Hayadan > Space and astronomy > Astrophysics > White dwarfs
White dwarfs
- Avi Blizovsky
- March 24, 2024
- No comments
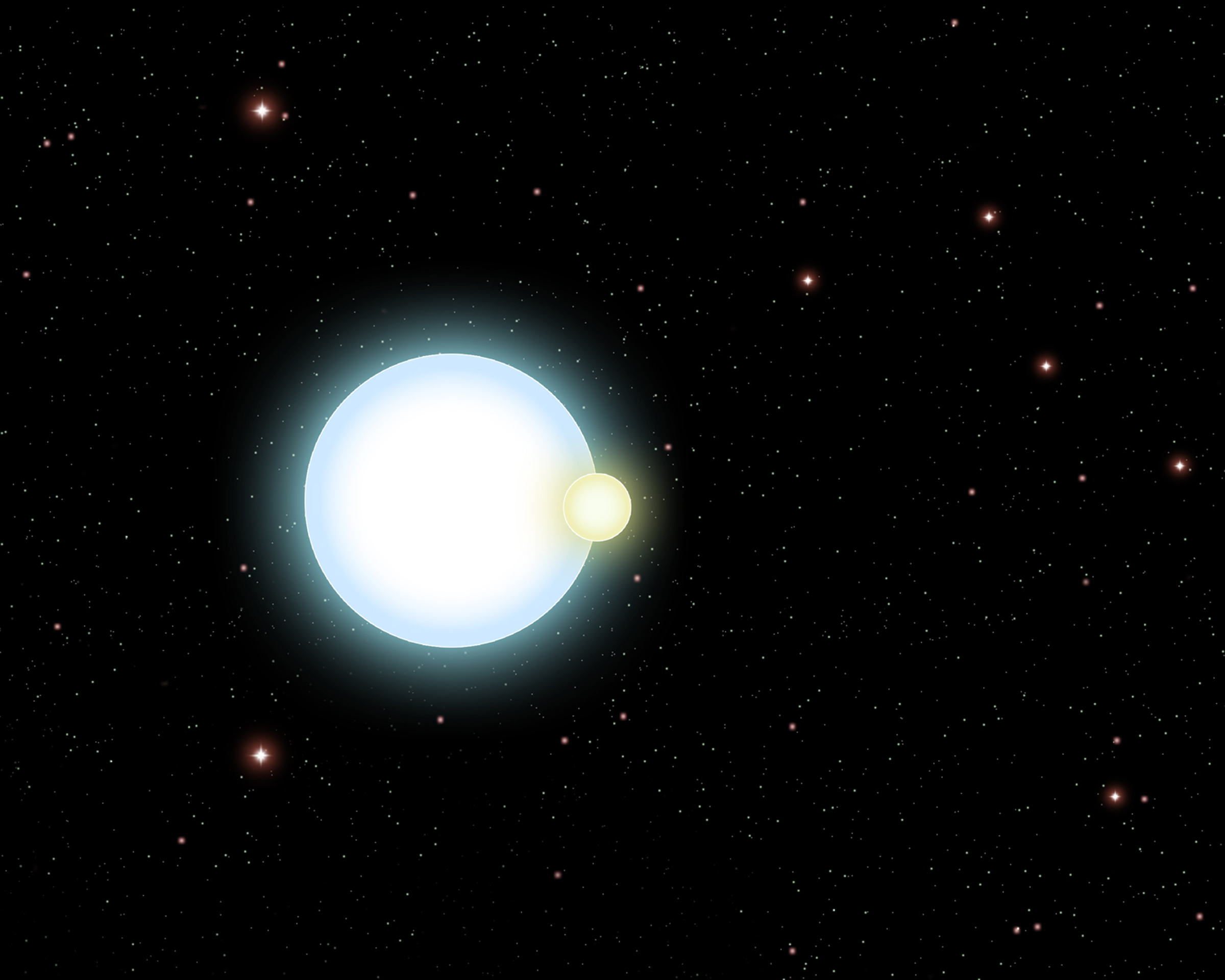
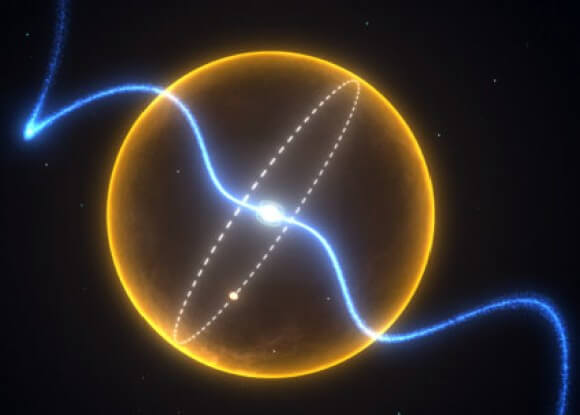
According to the new paper, in some white dwarfs, the dense plasma in the interior doesn't simply freeze from the inside out. Instead, the solid crystals that form upon freezing are less dense than the liquid, and therefore want to float, then push the liquid inside
- Avi Blizovsky
- July 5, 2022
- No comments
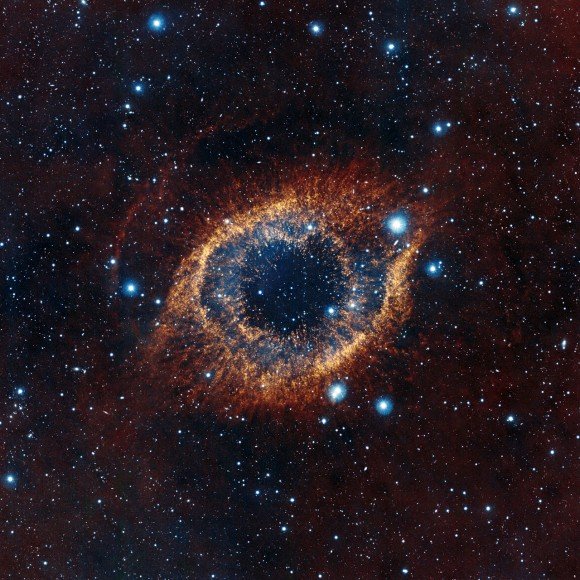
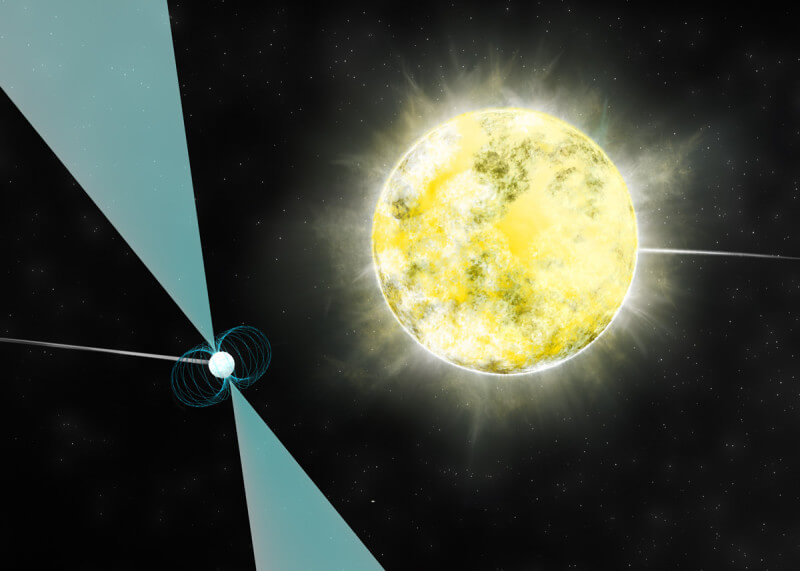
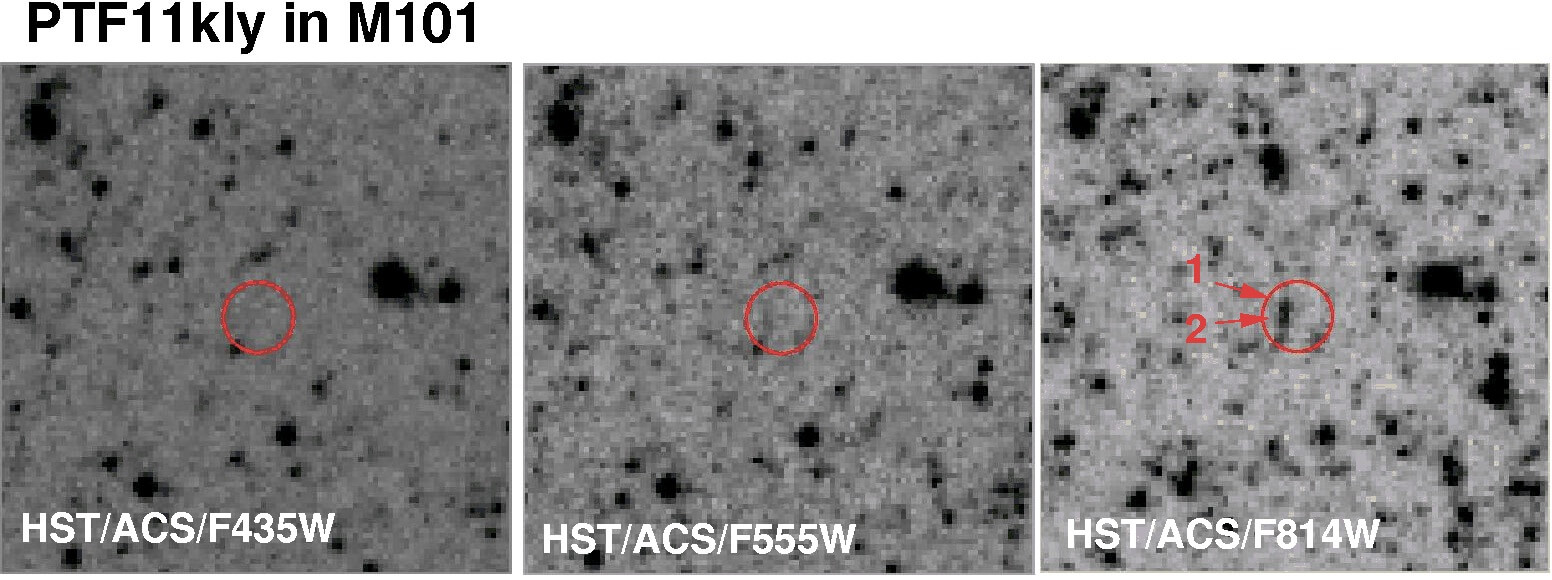
A white dwarf provides insights into the systemic chaos that occurs when a star dies
- Avi Blizovsky
- May 20, 2018
- 2 תגובות
- Uri Brock
- November 18, 2017
- 5 תגובות
- Avi Blizovsky
- June 25, 2014
- 26 תגובות
- Avi Blizovsky
- March 3, 2013
- 14 תגובות
- Universe Today
- January 20, 2012
- 4 תגובות
- Avi Blizovsky
- September 6, 2011
- 2 תגובות
- Universe Today
- August 27, 2011
- 7 תגובות
- Dr. Gali Weinstein
- November 8, 2010
- 36 תגובות
- Dr. Moshe Nahamani
- August 7, 2010
- 3 תגובות
- Avi Blizovsky
- May 23, 2010
- 2 תגובות
- Weizmann Institute
- March 9, 2010
- 2 תגובות
- Yael Petar
- January 22, 2010
- 8 תגובות
- Universe Today
- December 29, 2009
- 3 תגובות
- Avi Blizovsky
- February 27, 2009
- 19 תגובות
- Universe Today
- January 17, 2009
- 12 תגובות
- Avi Blizovsky
- September 28, 2007
- 4 תגובות
- Weizmann Institute
- August 31, 2007
- One response
- Avi Blizovsky
- May 23, 2007
- One response
- Avi Blizovsky
- February 15, 2007
- 6 תגובות
- Avi Blizovsky
- February 14, 2007
- 2 תגובות
- Avi Blizovsky
- January 19, 2007
- No comments
- Avi Blizovsky
- February 17, 2004
- 3 תגובות
- The science service
- April 30, 2000
- No comments