Hayadan > Biology and Medicine > medicine > Diseases > Page 5
Diseases
- Avi Blizovsky
- September 2, 2021
- No comments
Researchers from Tel Aviv University have shown that silent mutations, i.e. those that do not change the amino acid sequence of the proteins, are also not innocent
- The Hebrew University
- September 1, 2021
In a study conducted on blood samples from patients and those recovering from leukemia, unique sequences were found that control genes that contribute to the spread of the disease. "By investigating these genes we can learn how to prevent the disease from progressing and even develop future drugs to prevent it"
- The Hebrew University
- August 19, 2021
- The Technion
- August 17, 2021
- No comments
Researchers at the Rappaport Faculty of Medicine at the Technion deciphered new aspects of the aging of the immune system - and discovered that it is possible to restore its youth
- The Hebrew University
- August 16, 2021
Prof. Yigal Aral: "In light of the expected dramatic increase in the production of lead and other toxic metals, we warn of a large-scale health risk, especially in countries where there is no regulation and orderly monitoring of environmental pollution and human poisoning"
- Avi Blizovsky
- August 3, 2021
- One response
The findings are of great importance because they may allow diagnosis and preventive treatment before the appearance of the fatal metastases
- The Technion
- July 22, 2021
- No comments
Researchers at the Rappaport Faculty of Medicine at the Technion discovered that the connection between tendons and muscles is formed by hybrid cells that merge with the muscle fibers and "know" how to cause the ends of the muscle to express tendon characteristics
- Young Galileo
- July 17, 2021
- No comments
- Weizmann Institute
- July 14, 2021
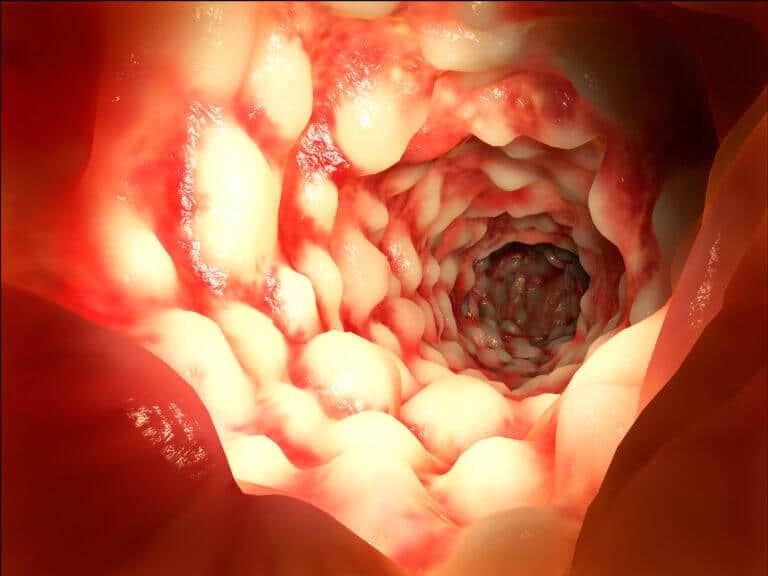
Changes in the intercellular texture may predict inflammatory bowel disease
- Tel Aviv University
- July 6, 2021
- No comments
The researchers relied on the CAR-T technology, which uses genetic engineering to improve the function of the immune system's T cells in their war on cancer cells. According to the researchers, the method they developed may help patients with various types of brain cancer, as well as solid tumors in other organs
- Tel Aviv University
- June 30, 2021
- One response
Prof. Dan Farr, Tel Aviv University: "Our development actually changes the world of antibodies. Today we flood the body with antibodies that are indeed selective, but also damage the healthy cells. We removed non-inflammatory cells from the game, and with a simple injection we succeeded in damaging only the inflammatory cells at that moment Given"
- The Hebrew University
- June 3, 2021
- One response
A protective protein, which was generally known to be effective against blood clots, was found to be capable of inhibiting the most violent means of cancer in the human body - metastasis. Prof. Tal Borshtin-Cohen, the leader of the research, believes that the surprising discovery explains why there are quite a few anti-cancer treatments that fail: "The understanding that protein S helps the body fight metastases is a warning light for anti-cancer treatments, which are designed to inhibit this protein's pathway"
- Avi Blizovsky
- May 31, 2021
- No comments
In a healthy person, these cells do not exist at all. In patients with malaria, AIDS and lupus, they make up 15%-25% of the B cells
- Tel Aviv University
- May 10, 2021
- 2 תגובות
Researchers from Tel Aviv University have developed a product that protects the bone tissue and it will be registered as a new patent * The product is designed to prevent bone loss around orthopedic implants, dental implants and teeth
- The Technion
- April 27, 2021
- 2 תגובות
- Weizmann Institute
- April 25, 2021
Scientists at the Weizmann Institute and the Technion have discovered clues to the existence of a slow regulatory mechanism in heart muscle cells designed to regulate the rhythm of their beats, and to ensure that it is as close as possible to a cycle of one beat per second
- Tel Aviv University
- April 12, 2021
- 2 תגובות
Researchers from Tel Aviv University have identified a failure in the brain's immune system that increases the division and spread of glioblastoma cancer cells instead of inhibiting them. Now they are looking for ways to turn the situation around
- The science service
- April 6, 2021
An alternative report on the state of health of Israelis: Who gets more cancer - men or women? Where are more affected by diabetes - in the north or in the center? What are the most common surgeries?
- Yoram Soreq
- March 26, 2021
- 2 תגובות
This week we were informed of the return of the Prime Minister's wife, Sara Netanyahu to her family after surgery to remove the appendix. Along with the sigh of relief, interest arises in Neta's question: why do you need the appendix if you take it out and you can live without it?
- Avi Blizovsky
- March 9, 2021
- No comments
In May 2020 preliminary results from CORONADO with a smaller sample showed that 10% of patients with diabetes and corona died within 7 days of hospital admission.
- Yoram Soreq
- March 5, 2021
- 2 תגובות
His mouth is lethargic and the hum of the drill still echoes in his ears. He turns to C with a desperate question: Who needs wisdom teeth?
- The Hebrew University
- February 28, 2021
- The Technion
- February 8, 2021
- No comments
The research group of Prof. Tomer Shlomi from the Faculty of Computer Science, the Faculty of Biology and the Lockey Center for Life Sciences and Engineering at the Technion discovered a process based on which it is possible to selectively and specifically damage cancer cells without causing damage to healthy tissue
- Tel Aviv University
- January 28, 2021
- No comments
Researchers from Tel Aviv University shed light on a 140-year-old mystery in an article published in Nature. The research shows for the first time how an abnormal number of chromosomes (aneploidy) - a unique feature of cancer cells that has been known to researchers for decades - can become a weak point of these cells. The research may in the future lead to the development of drugs that will take advantage of this weak point for targeted damage to cancer cells
- Avi Blizovsky
- January 15, 2021
- No comments
A marker developed in a new Israeli study by the University of Bar-in and applied by the start-up company Isotopia will not only determine if it is a malignant or benign tumor but also determine how aggressive it is, and all this will be done in one image and avoid a biopsy