Hayadan > Biology and Medicine > Page 12
Biology and Medicine
- The Voice of Science website - the Israel National Science Foundation
- February 15, 2023
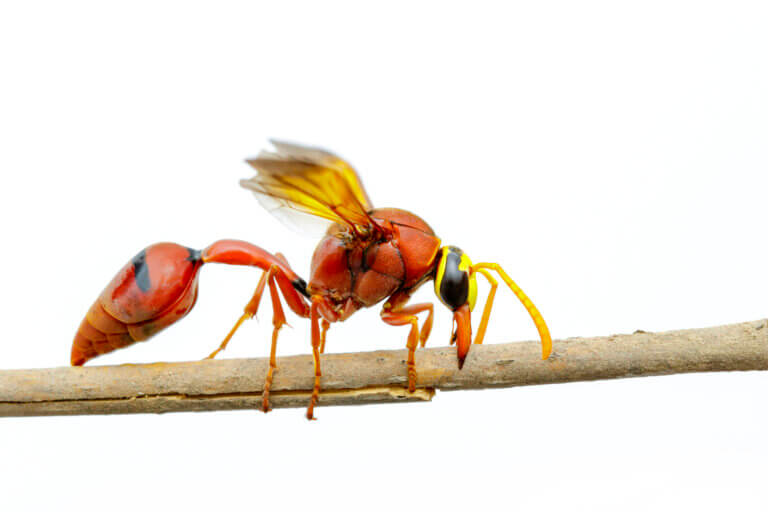
A wasp gathers as food for its future offspring larvae that contain maggots of another wasp in their bodies, thus harming their survival
- The Voice of Science website - the Israel National Science Foundation
- February 14, 2023
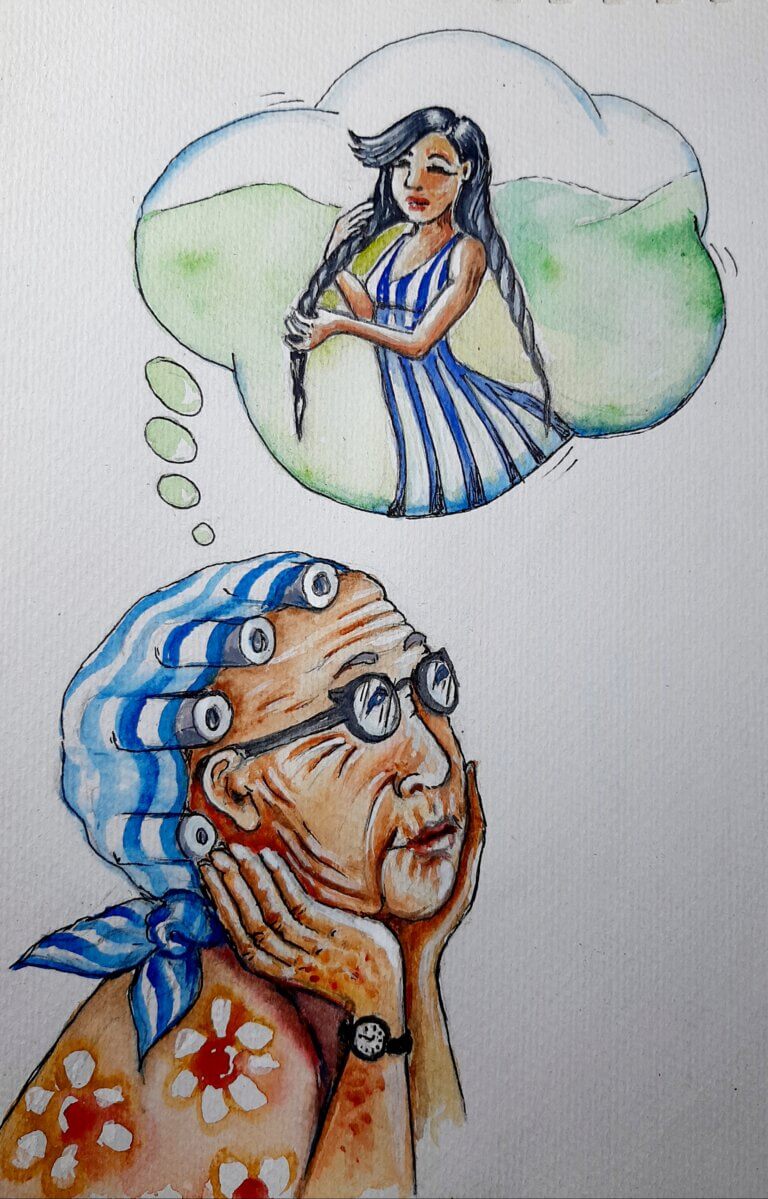
Perceptions of aging by elderly patients affect their health after hospitalization
- Tel Aviv University
- February 13, 2023
- No comments
The researchers believe that they have succeeded in finding all the roles played by the ELG1 gene. The gene in question is also evolutionarily conserved in humans and mutations in it cause cancer, understanding its meaning in yeast can help fight the disease.
- Tel Aviv University
- February 10, 2023
As part of the study, the Ashona researchers were able to identify proteins whose role is essential for the development and activity of the tissue affected by the disease, to precisely locate their location in genomic regions outside of the genes, and to identify the relationship between the changes in these regions and the risk of developing AMD
- Weizmann Institute
- February 9, 2023
Not only breast cancer: mutations in the BRCA gene, which are especially common among Ashkenazim, increase the risk of various types of cancer - also in men. The institute's scientists reveal how they turn healthy cells in their environment into collaborators
- Avi Blizovsky
- February 8, 2023
- No comments
The winners are: Chuan Ha, University of Chicago, USA, Jeffrey Kelly, Scripps Research Institute, USA, Hiroaki Shuga, University of Tokyo, Japan
- Avi Blizovsky
- February 7, 2023
- 4 תגובות
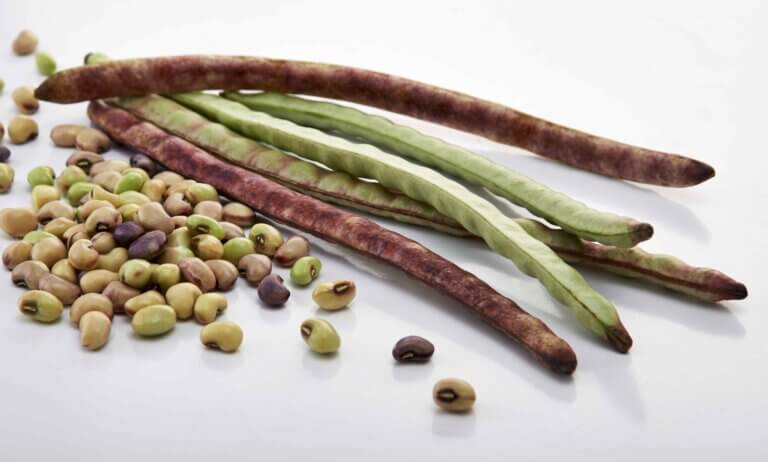
The Israeli genetics and seed company BetterSeeds has genetically redesigned the architecture of the Luvia plant and the uniformity of the appearance of its pods in a way that is suitable for mechanized harvesting * The improved Luvia will be tested in the United States during the spring of 2023
- The Hebrew University
- February 5, 2023
- 4 תגובות
In an official letter, published on Thursday 02.02 in the leading medical journal The Lancet, a list of senior researchers and experts in the world in the fields of public health, health economics and nutritional sciences, express deep concern in view of the decision to cancel the tax on sugary drinks
- Weizmann Institute
- February 4, 2023
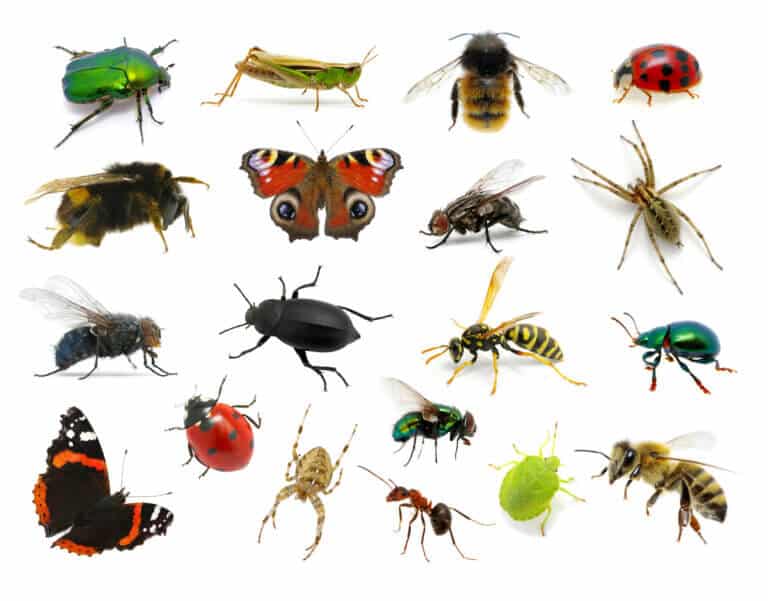
In a first calculation of its kind, the weight of all the insects, spiders and their terrestrial relatives in the world was found
- Weizmann Institute
- January 29, 2023
In response to environmental and intracellular changes, the proteins in our body don a variety of costumes that change their properties and make their identification difficult. The institute's scientists have developed a ground-breaking search engine capable of identifying these proteins with unprecedented efficiency
- Angle - a news agency for science and the environment
- January 27, 2023
- No comments
Bad surprise: Israeli research has found large amounts of mineral matter in the eastern Mediterranean whose formation process releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. What it means? That our ocean emits more greenhouse gases than we thought until now
- Weizmann Institute
- January 25, 2023
Weizmann Institute scientists offer a solution to a 50-year-old mystery
- Ehud Amir
- January 23, 2023
- One response
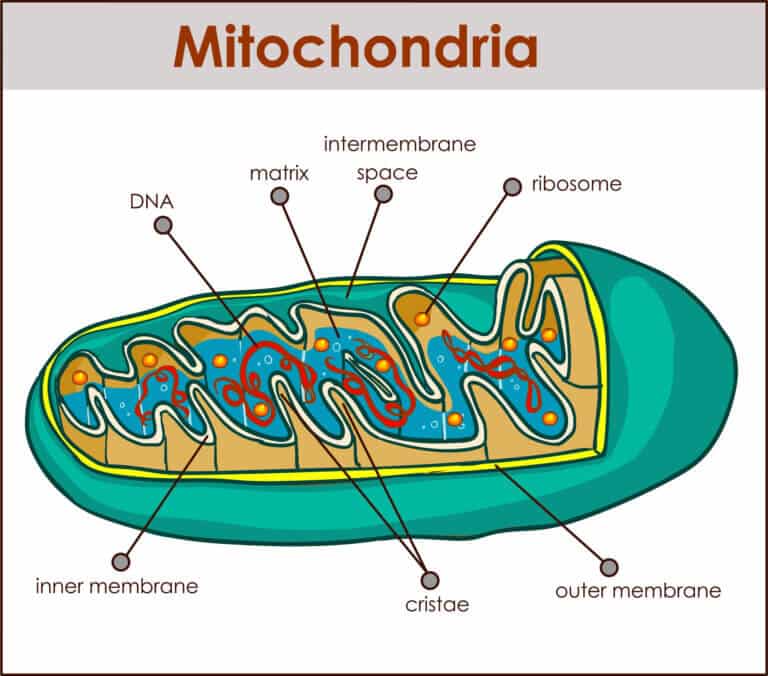
For 1.5 billion years, the mitochondria - the powerhouse of the cell - have been sending DNA segments to the cell nucleus, and they merge with the DNA in the nucleus. A new study found that the contribution of the mitochondria to the DNA in the cell nucleus gradually decreases. This process is expected to reduce the incidence of some hereditary diseases
- Weizmann Institute
- January 20, 2023
Weizmann Institute scientists have discovered that certain fish are born with immunity to stressful situations, which accompanies them throughout their lives and is even inherited. The findings may pave new directions for the treatment of post-trauma
- Dr. Moshe Nahamani
- January 19, 2023
- No comments
However, the harsh and acidic conditions of the stomach cause the breakdown and neutralization of this important hormone even before it reaches the intestines and from there into the bloodstream. To overcome this, the researchers remove the insulin molecules through the walls of the stomach using a kind of robot
- The Hebrew University
- January 18, 2023
- No comments
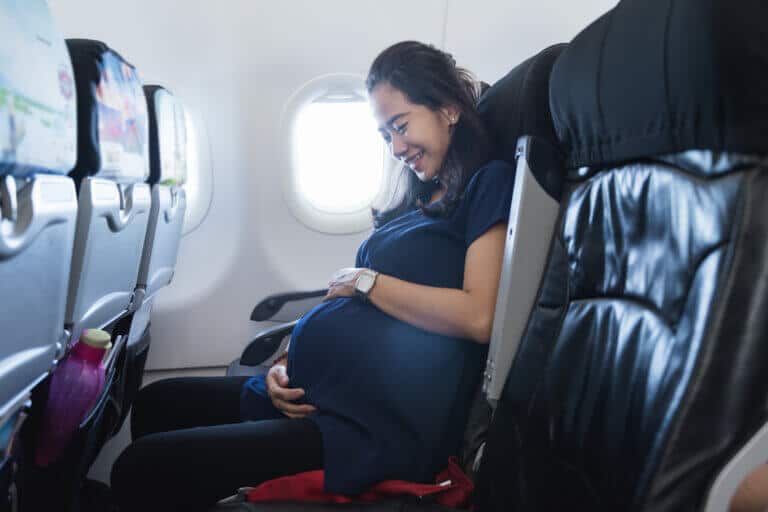
The Hebrew University and Ichilov Hospital researchers found that pregnant women have a 40% increased chance of developing a blood clot in the deep veins of the legs and lungs following a flight. This risk is found in a period of time of up to two months from the flight
- Dr. Moshe Nahamani
- January 16, 2023
- No comments
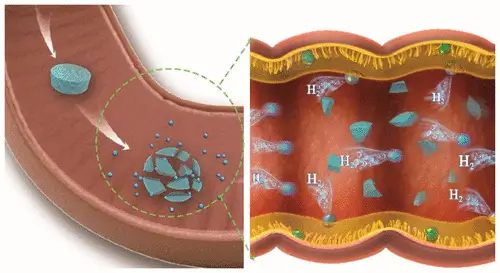
An innovative macroring material can trap a variety of drugs in overdose cases, including opioids, hallucinogens and stimulants, thanks to its hydrophobic niche
- Avi Blizovsky
- January 16, 2023
- One response
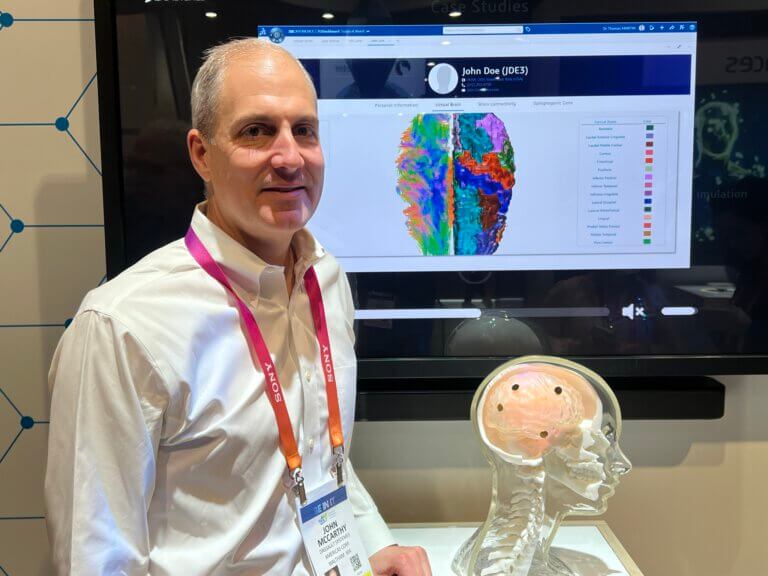
The living brain project of Dassault Systèmes makes it possible to develop treatments for epilepsy patients who do not respond to drugs, says John McCarthy, head of life sciences and health at Dassault Systèmes in an interview with the science website at the CES conference
- Tel Aviv University
- January 15, 2023
A new model offers an explanation for the huge variety of sizes of DNA in nature
- Tel Aviv University
- January 15, 2023
For the first time in the world of science, a robot was able to "smell" using a biological sensor
- Weizmann Institute
- January 14, 2023
Unprecedented abilities to produce thousands of enzymes pave the way for a green industrial revolution
- The Technion
- January 13, 2023
- No comments
The Technion recently launched Tech.AI, a center that brings together the Technion's biomed activity in the field of AI and makes research and application at the forefront of AI accessible to researchers from all units at the Technion
- The Voice of Science website - the Israel National Science Foundation
- January 12, 2023
- The Voice of Science website - the Israel National Science Foundation
- January 8, 2023
The creation of double-strand breaks in the DNA of certain cancer cells may help inhibit the growth
- Tel Aviv University
- January 7, 2023
The new study contradicts the popular opinion that people with autism are apparently "indifferent to pain"














![The macrocyclic compound P6AS can trap a variety of drugs that can cause overdose, including opioids, hallucinogens and stimulants, thanks to a hydrophobic internal niche. [Courtesy: © Brockett et al., Chem 9, 1–20 April 13, 2022 Elsevier Inc]](https://www.hayadan.org.il/images/content3/2023/01/fx1.jpg)