The laying tube can penetrate up to a depth of about 20 mm into the tree, and its diameter is about 0.2-0.3 mm, which allows the eggs to pass through it. What is special about the drilling mechanism of the laying tube is the structure, which allows the insertion of the eggs into the tree without the tube rotating
By: Rinat Barko-philosopher
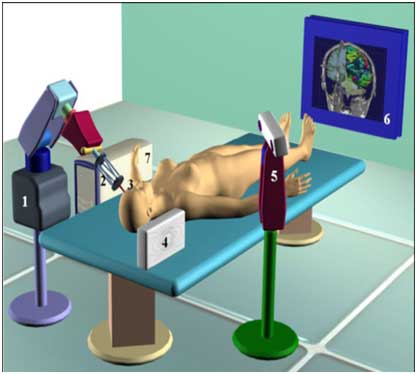
Some of the procedures that are common today in modern medicine involve the insertion of needles and catheters, to perform various operations such as taking a biopsy, or to perform minimally invasive surgeries. Such invasive procedures can cause harm. In surgical intervention, the trend today is to be as minimally invasive as possible, in order to minimize damage.
Nature is often a good inspiration as a response to engineering challenges, as is the case when it comes to a flexible needle that is convenient to insert, such as the wasp's dropping tube. The wasp has an organ capable of penetrating various types of tissue, including wood (where they lay their eggs). The laying tube can penetrate up to a depth of about 20 mm into the tree, and its diameter is about 0.2-0.3 mm, which allows the eggs to pass through it. What is special about the drilling mechanism of the laying tube is the structure, which allows the insertion of the eggs into the tree without the tube rotating.
The wasp's spawning tube is made of two parts that are integrated into each other, like a zip-lock bag, and slide against each other. One part has teeth that point backwards, grip the substrate, and resist the forces of gravity. The gravity applied to this part provides stability along the entire length of the casting tube, preventing bending. Thus the other part can be pushed with an equal and opposite force, to balance the opposite force, so that the overall balanced force tends to zero. Since there is no equal force in collecting the casting tube, there is no stability problem, and there is no theoretical limit to its length.
The biomimetic development
These days, Imperial College University in London is developing a flexible insertion needle inspired by the wasp's fallopian tube, which aims to allow access to deep brain areas with low to zero risk of causing damage, in order to perform clinical and diagnostic analysis (biopsy, samples), without using invasive devices.

One response
And here is a slightly clearer explanation (in English).
http://www.technovelgy.com/ct/Science-Fiction-News.asp?NewsNum=2103