This is according to the Taub Center's annual report published this week, which presents a picture of Israel's socio-economic situation in 2015 in relation to other countries and in comparison to the past * From the chapter - Professions at risk: IT trends in the labor market in Israel

Comet Madhala-Brik )researcher at the Taub Center)
About 40% of employment in Israel is in professions that are at high risk of going through a computerization process in the next two decades. This is evident from the chapter "Professions at Risk: Computing Trends in the Labor Market in Israel" from the Taub Center's annual report published this week, which presents a socio-economic picture of Israel in 2015 in relation to other countries and in comparison to the past.
According to the study led by Shavit Madhala-Brick from the Taub Center, this trend is similar to what is happening in advanced countries in the world. In the USA and Germany, for example, the rate of high-risk employment is even wider: 47% and 49%, respectively.
The research conducted at the Taub Center is based on a model that categorizes all professions according to their level of risk of becoming computerized in the future. The professions at the highest risk of computerization are characterized by repetitive and technical operations, for example bookkeeping and data entry. In contrast, low-risk occupations require skills such as creativity, social intelligence, complex perception and negotiation skills. According to the analysis, professions such as economists, historians and bus drivers are moderately likely to be computerized, and professions such as doctors, social workers, choreographers and psychologists are defined as low risk.
Many of those employed in professions with a high risk of computerization belong to the most vulnerable groups in the population: those without an academic education, those with low hourly wages and young employees. The group most at risk is non-Jewish men. 52% of the working hours of those employed in this group are in industrial and construction professions - a profession in which most of the professions are at high risk of computerization. In 2011, 59% of the working hours of those aged 24-15 were in professions with a high risk of computing. Taub Shavit Center researcher Madhala-Brick asks: "What will young people be doing in twenty years, after the professions they are employed in today will become computerized?"
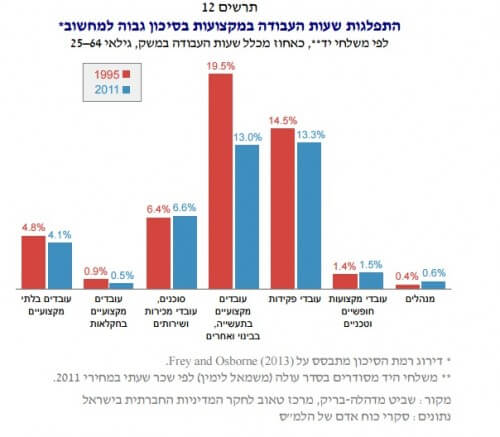
In the last two decades, the impact of the computerization process was already evident, and a 9% decrease was recorded in the relative share of high-risk working hours out of the total working hours in the economy in those years. For example, between 1995 and 2011 the relative employment rate of locksmiths, tinsmiths, blacksmiths and welders decreased by 38%. Also, it was found that there is a widespread transition of workers without academic education to professions in the field of services (similar to the trend in the USA).
According to the Taub Center's research, the required preparation for the changing labor market can include several steps, among them: expanding the use of professional training tools and their focus, so that they are adapted to the relevant characteristics of those who leave the labor market and at the same time are oriented to the future labor market; regular updating of the existing study programs; and the establishment of a government body that will coordinate the handling of the issue and work with training institutions, academic institutions, schools and more.
For the full report Professions at Risk: Computing Trends in the Labor Market in Israel
- More of the topic in Hayadan:
The most masculine profession in the field of science - electrical engineering, the most feminine profession - life sciences - If we don't change the education system from the ground up, we will have hundreds of thousands of unemployed
- The future of the future - the fourth wave - creative entrepreneurship / Yankee Margalit

2 תגובות
The research of the Bank of Great Britain is more comprehensive and accurate and it predicts that in Western countries 50% of the employment force will be replaced by robots, software robots and artificial intelligence within only a decade from today. It sounds more accurate if we take into account that most developments in the field of automation are aimed in advance at the fields in which the largest masses of people are employed and in which the profit potential from the development in a global perspective is the highest.