The mysterious X-37B space vehicle, a small and unmanned version of the space shuttles, was launched into space almost two years ago for its fourth mission around the Earth, on a secret mission of the US Air Force. Yesterday the vehicle reached its 675th day in space, thereby breaking the record for staying in space for its previous mission.
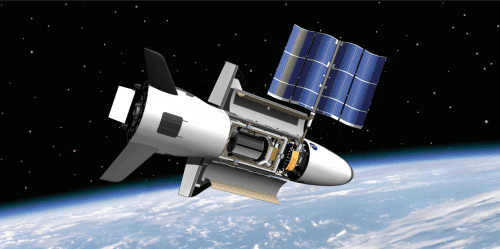
The US Air Force's secret vehicle, the X-37B, was launched on its fourth mission on May 20, 2015, and has continued to orbit the Earth in low-Earth orbit ever since. Yesterday (March 25) he broke his previous stay record In space, 674 days, which he recorded in his previous mission that ended in 2014. Its declared nominal duration of stay in space is 270 days, and these missions proved that the vehicle is capable of much more than that.
The vehicle's missions and goals are shrouded in heavy mystery. The US Air Force has not released what payload it carries or what specific missions it performs, andProvided A general description of its goals: "The X-37B Orbital Test Vehicle is an experimental project to demonstrate the technologies of an unmanned, multi-purpose and reliable space platform for the US Air Force. The main goal of the vehicle is twofold: multipurpose space vehicle technology for the American future in space, and the activation of experiments that can be returned and tested on Earth." According to the US Air Force, the plane is designed to test advanced technologies and materials, such as autonomous navigation and control systems. Although the Corps did not officially state this, Some appreciate it Because the vehicle is also designed to test satellite spying technologies.
X-37B is a multipurpose space vehicle, which is very similar to the space shuttles and is actually a small, unmanned version of them: it is launched vertically, and when its mission is finished, it returns to earth and uses its wings to land like a glider. Similar to the space shuttles, its bottom is covered with ceramic tiles, which protect it during penetration into the atmosphere. Its length is 8.8 meters, its height is 2.9 meters and its wingspan is 4.6 meters. The length of the space shuttles, for comparison, was 37 meters, and their wingspan was 24 meters.

Unlike the space shuttles, the X-37B has deployable solar panels, which greatly extend its possible stay in space. The space shuttles relied on hydrogen fuel cells for power generation, and were therefore limited in the duration of their missions. The longest space shuttle mission was STS-80 of the shuttle Columbia in 1996, which lasted only 17 days.
The development of the X-37 vehicle began by NASA in 1999, and in 2004 the development was transferred to the agency DARPA of the US Department of Defense. Two years later, the US Air Force announced that it would develop the X-37B space vehicle based on these plans, and Boeing built for the force Two identical versions of the vehicle. Together, the two identical vehicles have been launched into space four times so far. In 2010, the first space flight of the vehicle was successfully carried out, which lasted 224 days. Since then, in each new mission he has re-broken his previous stay record. Its previous mission lasted 674 days, from December 11, 2012 to October 17, 2014.
The vehicle's current mission, as mentioned, began on May 20, 2015, with its launch aboard Atlas 5 from the Cape Canaveral Spaceport in Florida. Similar to the great secrecy surrounding its missions and payload, the Air Force refused to publicize its intentions regarding its future landing date. "The landing date will be determined based on the completion of the orbital demonstrations of the program and the objectives of the mission," a spokeswoman for the US Air Force said. to space.com.
See more on the subject on the science website:
