Hayadan > Computing and technology > exact sciences
exact sciences
- The Voice of Science website - the Israel National Science Foundation
- April 15, 2024
Researchers have built a model according to which the mass of the Higgs boson, which helps produce the mass of elementary particles, changed in the early universe, and is therefore much smaller than the standard model of particle physics describes
- Avi Blizovsky
- April 11, 2024
- No comments
Last year, Prof. Wigderzon, who also received the Abel Award, received an honorary doctorate from the Technion
- Avi Blizovsky
- March 16, 2024
- No comments
The facility, named JUNO, consists of a huge tank that surrounds an array of detectors. The container contains a substance that causes a scintillation which is recorded in the detectors and thus allows to identify a neutrino event, its type and mass, since the neutrino particles change into different types upon their formation
- Avi Blizovsky
- March 16, 2024
- No comments
The purpose of the mission is to test the materials' resistance to radiation and the potential for the compatibility of printed parts in future space missions
- Avi Blizovsky
- March 6, 2024
- 12 תגובות
Their research, published in Nature Communications, shows that in normal listening contexts, we do not necessarily prefer chords that are in these exact mathematical relationships but prefer small deviations from them
- Tel Aviv University
- March 5, 2024
The new system makes it possible to observe the phenomena that occur inside special "topological" materials by photographing the movement of pendulums using a normal camera
- The Hebrew University
- March 2, 2024
- 3 תגובות
New research from the Larkach Institute of Physics reveals a significant advance in chaos theory, by confirming in detail the flux-based statistical theory that predicts chaotic outcomes in non-hierarchical Newtonian three-body systems. This breakthrough has practical implications for fields such as celestial mechanics, astrophysics and particle dynamics.
- Tel Aviv University
- February 27, 2024
Researchers have discovered that the original way to speed up chemical processes is to reboot
- Noam Chai
- February 24, 2024
- 3 תגובות
The non-Abelian anions are quasi-particles with fascinating statistical and topological properties. Until recently, these particles were only theoretical, but now a research group from Harvard University has created them for the first time in the laboratory. The discovery may encourage companies in the field of quantum computing to use non-Abelian anions to create durable qubits.
- The Technion
- February 1, 2024
- No comments
Technion researchers answer this question and pave new paths for applications in communication, imaging and quantum computing
- Dr. Moshe Nahamani
- January 31, 2024
- One response
New structures of carbon rings raise doubts about the current accepted definition of the concept of aromaticity
- The Technion
- January 3, 2024
- No comments
The development is a spin laser from a single atomic layer - a development by Prof. Erez Hasman from the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Prof. Elad Koren from the Faculty of Materials Science and Engineering.
- Avi Blizovsky
- December 10, 2023
- 26 תגובות
Two articles by University College London researchers have been published in Nature Communications and Physics Magazine in which the researchers offer an elegant way to reconcile the contradiction between the two theories, each of which affects on a different scale
- Dr. Moshe Nahamani
- December 2, 2023
- No comments
Researchers have used a variety of methods in order to reveal the different polymorphs that can be prepared from a common crystalline material and the paths of conversion of one configuration to another depending on the temperature and the method of preparation
- Avi Blizovsky
- November 27, 2023
- 7 תגובות
While Einstein's theory of relativity shows the relationship between time and speed. Theoretical ideas such as wormholes offer possible methods, but practical challenges and paradoxes, such as the "grandfather paradox", complicate the feasibility of time travel in practice
- Avi Blizovsky
- November 26, 2023
- No comments
Prof. Ashkenazi from the chemistry department at Ben-Gurion University is engaged in a new field - chemistry of complex systems. The grant was given to him and an international research group of which he is a member
- Avi Blizovsky
- November 24, 2023
- 3 תגובות
"The observations will be made possible through the control we have developed over the wave nature of free electrons," explains Prof. Kaminer
- Dr. Moshe Nahamani
- October 21, 2023
- One response
Metal-organic frameworks (MOF) can safely trap fluorine compounds within their pores at room temperature and release them when needed
- Dr. Moshe Nahamani
- October 4, 2023
- 2 תגובות
Today, quantum dots, which are tiny nanoparticles whose size determines their properties, illuminate computer monitors and TV screens when these are based on QLED technology. In the field of medicine, quantum dots are currently used to map biological tissues
- Dr. Moshe Nahamani
- October 3, 2023
- One response
The 2023 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to three researchers: Pierre Agostini, Ferenc Krausz and Anne L'Huillier for "the development of their methods that produce extremely short attosecond pulses of light For the study of the dynamics of electrons inside the material"
- Ben-Gurion University
- September 30, 2023
- 3 תגובות
"This is the first measurement ever made of the free fall of antimatter (antihydrogen) atoms that directly shows that they really fall down," explained Prof. Eli Sharid from the Physics Department at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, the member of the ALPHA collaboration group
- The Hebrew University
- September 29, 2023
- 2 תגובות
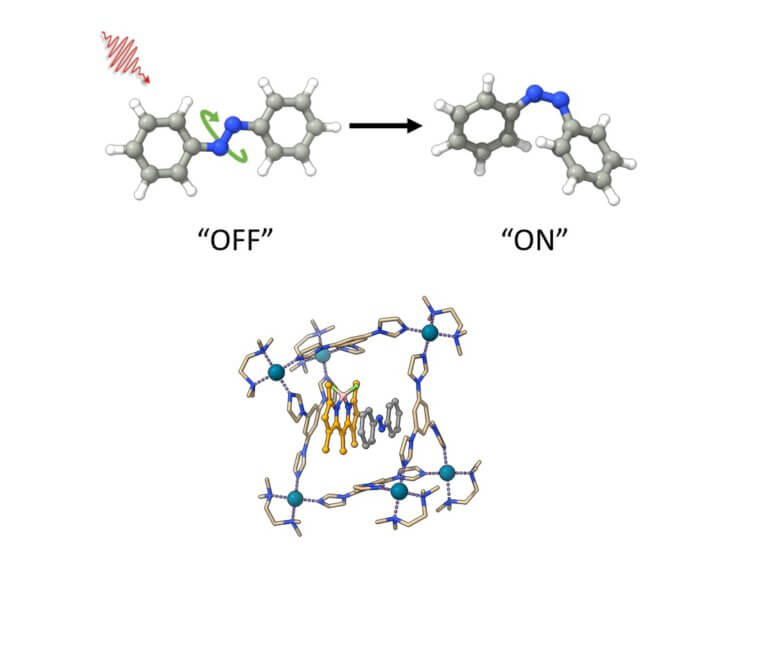
Azobenzenes are versatile compounds with many potential uses, such as advancing technology through the production of tiny machines, as well as creating light-activated drugs. These molecules can be found in two different forms called "E" and "Z" which can be exchanged between them through irradiation. However, under irradiation conditions both forms are in equilibrium, which prevents optimal utilization for different applications
- The Hebrew University
- August 8, 2023
- 2 תגובות
The quick color switch allows an immediate change of the emitted color. The discovery has implications for diverse technologies in which fast color adjustment is required, such as display screens, quantum communication and miniaturized light sources
- The Voice of Science website - the Israel National Science Foundation
- July 3, 2023
Quantum effects in X-rays make it possible to improve the resolution of the scan and protect the health of subjects and doctors
- Bar-Ilan University
- July 2, 2023
Meet Dr. Ohad Klein, PhD graduate in the Department of Mathematics at the Faculty of Exact Sciences, postdoctoral student at the Hebrew University and working at a startup company as an algorithmist












![Researchers have used a variety of methods in order to reveal the different polymorphs that can be prepared from a common crystalline material and the paths of conversion from one configuration to another depending on the temperature and the method of preparation. [Source: Thomas Rades/University of Copenhagen]](https://www.hayadan.org.il/images/content3/2023/12/530514_d3sc02802jf1_hires_357208-768x346.jpg)