Innovative technology in the field of minimally invasive surgery will soon change the way doctors will look inside the body cavities during surgery. The magic word: XNUMXD When the mission recruited an innovative technology that is currently used in Microsoft's video game console. The first exposure of the development coming from the Institute of Medical Technology (ZiMT) in Germany - in the week of Biomed Israel which opens next week
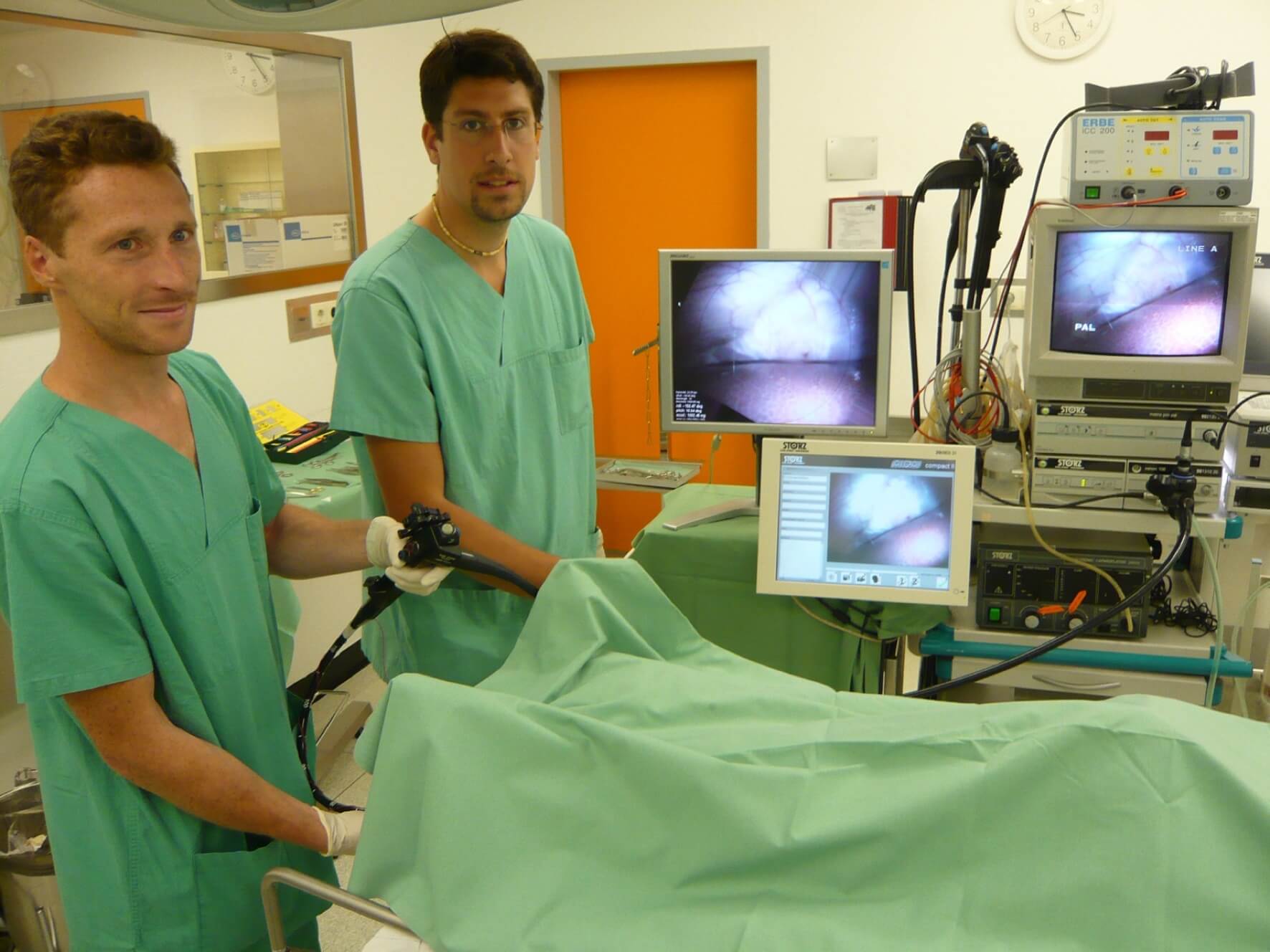
Minimally invasive surgery is the most common operation in the world of surgery. This is a surgical technique that is performed by making a minimal cut in the exposed skin and penetrating the surgical space using a conductor with a camera on it, or a very small diameter surgical tool. Minimally invasive surgeries are a very important and most common surgical option nowadays. Such operations are performed in a wide variety of indications due to the significant advantages inherent in this type of operation, among which is the shorter recovery time.
Surgeries of this type require motor skills and hand-eye coordination at the highest level. Not infrequently the surgeons are faced with complex technical difficulties. A very important aspect, derived from the advantage of minimally invasive surgery, is the absolute dependence on the camera, which is the doctor's "eyes" during the operation.
At the Biomed Israel 2013 conference and exhibition, the German delegation is expected to present a number of innovative and leading technologies in the field of minimally invasive surgery. The delegation, which includes representatives of four "clusters" of life sciences and medical devices from Germany, will arrive in Israel to demonstrate the latest innovations and developments of German research, development and production bodies, in the fields of medical technology and bioengineering, and the representatives, which include researchers from diverse fields of research and development, will take part in the lectures planned for three days The conference will even present in a booth that will also serve as a meeting point with their colleagues from Israel.
The delegation's visit is organized as part of an international campaign under the title "Germany - Partner for Medical Technology", which is the responsibility of the Government Ministry of Education and Research in Germany, which aims to present the innovations of medical technology and promote international cooperation in research and development between Germany and potential partners, such as Israel .
The Institute of Medical Technology (ZiMT) at the Friedrich Alexander University of Erlangen (FAU) in Germany is a center and responsible for many studies in the field of biomedical engineering. Dr. Kurt Höller, director general of the institute, says that he sees importance in international cooperation in the field. According to Dr. Holler, the German delegation is coming to Israel to present their innovative work and to create cooperation with companies and organizations from Israel.
One of the technologies that will be presented is a new 100D photography technology - Time To Flight - used in advanced video games (for example on the XBox One console), which can provide up to XNUMX images per second, which will be integrated into a variety of minimally invasive surgeries, and will allow surgeons to examine the progress of the surgery from several angles (and not just directly forward) and differentiate clearly between different tissues.
The camera that is being developed these days as part of the German R&D cluster 3-D Imaging in Medicine is currently used mainly in automotive applications, for example in active safety systems to protect pedestrians and distance keeping systems, in commercial measurement applications and machine vision and especially in advanced video game consoles.
Minimally invasive surgery is a very common operation in the field of surgery. This is a surgical technique that is performed by making a minimal incision in the exposed skin and penetrating the surgical space using a conductor with a camera or a very small diameter surgical tool on it. Minimally invasive surgeries are a very important and most common surgical option nowadays. Such surgeries are performed in a very wide variety of indications due to the significant advantages inherent in this type of surgery, including the shorter recovery time. Surgeries of this type require motor skills and hand-eye coordination at the highest level. Not infrequently the surgeons are faced with complex technical difficulties. A very important aspect, derived from the advantage of minimally invasive surgery, is the absolute dependence on the camera, which is the doctor's "eyes" during the operation.
Natural Orifice Translumenal Endoscopic Surgery (NOTES)
In recent years, a new surgical technique has developed in the field of minimally invasive surgery. This is a technique called Natural Orifice Translumenal Endoscopic Surgery (NOTES). In this emerging technique, the surgeon accesses the abdominal cavity using an existing anatomical cavity (for example, through the digestive tract or through the genital tract in women). Dr. Holler says that "as of today, minimally invasive surgery is performed by surgeons who use a rigid guide (endoscope). Gastrointestinal doctors, on the other hand, perform various procedures inside the digestive system cavity (colonoscopy, gastroscopy) using a flexible endoscope. The new approach, called NOTES, requires the use of a flexible conductor inside the abdominal cavity. But the surgeons are used to using a rigid guide and therefore to a straight relationship between the tip of the endoscope and the internal cavity of the patient without change during the operation. The change between the physical orientation and the display leads to an impairment of the horizontal orientation ability and thus to an impairment of the surgical ability. We developed a sensor that is placed in the remote part of the endoscope and manages to provide a horizontally balanced image."
The Institute of Medical Technology (ZiMT) at the Friedrich-Alexander University will present, as part of Biomed Week 2013, the first prototype of its kind in the world of an endoscope based on a Time To Flight camera. A XNUMXD camera is more advanced than those available today when performing minimally invasive surgery. The camera is mounted on the end of the endoscope and gives the surgeon an ability to see that is not available today. Using the new camera, the doctor is able to observe from several angles (and not just straight ahead), with the new ability making it easier for the surgeon to differentiate between different tissues and carry out his task. "When using a flexible guide (flexible endoscope) there is difficulty in horizontal orientation. We developed a sensor that is placed in the remote part of the endoscope and manages to provide a horizontally balanced image." According to Dr. Holler, the technology is not yet in medical use, "but we performed extensive studies on animals in which we tested the technology before future clinical application."
Dr. Holler points out that a combination of these different technologies will lead to a significant improvement in the capabilities of the surgeon when performing both complex and simple minimally invasive operations and surgeries. According to Dr. Holler, he sees the importance of international cooperation in the field and that the German delegation is coming to Israel in order to present their innovative work and create cooperation with companies and organizations from Israel.
Germany is a leading global factor in the field of 3D imaging (14.6-D Imaging in Medicine). Many resources are invested in the field with an understanding of its importance in the medicine of the future. Many studies in the field of XNUMXD imaging conducted in Germany are published in important scientific journals around the world. Germany is also a significant factor in the medical technology market, and is responsible for XNUMX% of the global market, second only to the United States.

2 תגובות
A new technology that I think will fit nicely with this field is going to be released soon:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fEds92tY9QQ
Not new at all... The Israeli company VisionSense (formerly Envision) developed something similar already 10 years ago.
Visionsense.com