It's no secret that Google is the most advanced and sophisticated search engine in the world thanks to its unique algorithm. To understand what makes the new part of its algorithm, Rankbrain, unique, you first need to learn a little about Google's history and how it was different from all the search engines before it:
In 1998, when Google was just entering the search engine arena, most engines were not very smart and were based on simple matches of keywords that the user typed in the search box to the text found within the pages that they were scanning. It was very easy for websites to trick search engines by combining the words they were looking for, even if the text on the page was of very low quality or completely irrelevant to what the user was looking for. Therefore, SEO (SEO) was very easy at the time - which does not exist today.
Google, on the other hand, integrated a new element called Pagerank into its algorithm. Pagerank gave credit to sites based on the number of other sites that linked to them, assuming that a site that receives more votes online will also be a higher quality site. In order for Google to start working, the two founders of Google (Sergi Brin and Larry Page) chose a number of "core" sites that they thought were of the highest quality.
Although at this stage (the end of the 20th century and the beginning of the 21st century) Google's engine was indeed the most advanced on the market and took the web by storm, sometimes its reliance on links was at its worst. why? Those who wanted to manipulate the search results simply had to plant links on various sites to trick Google. Besides that, even manipulating the words in the text still worked when done in a certain way.
Google, of course, did not remain obliged, and in order to fight these manipulations continued to refine and change its algorithm on a regular basis in addition to the original Pagerank. For example, some of the innovations in the algorithm such as the "panda update" are designed to handle very poor quality texts (actually spam) and the "penguin update" is designed to combat those who have made extreme use of manipulative links.
Another limitation of Google was new queries that were not asked before. Usually, when Google is asked about a search that has already been typed in the past, it can at least know what the related searches are and whether users have also typed similar searches until they found the answer they were looking for. On the other hand, a new query can be a problem because Google has much less information to rely on. That's why Google had to find a way to handle even unfamiliar queries that made up between 20% and 25% of all queries.
How did Pagerank solve the new query problem?
Google has started working on an auxiliary engine that will deal with machine learning of artificial intelligence. This is an engine that can learn by itself about the connections between words or concepts and therefore provide the correct answers even if all the words that the user searches for do not necessarily appear in the text.
For example, Google does not necessarily know that Berlin is the capital city of Germany, but it does know that they have a connection similar to the connection between Jerusalem and Israel. These connections can also be referred to as "concepts" or "vectors".
This element was nicknamed Rankbrain for many days and was first introduced at the end of 2015. Today, Google has added a few extra wheels to it such as BERT, but the principle itself remains the same.
To explain the ear, two examples are given, one relatively simple and one complex:
1. If we click in English "the gray game console produced by Sony" we will get the answer Sony Playstation (for those who did not grow up in the 90's we will remind you that the original model was indeed gray...).
2. A more complex example (also in English): if we are asked "what is the name of the highest consumer in the food chain" we will get an explanation of the food chain in its biological context: Google realized that we are looking for a term from the field of biology and not something from the field of the food we eat and therefore websites that deal with this topic .
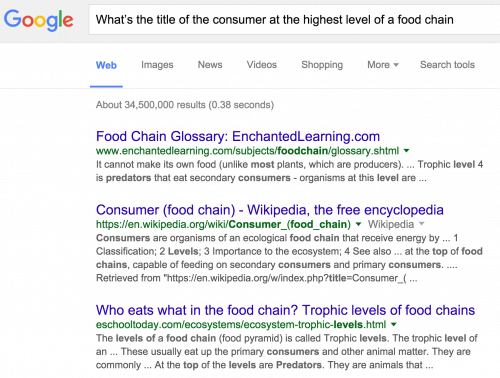
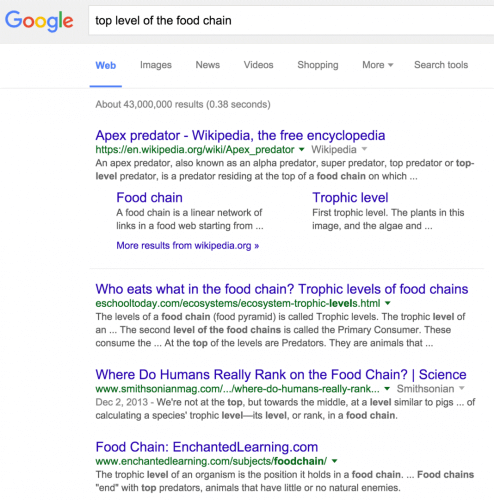
3. A very similar and even more impressive example is "Who is at the top of the food chain". Here Google displays on the first page the specific page about "top predator" from Wikipedia.
How much does Rankbrain influence Google?
Google originally stated that Rankbrain was the third factor in its thinking in how its engine ranks websites, but since there are so many parameters that affect search and they change every day, today that statement should be taken with a grain of salt.
However, people who try to follow the changes in Google's algorithm did notice that in recent years it is not enough to just write quality texts with the right keywords, but the relevance to what the user is looking for is also very important. In other words, a site that does not provide the exact answer (or as accurate as possible) to what the surfer wants to find will not appear in first place even if it is a quality site in general.
What other abilities does Rankbrain give to Google?
You must have seen sometimes that Google provides general details about a certain band, place or personality. This is possible, among other things, through Rankbrain's technology. Most of the information is accurate, but Google doesn't always know how to cross-reference sources, so mistakes still happen. In the most embarrassing cases, Google may claim that a famous person has died based on rumors or fake news on certain sites.
Another, perhaps even more important, ability is to give direct answers to the questions that the surfer asks without having to go to a certain website at all. One format of these answers presents the answer in prominent text and another format takes parts from websites and highlights them (sometimes the surfer sees answers from several websites).
The most striking answers are often absolute and uninterpretable. For example, "How many meters are there in a kilometer".
Does Rankbrain work the same in all languages?
Rankbrain has improved a lot in recent years, but since the contexts are different in every language, its helpfulness is not uniform in all languages. For example, if we take the two examples we presented earlier and type them into Google Israel in Hebrew, we will not get appropriate answers, but a list of standard websites that do not really provide the answer. In fact, it is quite difficult to find prominent examples in Hebrew except for simple answers such as capital cities of certain countries that return a block of facts about that capital city without having to enter a certain website. (A specific example is the capital city of Sudan, Khartoum).
The main reason for this is apparently the differences in the vocabulary, the relationship between them and the different grammar between Hebrew and languages from other and more popular families such as English and various European languages. John Muller, a Google executive who works with website owners, replied in an interview held with him at the end of 2019 during his visit to Israel that Google does not always manage to understand all languages in the same way even with the backing of a machine learning system like Rankbrain.
This article is promoted content in collaboration with Daniel Zarihan.
