The research findings indicate that when the dust storm heats the atmosphere, winds are created that throw water vapor to much higher heights than usual. At these high altitudes, the Martian atmosphere is thinner and water molecules are more vulnerable to UV radiation, which breaks them down into their lighter components, hydrogen and oxygen
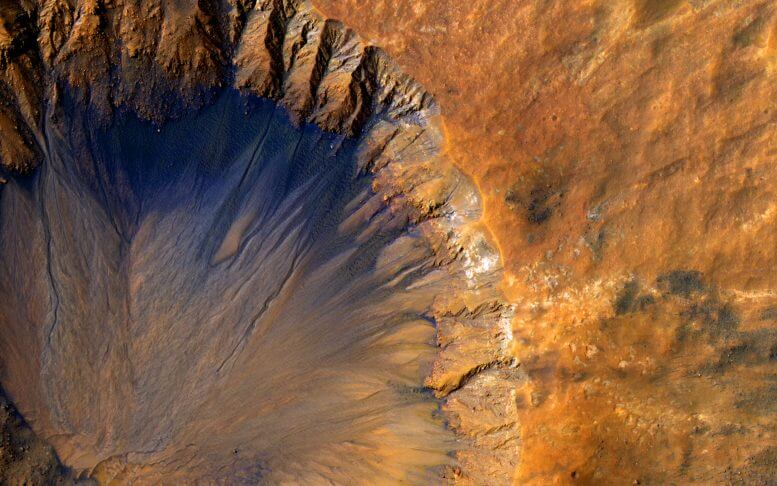

The HiRISE camera on NASA's Mars Orbiter captured this close-up image of a "new" impact crater (on a geological scale, but very old on a human scale) in the Sirnum Posei region of Mars on March 30, 2015.
Mars scientists have long suspected that the Red Planet, once as hot and humid as Earth, has lost most of its water to outer space. Since water is one of the important components of life as we know it, scientists are trying to understand how long it flowed on Mars and how it was lost.
A new study published now in Nature Astronomy, led by Michael Chapin, a researcher at the University of Colorado Boulder's Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, shows that regional dust storms could play a significant role in the drying of Mars.
Although Martian scientists like Chapin assumed that global dust storms, which typically strike one to three each Martian year, along with the hot summer months in the southern hemisphere, play a role in drying the planet, they lacked the measurements needed to piece together the whole picture. But in January and February 2019, simultaneous observations from three spacecraft orbiting Mars allowed an international team of researchers to collect unprecedented data during a regional dust storm. The results show that Mars loses twice as much water in these storms than in quieter periods.
"Until now, Martian scientists did not understand the magnitude of the impact of the regional dust storms on the Martian atmosphere," says Chapin.
The research findings indicate that when the dust storm heats the atmosphere, winds are created that throw water vapor to much higher heights than usual. At these high altitudes, the Martian atmosphere is thinner and water molecules are more vulnerable to UV radiation, which breaks them down into their lighter components, hydrogen and oxygen. The lightest element, hydrogen, is easily lost to space. "All you have to do to lose water permanently is to lose one atom of hydrogen, because then the hydrogen and oxygen don't combine into water," says Chapin. "Therefore, when you lose an atom of hydrogen, you lose a molecule of water."
The study would not have been possible without the five simultaneous measurements from four instruments on the spacecraft. NASA's Mars Orbiter measured the temperature, dust and water ice concentrations from the planet's surface to about 100 km above them. In the same altitude range, the European Space Agency's Gas Residue Survey measured the concentration of water vapor and ice, and the UV imaging spectrometer in NASA's MAVEN spacecraft finished the measurements with a report on the amount of hydrogen at the highest altitudes in the atmosphere of Mars, a thousand km above the planet's surface. .
More of the topic in Hayadan:
