Realize that utilizing sunlight in order to split a water molecule and obtain hydrogen from it is one of the most interesting ways to obtain clean energy
[Translation by Dr. Nachmani Moshe]
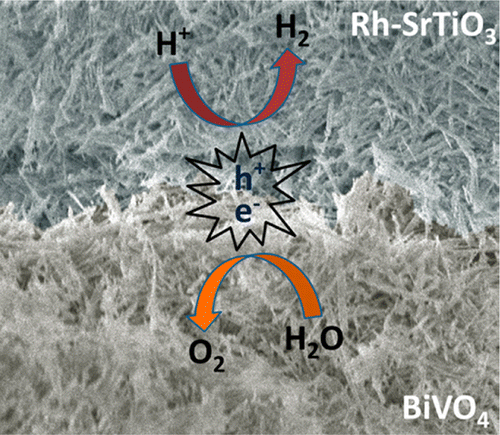
For many years scientists have been trying to develop an "artificial leaf" technology - a green approach to producing hydrogen fuel that mimics the ability of green plants to convert the sun's rays into a usable form of energy. Now, a team of researchers has managed to advance another step in the development trend of an independent system that will lead to mass and cheap production.
Researchers Peidong Yang, Bin Liu and their colleagues realized that using sunlight to split a water molecule and obtain hydrogen from it is one of the most interesting ways to obtain clean energy. Car manufacturers have started selling vehicles powered by hydrogen fuel cells that emit only water during operation. However, the production of hydrogen, usually obtained from the processing of natural gas, requires the consumption of electricity, which itself comes from conventional power plants that emit carbon dioxide. Producing hydrogen at a low cost from water, using clean energy from the sun, will make this type of energy, which can also supply electricity to private homes and businesses, more environmentally friendly.
The researchers took advantage of one of the processes in the paper industry in order to create a flat network made of nanowires of a light-absorbing semiconductor material which, after being immersed in water and exposed to light, emits hydrogen gas. The scientists claim that the method could allow their technology to reach an industrial scale and at a low cost. Despite the fact that increasing the efficiency of the method still remains a challenge, the new approach - unlike other artificial leaf systems - is independent and does not require the addition of additional external components or devices that cause damage to the environment.
