These days, the Webb Space Telescope is expected to take the place of the Hubble Telescope after more than 30 years of operation. How far in space and time (!) can the web reach? What does he see that the human eye is unable to perceive? And how could he help us discover the secrets of the creation of the universe?
Reporter: Gilad Yas'our, Young Galileo
Click for a digital gift sheet HERE
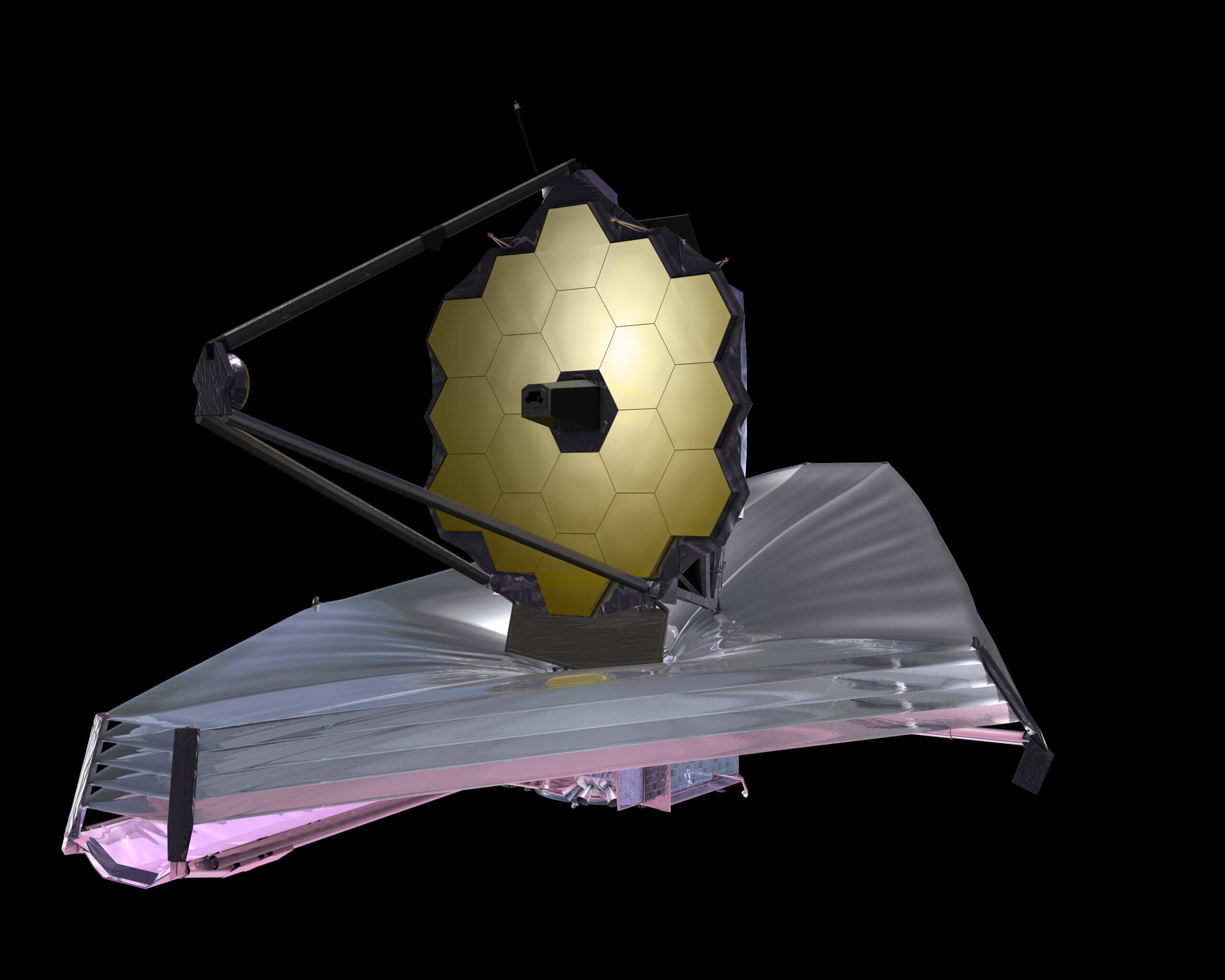
On April 24, 1990, the Hubble Space Telescope was launched. Over the years, he provided us with spectacular images and made possible countless discoveries that advanced science. These days a new space telescope is being launched - the space telescope named after James Webb. Thanks to it, we can make distant observations towards the universe as it was not long after the big bang, look into the hidden places where stars are born in order to deepen our knowledge about the process of their formation, and study extrasolar planets (planets that are outside the solar system).
What is special about the space telescope and that thanks to it we can discover all these things? First of all it is big, very big. The diameter of Hubble's main mirror is 2.4 meters. A telescope's main mirror is what allows it to collect light. Unlike the first telescopes that were made with lenses, modern telescopes, especially the largest ones, are based on mirrors. The larger the mirror, the higher the light gathering ability of the telescope. The diameter of Veb's main mirror is 6.5 meters, which means it will be able to collect much more light than Hubble and observe dim and very distant objects.
Another peculiarity of it is the type of radiation it is able to absorb. Humans are able to see light in the range of colors between red and violet - the range of visible light. But this is only a very small part of all the types of radiation that exist in nature. Every warm body, for example, including us, emits infrared radiation - light that we cannot see. Different animals manage to recognize this light, and so for example the mosquitoes know how to find us even in the dark. What about a spider and mosquitoes? Before that we will explain about the expansion of the universe.
Looking to the past
At the end of the 20s of the 20th century, the scientist Edwin Hubble (after whom the space telescope is named) announced his revolutionary discovery: the universe is expanding. He looked towards many galaxies in the universe and saw that they were moving away from us. He recognized that the more distant the galaxy, the faster it is moving away from us. What can explain this?
Are we a very unpleasant galaxy and everyone wants to stay away from us, or is this a general phenomenon of the universe? The second option is the more likely, and so Hubble realized that the only way any point in the universe would see the rest of the universe moving away from it, is if the universe itself is expanding.
The expanding universe can be compared to a loaf of puffed bread with raisins. As the bread rises, the distance between the raisins increases, and each raisin sees the others move away from it. If we were a raisin, the further away we look at a raisin, it will move away at a higher rate, because the distance between us is full of puffed dough. If there was a thread connecting two raisins before the swelling, in order to continue connecting them it would have to lengthen and lengthen all the time.
We will return to the web. And it is planned to watch very, very far. in space and time. As it looks further away, it will see galaxies whose light took longer to reach us, so in effect it will be looking into the past! And it is planned to look more than 13.5 billion years back in time, almost to the beginning of time, towards the galaxies most distant from us, and thus study the young universe after the big bang.
And the observer is so far away, therefore the light he will see travels in the universe for billions of years. Light is also redshifted because blue light changes to red and red light changes to infrared light (the general phenomenon is called the Doppler effect; most of you know it from the sound of an ambulance horn changing from high to low when the ambulance passes you).
And in the future we will look so far that the redshift effect will make the light, which was originally in the visible light range, appear to us to belong to the infrared range. Therefore, like mosquitoes, and looking at this frequency range.
See stars being born
Focusing on the infrared range will also help Webb observe stars being born. Many stars are born in nebulae. A nebula is a huge cloud of matter (made mostly of hydrogen and helium) that collapses in on itself, until the density of matter is high enough for a star to form. Because the process takes place in the heart of the nebula, the surrounding material obstructs the view of all the action taking place in the center.
Even though the material interferes with visible light, infrared radiation passes through the nebula almost unhindered. That way, Bev will be able to see the formation of the stars.
How do you launch a giant into space?
We said that Webb is a huge telescope, it is actually bigger than any spacecraft. So how do you launch it into space? To enter the launcher it folds, just like origami.
Unlike Hubble's main mirror, which is one complete mirror, Bev's main mirror consists of 18 small hexagon-shaped mirrors, all of which together form one large mirror. At launch, six mirrors (three on each side) fold out, and that's how it goes into the launcher. Only about two weeks after launch, when it will be further away from us than the moon, it will deploy the side mirror parts, and the main mirror will be completed.
Additionally, Bev's place in space will be very different from Hubble's. Hubble orbits the Earth at an altitude of 540 kilometers, but the distance between Hubble and us will be much greater. Why?
As we said, every hot body emits infrared radiation. The earth itself is a source of a lot of infrared radiation, as are the moon and the sun. If he wanted to make his observations from a place similar to that of Habel, it's like a birder would want to go out to listen to a rare, gentle and quiet songbird from the middle of busy Tel Aviv.
Therefore the goal is to launch Bev far from Earth, but not too far, so that it can easily communicate with us.
Where is there parking for the telescope?
The Lagrange points of the Sun and the Earth are five special points in space where, if a spacecraft is parked, it will stay there and orbit the Sun at exactly the same speed as the Earth orbits it. And launched towards the second Lagrange point - L2. To reach it, he takes off from the earth in the opposite direction from the sun, and flies a distance of one and a half million kilometers. The journey will last about a month.
That is, Bev will be almost 3,000 times farther from Habel. There, at point L2, the radiation from the Earth and the Moon will be much weaker, but will not disappear completely. And so that it does not heat up and burn due to the proximity to the sun, a "blanket" of five layers is installed on it, the function of which is to protect it from the sun and to maintain a very low temperature. This "blanket" will help him maintain a temperature of minus 223 degrees Celsius. That way it will be cold enough that its own heat radiation will not interfere with its sensors making the observations. Like the mirror, those protective layers remain folded at takeoff and will fully open, to the size of a tennis court (!), only about six days after liftoff, during its journey to the L2 point. The process must be very slow and gentle, since the thickness of each of the layers is a few microns, less than the thickness of a hair.
And it is the next great step that humanity seeks to climb on its way to understand the universe and everything in it.
The author is a student for a master's degree in physics at the Hebrew University and an instructor at the "The Great Bear" association for observational astronomy dubagdola.com
The article was published in the January 2022 issue of Galileo Young Monthly
More of the topic in Hayadan:
- The space telescope - the next generation is coming
- A cold region in space may be a remnant of the Big Bang
- Spitzer captured the oldest light in the universe
- On the occasion of the launch of the Webb Space Telescope: the five most exciting telescope images of the universe
- James Webb Space Telescope - Hubble's replacement successfully launched - live broadcast

14 תגובות
What bullshit - it is a fact that some who did not put telescopes did not see heaven and the angels and God.
It's all computer images and they hide the truth.
And if we see the big bang, can we also see what was before?
Fascinating, the thought of the small mirrors that open to a large view in space, and channel the infinity, beautiful!
Excellent article.
Waiting patiently until May 2022
For first photos.
don't understand anything
Probably rejects the possibility of looking back in time...
fascinating and want to understand more,
What can I look back on, the grandparents who were slaughtered in the Holocaust, the uncles, the family events. In what concepts can we look back?
shocked
Regardless of the telescope, it needs a period of 5 months for cooling, mirror calibration and system activation. However, it is already possible to point to breakthrough technologies that will affect us all in the future mainly thanks to its extraordinary sights. For example, eye surgeries will become easier and more precise. In the field of photography, we may be able to get rid of heavy lenses with a wide aperture to absorb as much light as possible and instead we will use reflective mirrors that absorb light. In short, exceeding expectations for new discoveries, the telescope also represents a breakthrough in the field of optics and visibility.
How amateur can you be?
Webb does not take Hubble's place because it is a completely different telescope.
Hubble is an optical telescope that sees in visible light.
Webb is a telescope that sees in infrared, meaning it only detects heat.
It's something else.
Great writing, thank you very much for the knowledge and information 🙏🕉️
Most fascinating! Explained in a simple and clear way for everyone. Cheers! I enjoyed it very much
The frequency of light decreases not due to the great distance. But because the light source is moving away from us.
Due to the expansion of the universe, the farther away a star is, the faster it moves away.
Therefore, the frequency of the light emitted from it decreases to a greater extent.
If he had not moved away, despite the great distance, the frequency would have remained as originally emitted. Only his strength is weakening
The article was published in a printed journal, hence the delay.
Most impressive writer creator creator writer
Much of what is written in the future tense actually already happened before the day of publication.
The mirrors have already been deployed, as well as the 'blankets' and it seems that he is already in L2 (or almost there)
In a few weeks they will already receive first data from him.