Today in 1655, Titan, Saturn's largest moon, was discovered by Christian Huygens. 350 years later, a spacecraft named Huygens landed on the surface of the moon using parachutes and transmitted images and data from it.
Tammy Plotner and Jeff Barber, Universe Today
Today in 1655, Titan, Saturn's largest moon, was discovered by Christian Huygens. 350 years later, a spacecraft named Huygens landed on the surface of the moon using parachutes and transmitted images and data from it.
Huygens was also the one who discovered Saturn's rings, even in 1655. Saturn is now high in the sky and you should take this opportunity to tour the system of rings and moons. Titan's siren song awaits you.
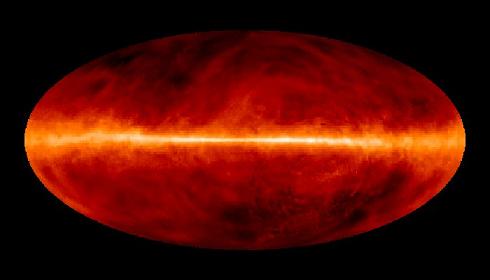
Today, in 1951, hydrogen radiation was discovered for the first time in the Milky Way - electromagnetic radiation 21 centimeters wide or with a frequency of 1420 MHz. However, the study of non-molecular hydrogen continues to be the basis for large parts of modern radio astronomy. The monatomic hydrogen (H1) regions of the Milky Way are mostly star-free. Stars usually heat the gas and make it glow.
By using a radio telescope with a frequency of 21 centimeters, astronomers can map the distribution of interstellar matter - the huge regions between the stars.
Because the radio waves can penetrate through dust, which is also in the interstellar medium, we know much more about the distribution of hydrogen gas in our galaxy than would otherwise be possible. Stable hydrogen gas is transparent in the visible light range, and its presence is concentrated along the galactic disk and especially in the vast galactic arms. Such an area is also found in the Orion system. It is therefore worthwhile to look in the sky south of the star Eta Orionis whose magnitude is 3.4, and see how few stars can be seen between it and 29 Orionis whose magnitude is 4.2, about 5.5 degrees away. Such regions are known to have a high concentration of 21cm radiation emitted from hydrogen atoms as they begin to fuse to form a sun like ours.
