that sometimes, it is possible to take a two-dimensional space in which the Pythagorean theorem does not hold and "inhabit" it in a three-dimensional world in which the Pythagorean theorem does hold. In this way it is possible to look at such a space from the outside and examine its properties - this is the case of the two-dimensional sphere.
However, it is important to understand a few points:
- The two-dimensional sphere is two-dimensional - there is nothing to talk about what is outside of it and it exists even without the three-dimensional space in which it was placed. The meaning is that there is no center, the center of the sphere is a result of the fact that we put it in three dimensions, but when we talk about a three-dimensional universe that looks like a four-dimensional sphere envelope, this 4-dimensional sphere does not exist!
- There are shapes that cannot be accommodated in a higher dimension - for example, the sphere has a sibling with an opposite curvature in sign (that is, a triangle in which the sum of the angles will be less than 180 degrees) which is not recognized in analogies of this type because it is not possible to describe what it looks like inside a triangle Dimension - is simply something that does not fulfill the Pythagorean theorem but does fulfill all other geometry (which does not derive from the Pythagorean theorem) and that's it.
ב
You wrote "And what is not good is that incorrect explanations enter the mind and are treated as if they were correct explanations." - That's what I was referring to. Newton's equations are also incorrect, but they are very useful. Same as Ohm's law in electricity. There are many more such cases. What I am saying is that in many cases, an abstract model is enough to understand, or at least know what it is about. Darwin discovered evolution without understanding anything about genetics.
Those who want to understand deeply, need to know a lot. This is especially true in the exact sciences. There is nothing wrong with that.
But - giving an explanation for the expansion of the big bang with the help of de Sitter spaces will not help most of the readers here, will it?
Miracles:
There is nothing wrong with trying to understand.
On the contrary
The more the better.
ב
Not true. The fact that I try to understand the expansion of the universe by abstraction does no harm. I do not develop mathematical models based on such an abstraction. I generally try to explain things to myself that are beyond my understanding and knowledge.
In principle this is an extremely useful tool. I develop computer software, without understanding quantum theory at a high level. A carpenter builds furniture without knowing the chemistry behind the adhesives he uses.
Again - you want to understand in depth - you will have to study a lot. There is nothing wrong with that. That way you can specialize in a narrow field. If you want a broad understanding of the world - you will have to accept that things need to be simplified.
for miracles:
What is clear is that nothing is clear yet.
"I don't know what I don't know".
And what is not good is that incorrect explanations enter the mind and are treated as if they were correct explanations.
ב
A serious answer requires a serious understanding of mathematics and physics. You are invited to post-graduate studies at Stanford.
Good luck with that 🙂
With all due respect:
The image of the balloon (or the raisin cake) is just an image.
It does not give even a hint of real understanding.
The balloon is a two-dimensional surface located in a three-dimensional space.
The raisin cake occupies part of the space and swells within the space. It does not change the data of the space.
According to the definition:
Speed is distance divided by time.
If the distance between galaxies increases over a certain time, then there is a mutual velocity between the galaxies.
And the question arises:
Are there two types of speed?
1) Speed at which there is kinetic energy (the normal speed).
2) Speed where there is no kinetic energy (speed that is obtained from a change in the distance between the galaxies as a result of the swelling of the dimensions).
This is not a marginal problem.
This is a very major problem.
It is impossible to hide an answer.
The answer should be well reasoned and stand the test of reality.
Miracles,
Thanks for the explanation and the reminder of this amazing book!
Shmulik
There is no middle for the balloon. Do you know the book Flatland by Edwin Abbott? It tells about creatures in a two-dimensional world who try to understand what a three-dimensional world is (a book from 130 years ago!!). The balloon is the space, and the ants live inside the space, meaning only on the surface of the balloon.
Movement towards the middle of the balloon is to move backwards in time. "Blowing water" is an expert on it……
By the way - if you press your finger on the balloon, you simulate a massive body that distorts the space 🙂
Miracles,
Easy question.
In the classic explanation above, does it make sense to ask the ant to move to the middle of the balloon or does the analogy collapse here and there is no middle of a balloon but only an envelope?
ב
The classic explanation is by an inflatable balloon. Imagine that the balloon is strewn with ants. Imagine that each ant is standing still - it will still see that all the other ants are moving away, due to the inflation of the balloon. Now, if you apply a force to a certain ant, it will cause this ant to move across the balloon and this will be felt especially by the neighboring ants.
What is not clear to me is - that out of nowhere there is one reference system that is absolute, and this goes against what I understand in the theory of special relativity. This system is the system in which the distance of the distant stars is the same in all directions.
B,
From the link I attached:
Basically, space-time is the three physical dimensions of our existence-length, breadth and depth-combined with the additional dimension of time; think of it as a wire grid that connects every part of the universe to every other part. When we say an object has motion, we're referring to its change in position relative to the space-time grid. The speed of light is only a constraint for objects that exist within space-time, not for space-time itself
That is, movement occurs only when there is a displacement relative to the grid and it is a movement with kinetic energy, while the expansion is not a type two movement because there is no displacement relative to the grid, this is my understanding. I guess Zvi can tell more about the subject
Shmulik:
Are there two types of motion in the universe?
Is there normal motion in which there is kinetic energy and motion that results from the inflation of the universe in which there is no kinetic energy?
B,
There is no contradiction.
Matter cannot move and exceed the speed of light, but space itself has no such limit because actually space does not move but expands. That is, Einstein's theory of relativity did not put an upper limit on the rate of expansion to the same extent that it put an upper limit on motion, so there is no contradiction.
http://scienceline.org/2007/07/ask-romero-speedoflight/
Miracles:
If the measurement shows that the bodies are moving then they are moving. If they are moving they have kinetic energy.
If their speed is increasing then their kinetic energy is increasing.
Unless you claim there are two types of speed.
That is, if you claim that there is a type of speed that does not have kinetic energy.
But even such a claim does not solve the problem.
And in particular the paradox of the two sections I already mentioned and I mention again:
The contradiction that is obtained when referring to the following two sections:
1) According to the theory of relativity, the speed of light is the upper limit of the speeds of the masses in the universe.
2) According to the theory of relativity (the big bang) there are galaxies that move faster than the speed of light.
ב
Think for a moment about the earth. We see all the bodies moving away from us. We feel like we're not moving, right? According to the cosmological principle - everyone in the universe feels the same. The distant bodies do not move at high speed, but the space expands - and every body sees the distant bodies moving away from it, as if it were in the center.
Is our kinetic energy increasing? I don't think so, after all there is no force acting on us that accelerates us. Therefore, by the same principle, it is true of every star.
That's how I understand things. I don't know if my understanding is correct, but it seems consistent to me at least 🙂
for miracles:
I have no explanations. Just trying to understand. And sometimes I also get tired of even trying to understand. But still there is an urge to try to understand.
From the attempt to understand, questions arise:
like for instance:
a) The contradiction that is obtained when referring to the following two sections:
1) According to the theory of relativity, the speed of light is the upper limit of the speeds of the masses in the universe.
2) According to the theory of relativity (the big bang) there are galaxies that move faster than the speed of light.
Or for example:
b) The kinetic energy of the galaxies is increasing because their speed is increasing.
So where do they get their kinetic energy from?
ב
I would be even more extreme - I can't think of a case where reality dictated any formula. Let's take Kepler's laws. There were lots of measurements and Kepler fitted 3 formulas to them. But, the formulas are only an approximation of reality. A planet does not move according to the equation of an ellipse. The ellipse equation is only a good approximation of the true trajectory.
ב
I half agree with you. We have no way of knowing what really happened. All there is are two things - mathematical models and confirmations. The mathematical model predicts that there will be a certain polarization to the CMB due to gravitational waves, and now apparently there is confirmation for this.
Are you claiming that there is another way to understand the 380 thousand years we are talking about?
Miracles:
Reality is not determined by the formula.
On the contrary:
The formula is determined by reality.
Therefore there is an error in the wording:
"Then you will know the state of the universe at time t."
The more accurate wording would be:
Then you will know the values of the functions at time t.
If these functions do indeed describe the universe, that is exactly the question, and I think we don't have an answer to that yet.
privileged
This is not a measured time of course... Physicists have mathematical equations that describe what they think happened then. In these beacons there is a variable t that you can put any value you want and then you will know the state of the universe at time t. In principle, this is similar to the parabola equation that describes the trajectory of a stone thrown at time t=0. This equation also has a lot of assumptions. In the case of the stone, the main assumption is that Newton's equations of motion are correct. In the case of the Big Bang, the assumptions include the theory of inflation, etc.
Miracles,
And how do you measure roughly how the time was there relatively? (I hope the answer is not too complicated)
I just asked
Time is "local time", meaning - the time of those who are there. This time is called "proper time". Those who were inside the bang would have measured a time of 380 thousand years. In this case there is no other time, because there are no external observers for these events.
It's a little more complicated than that, but that's pretty much it, as I understand it.
Time is warped by gravity, so what does 380,000 years after the big bang mean? Is a year our year? As for the microseconds after the bang. What do these mean?
There were opinions against the theory of inflation, not negligible at all. Does anyone here know anything: has the inflation theory been confirmed beyond doubt, or is it supportive but inconclusive evidence other theories have been ruled out.
Zvi, a quote from your response "When the universe reached a certain age, inflation began". Isn't it better to say that inflation started a micro micro micro second after the bang?
the questioner hello,
The cut as if the universe has an edge or a center and their location depends on the wrong galaxies. The Big Bang was initially accepted by Friedman from writing Einstein's equations for the universe under the assumption that it is homogeneous and isotropic - that is, that it has no special points such as an edge or a center and as of today there is no evidence that contradicts this principle.
Furthermore, the assumption that a space of finite size must have boundaries is wrong when the matrix is not Euclidean (as for example in front of a spherical shell - see Nissim's response). Finally, nothing guarantees that the universe is finite - all we know is that the visible universe contained within our horizon is finite.
Peace be upon you
Thanks for the answer, you wrote "I don't understand the sentence "the galaxies create space and movement creates time". The meaning is, when space is created, the material in the shell of space is what determines the size of space, therefore today space is determined by the galaxies, and if there is space it also has a center of gravity, and if all space is in motion then the center of gravity is also in motion. And if so, to determine the time from the moment of the big bang, it is necessary to know the speed of the shell, and the distance of the shell from the center of gravity.
That's how I understood things.
Asks,
Hawking is not relevant to the discussion and I did not create any hybrid creature.
The big bang resulting from Einstein's equations did not happen in any specific place - space and time are defined only after it.
Beyond that, I don't understand the phrase "galaxies create space and movement creates time".
I tell you on one leg the summary of the story following what Nissim said.
There was a big bang from that moment space began to expand and while cooling. When the universe reached a certain age, inflation began and it caused gravitational waves to exist and these spread throughout the universe (at least according to what they discovered a few days ago).
After inflation, the universe continued to grow and at some point it got cold enough, the hydrogen became atomic and the universe became transparent.
Now, many years later, we look up into the sky - the farther we look, the earlier we look, and if we look far enough, we will see the moment when the universe became transparent - from here on, we will no longer see back in time and this sight of an opaque universe with an almost uniform temperature As it was at the age of 380,000 is the CMB that was discovered already in the 60s and was the decisive proof for the Big Bang.
But the temperature of the CMB is not uniform because the universe then was not completely uniform - for example, gravitational waves from inflation ran through it and these create non-uniformity in the CMB. Therefore, when we look at the CMB we can see the traces of these gravitational waves and from that learn that there was inflation.
The questioner
You wrote "we are moving away from the center of the bang at a speed lower than the speed of light" - we are not moving away from the center, because we are exactly at the "center". You imagine the Big Bang as an explosion spreading through space, but that is not the intention.
The universe is four dimensional and we are not used to thinking like that. Look at a more understandable example: imagine that the Earth begins to spread. what will you see You will see that everything you look at, moves away from you, and the farther away the object you look at, the faster it will appear to move away. Therefore, each point sees itself as a center.
Now - they say we see the CMB, radiation that exists at a huge distance, but that is not the case. This radiation is here, it is everywhere, it originates about 380 thousand years after the big bang, and the reason for this time is complicated, and is called recombination (or non-bonding, which is something similar). What they have now discovered is radiation (gravitational waves) created before this time, and the discovery confirms a prediction of the Big Bang model.
To summarize - we are not moving away from the center....
Peace be upon you
My question was "How is it possible to measure energy spreading at the speed of light from the bang, when we are moving away from the center of the bang at a speed lower than the speed of light. The only possibility is that we are measuring energy coming from the galaxies that are from the second past of the center of the bang. That is, the galaxies that are moving away from us at a speed twice as fast as we are moving away from the center of the bang. But still, I don't find the possibility to measure the rotation waves. Unless we do, we are moving away from the point of the explosion, at a speed close to half the speed of light."
Unfortunately, I do not see your answer as an answer to my question.
Peace be upon you
It is clear to me now that you created hybrids between Hawking's method and the one derived from Einstein's equations. The equations of A state that the big bang started from a singular point. And so it is simple, that before there was no space and time. If yes, the galaxies create the space and the movement the time, how is it possible that there is no vector source of movement when the driving force is singular.
If so, the starting questions are repeated.
The questioner
The wording should be "nothing outside our universe"...
As far as I understand, the point is that photons were created only 300,000 years after the big bang, but before that there was already mass. Therefore, we would expect to find gravitational waves from this material, at a greater distance than the distance where the photons (the CMB) were created.
Peace be upon you
Correction of a mistake, instead of Hopkins, of course, Stephen Hawking. This is what happens when you lack sleep.
Peace be upon you
If I understood correctly, outside of our universe, there is no space and time. So the whole universe is, in fact, not "existent" in relation to another universe. In fact you are incorporating Hopkins' method into Einstein's equations. But still, why do we know the source of the waves, when it is judged at distances of billions of light years, and without knowing the speed of the Milky Way relative to the source.
deer,
What about the other part of the question? How do we still measure gravitational/light waves. Why didn't these pass us by a long time ago?
The questioner
I will answer you on the relevant page 🙂
Again regarding the "universe rabbi", first of all thanks to the various respondents.
Please 2 clarifying questions (and there are many):
1. Is there any effect like gravity between universe 1 and universe 2?
2. Can the same point in space/time contain elementary particles in different locations?
Asks,
In general, your question is very problematic.
There is nothing to talk about distance from the point of the explosion - before the big bang there was no space or time, so it is not possible to talk about its location in relation to some surrounding space. More than that, the question of where the big bang was in relation to today's universe is also incorrect - it was everywhere because then all that is our universe today was the point where the bang occurred.
.
for miracles
You wrote "they can reproduce with women with the same mutation". Is this a fact or a hypothesis?
And also, how do you determine that the fact that a transparent man cannot reproduce with a woman is due to a mutation.
And according to this, a large number of women or monkeys will come into contact, the result will be positive.
the questioner
The questioner
Did you perhaps mean Zvi/Nisim/Israel Shapira :)?
I guess the culprit is inflation. According to the description, after the big suck the universe went through a very fast inflation process, of 30 orders of magnitude (I take it from Prof. Lawrence Krauss, and I hope I am quoting him correctly) when the inflation process itself is not limited by the speed of light. Hence we can still receive information that arrives at the speed of light, 13.81 billion years after the big bang.
Friends, is this the answer or did I ramble?
The questioner
No - it's not a "defect". This is a genetic change, a type of mutation. They can breed with women with the same mutation.
I will give you a similar example. There is a common mutation in Africa that causes sickle cell disease. According to you this is a defect, but this mutation prevents malaria infection, so it is actually beneficial. It is useful - depending on the environment.
Short people suffer from a mutation - which causes a phenomenon called achondroplasia (the limbs grow at a slow rate compared to the rest of the body). We may see it as a "defect", but it is likely that such people are not recruited, they are not killed in wars, and therefore the percentage of those with the mutation increases. That is, the mutation has a survival advantage, and that's all that matters in evolution.
Now - think that these people I mentioned (who only have 22 pairs of chromosomes) have an advantage. It is quite possible that in the distant future - a new species of the "homo" type will be created. And maybe even cause our extinction.
What I was trying to show on the subject of birth is that you cannot claim that there is no continuous pathway from a single cell to a person. I gave one example that contradicts your claim, therefore the claim is invalid. That's how it works in science 🙂
Has evolution reached its optimum in man? Good question. As long as natural selection does not apply to man, then evolution will stop. There will be a lot of variation in the population, but as long as there is no advantage to this variation, the ratio of variation will be constant (say, the percentage of people with blue eyes will remain constant). But, if there is a choice, then surely there will be evolution (let's say - men will prefer women with blue eyes).
In evolution, it is very rare to have big changes in a short time, for two reasons. The first is that each species is the result of billions of years of evolution and is probably already well suited to its environment. The second reason is that the mutations are usually small, let's say - slightly sharper eyes, and it is unlikely that there will suddenly be a third eye...
Peace to Shmuel
correction,
instead of "waves of rotation". "Gravitational waves".
Peace be upon you
How is it possible to measure energy spreading at the speed of light from the bang, when we are moving away from the center of the bang at a speed lower than the speed of light. The only possibility is that we are measuring energy coming from the galaxies that are from the second past of the center of the bang. That is, the galaxies that are moving away from us at a speed twice as fast as we are moving away from the center of the bang. But still, I don't find the possibility to measure the rotation waves. Unless we do, we are moving away from the point of the bang, at a speed close to half the speed of light.
Do you have another answer, I would love to be updated.
lion,
True, my father changed the order. The news appears above.
Avi, is it possible to add numbers to the comments?
I think the responses are arranged in reverse; That is, the one that was written first, appears last
sympathetic,
Telling you more or less what I understand from reading on the Internet (unfortunately, I do not understand this complex subject).
Polarizations can be broken down into two components:
One component is called the E mode and it is the component without the rotor and the other is called B mode and it is the component without the divergent.
Disturbances in E mode are very easy to explain - if there are disturbances in the density of the universe, then there are denser and hotter areas (in terms of the cosmic background radiation). B mode disturbances are much more difficult to explain. One explanation could be gravitational damping, but this is of course not relevant to polarization in the cosmic background radiation (on such large scales). The second explanation could be gravitational waves originating from inflation.
The prediction regarding the existence of gravitational waves originating from inflation was put forward by Linde (according to Wikipedia). In the model he proposes for inflation, a treatment based on the tools of field theory in a curved space is done. The assumption made is that the distance b is curved, but flat in a sufficiently small area (as in conventional relations) - a treatment similar to that done by Hawking in the discussion of the Einstein-Hawking radiation, it is this approximation that prevents the need for a full quantum theory of gravity. From this treatment it appears that the existence of gravitational waves is expected and these are expected to cause the polarization of the cosmic radiation (the explanation for the last statement appears in the link I added).
I have yet to find a satisfactory explanation for why inflation is supposed to create gravitational waves and it seems that in other models of inflation this does not necessarily happen. This means that not discovering B modes cannot rule out inflation but discovering it can confirm its existence.
http://www.skyandtelescope.com/news/First-Direct-Evidence-of-Big-Bang-Inflation-250681381.html
Maybe he means they moved in different directions
Anonymous (unidentified) user
"Two galaxies that were adjacent within a millionth of a second are on the other side of the universe 27 billion light years away" - where does this confused sentence come from? He is wrong in so many ways…. At the beginning of the universe there were no galaxies at all, they were formed much later. And where does the number 27 billion light years come from? Is this supposed to describe the distance between 2 galaxies? how exactly??
deer,
Thank you very much for the explanation. I would appreciate it if you could indicate the source of the gravitational waves in the early universe, is the source simply the expansion of the universe? Why is radiation treated as an experiment that measures things that happen at very high energies or in other words what determines the energy scale of the gravitational waves? From the article it is implied that the waves were created at very high energies where the grotation has not yet separated from the other three forces, what is the indication for this? Is there a theoretical connection between the inflation model and the spontaneous breaking of the symmetry between the forces?
Enough with the Nobel Prize. Science is not measured by Nobels but by how well it describes reality.
This noble Nobel should be abolished.
Yaron
Please remind me where penicillin is mentioned in the Torah. I forgot….
It is not clear how a faster-than-light-speed inflation can create gravitational waves
Two galaxies that were adjacent within a millionth of a second are on the other side of the universe 27 billion light years away
Seems more scientific speculation than science
The article is just the right dose for laymen and those interested in popular science.
sensational new. That professor without tenure or some doctor along the way figured out how to do it.
There was no known about measurable gravitational waves before, and there was no evidence for the correctness of string theory before, and there was no confirmation of the inflationary universe, and neither
Such a definite confirmation of the theory of general relativity except for the COBE satellite that maps the background radiation in the universe.
The risk taken by that professor who worked on it for 3 years and was committed to publications every year is tremendous.
Yaron, so you are actually saying that gravitational waves are mentioned in the Bible? How come there are no rabbis who receive Nobel prizes for this to this day?
Tell me more discoveries for the future please
Joseph,
As far as I know, there are several options for "Rav Yakom":
One is quantum according to which the universe "splits" every time there is a collapse of the wave function, and the other is that there are clusters of universes, so black black actually constitutes a "big bang" of another universe
I read the article, as an engineer I must admit that I did not get any INSIGHT about anything
There are no explanations here, but a collection of obscure terms that, except for Avi Leib's completeness, no one else has any idea what they mean.
It would be nice if there were more detailed explanations about all the concepts and the like
When I studied physics in the distant past, there was a story about a lecture by Prof. Dror Sade, in which he claimed to have measured gravitational waves. Someone from the audience responded "Did you measure nad stuck in Australia"...
The physicist finds out and the banker gets the bonus. What are the laws of physics?
As for the multiverse,
Some of the speculations surrounding the idea of inflation produce a multiverse.
If (as some theories predict) inflation continues forever in certain areas of the universe, then these areas spread much faster than their surroundings. The reason for the move is easy to understand.
Let's assume that the volume of a cubic meter of space expands very quickly and becomes a cubic meter, while all the cubic meters around it remain cubic meters. Obviously, this MK will not be able to fit in properly and the solution is that it will fold a much larger space in a place that looks smaller from the outside (like the tents in Harry Potter or Mary Poppins' bag). This is a multiverse.
If this is indeed true, then in our universe there are many such pockets in each of which a much larger space is hidden (a baby universe) and it is possible that we ourselves live in such a pocket of a parent universe.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inflation_(cosmology)#Eternal_inflation
First of all, it is important to note that if all of this is indeed true, then this is indeed a huge discovery - there is a confirmation of a strange theoretical assumption that is about 30 years old that so far has not received any observational confirmation (the inflation assumption). And along the way an almost direct discovery of an elusive son of general relativity (gravitational radiation). If it turns out to be true, then this is one of the discoveries that will enter the list of discoveries that shaped and stabilized our understanding of the world.
A few words about what actually confirmed here.
The least important confirmation in my opinion is the additional clue to the existence of gravitational radiation.
General relativity links the metric of space (ie its curvature) to the existence of masses. One of the trivial prophecies of the Torah is that when a gravitational event occurs during which masses reorganize (under a number of well-defined limitations) light disturbances propagate in the mass similar to light, because these disturbances propagate as waves they are called "gravitational waves" and their effect is actually very simple to explain - if we look at A stick that a gravitational wave passes where it is placed, we will see it expand and contract.
The problem is that the strength of these waves is very weak. The power of the Earth's gravitational radiation in its orbit around the Sun is only about 200 watts, which is something like two light bulbs. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gravitational_wave#Power_radiated_by_orbiting_bodies
For this reason it is clear that one must go for more massive, more compact and faster objects in order to successfully detect gravitational radiation.
Indirect evidence for the existence of gravitational waves was indeed discovered in 1974.
When two massive and close bodies orbit each other the radiation that is emitted comes at the expense of their orbital energy. For this reason they will get closer to each other and their cycle time will get shorter and shorter. In 1974, a pair of scientists named Holes and Taylor discovered changes in the cycle time of a pair of neutron stars that exactly match the predication that comes from gravitational radiation. For this discovery they were awarded the Nobel Prize.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hulse%E2%80%93Taylor_binary
As of today, there is no real dispute about the very existence of gravitational radiation and since in the coming years direct detectors of gravitational radiation are expected to start operating, many physicists are engaged in the subject with the aim of predicting in advance what the patterns of gravitational radiation from various events look like, this is to understand the astrophysical origin of the signals that are expected to be detected there.
The more important discovery is the confirmation given to the idea of inflation.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inflation_(cosmology)
The idea of the big bang as it emerged from the equations of relativity and as confirmed by the discovery of the cosmic background radiation caused a number of problems mainly because it required very fine "fine-tuning". Quickly:
Suppose there is a very big explosion and the galaxies start moving away from each other:
If the explosion is too weak, the galaxies will move away from each other at first but at some point they will stop and start falling back towards each other.
If the explosion is too strong, the gravity between the galaxies will not be able to stop them and they will move away from each other forever and very quickly they will not see any other galaxy from any galaxy. Our universe is somewhere in a place that balances very nicely between the two situations - as if the power of the big bang was "intended" in a very precise way. This problem is called the "flatness problem" because it is expressed in a flat (ie Euclidean) universe in terms of the matrix it will have.
Another problem is the uniformity of the temperature of the cosmic background radiation, and here too it seems as if the temperature throughout the universe is intended to be very similar at every moment, even though different regions of the universe are very far from each other.
In 1980, an American named Alan Guth proposed the idea of inflation.
The idea is that if we assume (without a direct reason from the equation of the theory of relativity) that at its beginning the universe went through a phase of exponential growth during which it went through a significant part of its growth, these problems will be solved above them:
The rapid inflation will flatten the universe and erase any lack of tuning that was in it at the beginning and ensure a connection between distant areas of the universe - thus the two fine-tuning problems we talked about disappear. Furthermore, the non-uniformity of the contemporary universe is naturally explained as quantum fluctuations that existed in the ancient universe and simply kept increasing due to inflation (thus creating the concentrations of matter that later became the galaxies). Alan Guth also proposed a certain model that explains the origin of inflation and quantifies it and overall, despite many corrections that were introduced to the model later, it seems that this is a fairly successful idea.
The idea of inflation is the most significant correction (along with the discovery of dark energy in 1998 for which no satisfactory explanation has yet been given) that was introduced in the "classical" big bang of Friedman and Valmeter (the big bang as it emerges from the equations of the theory of relativity). This is therefore a very important idea, perhaps the most important yet to be proven in modern cosmology.
So far there has been no observational confirmation of inflation (ie beyond what we see in the universe), but now these scientists claim to have found confirmation of the idea. We'll see.
If the professor gets tenure he will stop working
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VxzxI5sCXfk
Instead of groping in the dark and discovering hypotheses that are hidden over and over again, simply open a Torah book written according to the Creator of the world
This multiverse means that there are many other universes that are similar to ours or different, when each universe has its own physical constants.
This means that we were created out of many possibilities, and if this is the hand of chance, then humanity is a very special thing.
What might be the theoretical and practical implications of the findings and their publication?
I would appreciate it if the respondents could indicate their authority of knowledge
Larya hide!
The word "universe" as I understand it includes all the particles of matter and the various fields, everywhere in space and time. Isn't that so?
There are other universes like ours. An array of universes is called a multiverse.
What is meant by the nickname "universe rabbi"?