Cigarettes are a product that has been adjusted (in a negative way), while abusing research tools and scientific knowledge to make it even stronger and more addictive than its natural state. New research shows that 25-10 percent of people will develop symptoms of cigarette addiction even after smoking one cigarette.
The main ingredient in cigarettes is tobacco - a plant that contains, among other things, a relatively high concentration of a substance called nicotine - which is the active and addictive substance in cigarettes. But it is a mistake to think that a cigarette is a 'natural' product. Since the 50s, tobacco companies, especially in the United States, initiated many scientific studies that produced many changes in the cigarette, to increase its biological and pharmacological (pharmacological) effect. In recent years - following legislative changes in the United States and lawsuits filed against the cigarette companies, the companies were forced Publish confidential documents for the research they have carried out over the years on the subject of smoking. The companies were also forced to disclose the ingredients they add to cigarettes.
From browsing the company website Philip Morris USA, the manufacturer of Marlboro cigarettes, L&M, Parliament, Next, etc., you can see the following list of ingredients, the ingredients of which are added to the tobacco mixture in the Marlboro cigarette (the list of ingredients also represents the other cigarettes):
The list in Hebrew:
- tobacco
- water
- A mixture of sugars
- propylene glycol
- glycerine
- Licorice extract
- Di-ammonium phosphate
- Ammonium hydroxide
- Cocoa and cocoa products
- Carob and carob extract
- Natural and artificial fragrances

It should be noted that even in the cigarettes of the rival cigarette company RJ Reynolds, which produces, among others, Winston, Camel, Pal-Mal and Lucky Strike cigarettes, you see exactly the same components. Here are the ingredients of Camel Blue cigarettes:
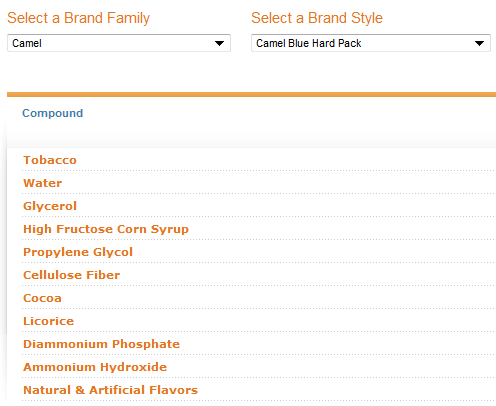
The claim of the cigarette companies is that the ingredients are intended to improve the taste of the cigarette, but if you go through the list of ingredients you can see that many of the added ingredients (the ones we wrote in bold) act on the human body or on the nicotine itself in a way that strengthens the effect of the nicotine as will be explained in detail later. Is this a case? Judge for yourself:
A mixture of sugars - in addition to changing the taste, which helps mask the bitterness of nicotine, when sugars heat up and burn, they emit a substance called acetaldehyde, and cigarette smoke is really rich in acetaldehyde. Studies show that when acetaldehyde is absorbed together with nicotine and reaches the brain, there is a strengthening effect (synergy) - that is, one of the substances increases the activity of another substance, so that their combination is stronger than the sum of the effects of each substance separately:
Controlled studies conducted on rats (which are used as a model animal for tobacco addiction) show that a mixture of nicotine and a small amount of acetaldehyde causes a much stronger addiction than nicotine alone, and caused the rats to consume much more nicotine compared to 'pure' nicotine. In addition, the strongest effect is found in young animals. It is likely that the mechanism of action is based on inhibiting an enzyme called monoamine oxidase (MAO) which is active in nerve cells in the brain and is responsible for breaking down neurotransmitters - and therefore causes a longer stay of pleasure-inducing substances that are released in the brain under the influence of nicotine - for example dopamine and serotonin.
Source 1 Acetaldehyde enhances acquisition of nicotine self-administration in adolescent rats,
Source 2 European Commission, Health and Consumer protection – Tobacco Additives
Source 3 Abuse potential of non-nicotine tobacco smoke components: acetaldehyde, nornicotine, cotinine, and anabasine
Licorice extract - the licorice (liquorice in Hebrew) is a spice plant with a characteristic taste - which also affects the taste of the cigarette. But one of the main components of the plant is a substance called Glycyrrhizin - which is also a bronchodilator, i.e. a substance that expands the air tubes in the lungs, thus allowing more smoke to penetrate the lungs, and to a larger area, therefore increasing the effect of smoking.
The importance of licorice and the extent of its use in modern cigarettes is evidenced by the fact that it occupies between 1 and 4 percent of the weight of the cigarette, and that 90 percent of licorice in the world is not used for food but is consumed in the cigarette industry.
Source 1 Cigarettes: Some things you probably didn't know were in there (including licorice)
Seeing Through the Smoke — The Secrets in a Cigarette Source 2
Source 3 Toxicologic evaluation of licorice extract as a cigarette ingredient
Di-ammonium phosphate and ammonium hydroxide - these are two chemicals that release ammonia gas (NH3(g)). Ammonium phosphate ((NH4)2HPO4(s)) releases ammonia when heated, according to the following chemical reaction:
(NH4)2HPO4(s) → NH3(g) + NH4H2PO4(s)
Ammonium hydroxide is simply a solution of ammonia gas in water. And what is the benefit of releasing ammonia into the smoke mixture? Well - ammonia, being chemically a base, helps free other bases to a pure state.
An explanation is needed here: nicotine, like other natural substances (eg cocaine) is chemically basic. Bases tend to react with acids and form salts. Indeed, inside the dry tobacco, the nicotine is found as a compound with acids as "nicotinic salt". When nicotine is in salt form, it is more difficult for it to be absorbed by the body. The ammonia sets it free by replacing it with the salt compound, therefore allowing it to be absorbed and act more powerfully and more quickly.
The faster a drug acts on the brain, the stronger the dependence that develops on it. This is exactly the difference between the drug cocaine and crack - the drug is the same drug, but baking soda (base) is added to the latter which makes it much stronger. On the same weight, it can be said that the addition of ammonia to tobacco turns the nicotine into "crack nicotine" which is much stronger than regular nicotine.
Cocoa and cocoa products - here, too, it is supposedly an innocent substance intended to improve the taste, but cocoa also contains a pharmacological substance that affects the lungs: Theobromine (Theobromine).
Theobromine has a dual effect on the human body - it dilates the bronchi, just like the substance found in licorice (in fact, this is its medicinal use), and it is also a powerful antitussive agent (a 2004 study found that it is more powerful than codeine - the active substance found in cough syrups ), in that it suppresses the activity of the vagus nerve (the stray nerve). That is, adding cocoa to smoke suppresses the body's natural reaction to smoke - coughing - and thus allows the smoker to hold the smoke longer in the lungs without feeling irritation or the need to cough. Indirectly, this also increases the action of nicotine on the body, in addition to expanding the airways in the lungs, because that way the smoke can stay in the lungs longer, and thus increases the absorption of nicotine from the lungs into the blood.
Source Theobromine inhibits sensory nerve activation and cough.
Natural and artificial flavorings - The tobacco companies do not publish individually on their websites substances whose concentration in the cigarette is lower than 0.1 percent, but group together all the other substances they add in this category. The category includes a long list of chemicals, which, as we have seen, it is reasonable to assume that the activity of some of them is not innocent and is not limited only to changing the taste or smell, but also has a pharmacological activity on the body: A book recently published in the United States, Based on Hundreds of documents that the US tobacco companies were forced to publish, found that in addition to all of the above, a substance called 'balloon acid' is also added to the tobacco mixture in cigarettes - which increases the adhesion of nicotine to receptors in the brain.
If so, the tobacco mixture in cigarettes contains many substances in addition to the tobacco, which act on many aspects to strengthen the addictive biological effects of the cigarette. They enhance the activity of nicotine, increase its concentration, shorten the time it becomes available, expand the airways and suppress the cough reflex. These substances were added to the mixture after long processes of research and scientific development initiated by the cigarette companies over the years.
In other words, cigarettes are a product that has been adjusted (in a negative way), abusing research tools and scientific knowledge to make it even more powerful and addictive than its natural state. New research shows that 25-10 percent of people will develop symptoms of cigarette addiction Even after smoking one cigarette.
Considering the many health dangers of smoking, and the very high chance of becoming addicted to it, which apparently the tobacco companies worked to increase even more because of all the reasons we mentioned, it is highly not recommended to try smoking even once.
Dr. Avi Saig
Davidson Institute for Science Education
Weitzman Institution of Science
The article was first published on the Dodison Online website

3 תגובות
Excellent article, as a quitter from smoking, the article allows me more tools to illustrate to quitters the lack of innocence of the cigarette companies and the importance of taking responsibility, taking the reins and stopping being suckers....
Very interesting, thank you very much!