Hayadan > Molecular biology
Molecular biology
- The Voice of Science website - the Israel National Science Foundation
- July 27, 2023
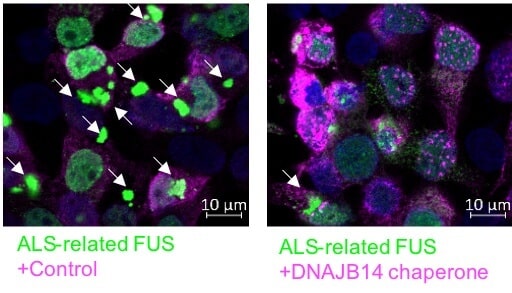
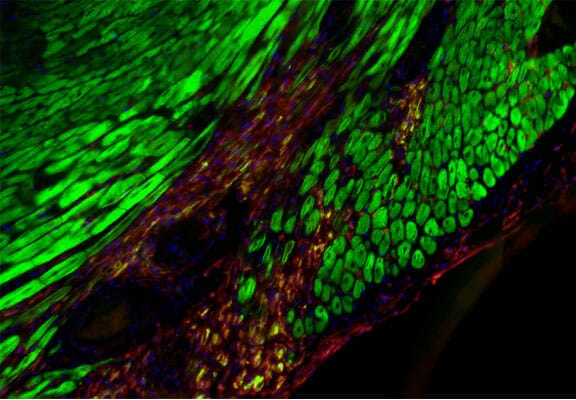
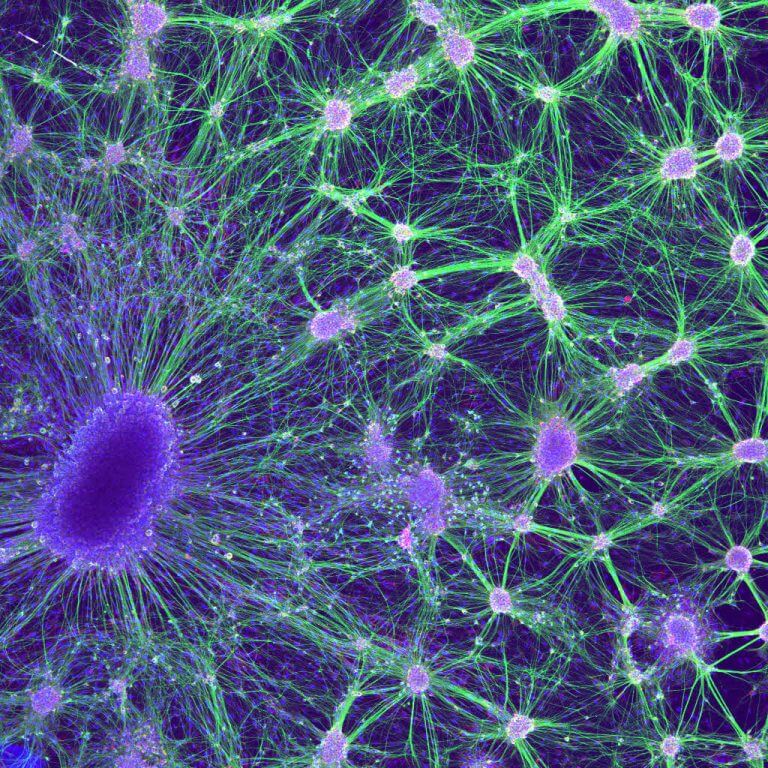
The proteins and mechanisms required to fight the protein accumulations that lead to neurodegenerative diseases have been identified
- Tel Aviv University
- June 28, 2023
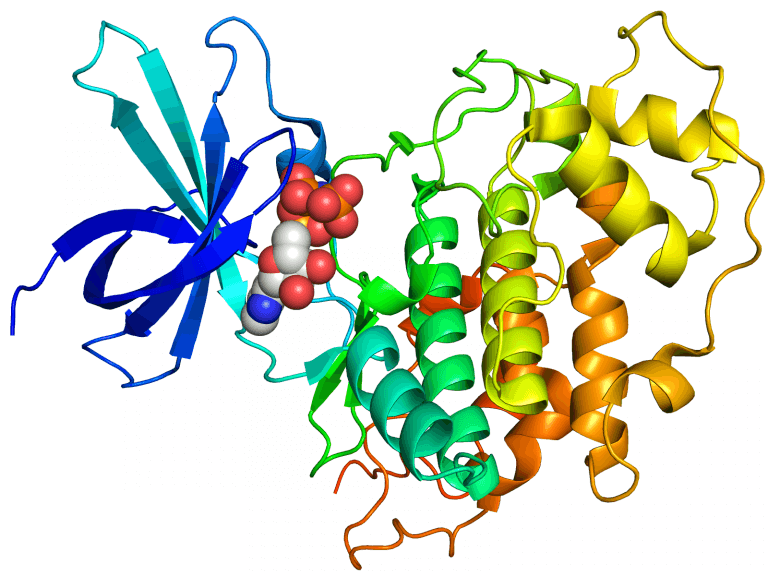
According to the researchers, it is a hormone, a small signal molecule, which controls the growth of plants. The decoding may help a lot in expanding agricultural crops and dealing with the global food crisis
- Avi Blizovsky
- February 18, 2021
- 2 תגובות
In the reasons for the award committee, it was stated that Prof. Ashhar, Dr. Steven Rosenberg and Dr. Carl John are dedicated to discovering molecular mechanisms of disease development, which can be used to develop new diagnostic, therapeutic and preventive tools for the benefit of humanity
- Weizmann Institute
- December 13, 2019
- 2 תגובות
- The Technion
- April 17, 2019
- No comments
- Weizmann Institute
- November 23, 2017
- No comments
- Weizmann Institute
- April 6, 2017
- One response
- Weizmann Institute
- March 22, 2017
- No comments
- Weizmann Institute
- February 23, 2017
- No comments
- Avi Blizovsky
- May 24, 2016
- No comments