Hayadan > Tel Aviv University Archives > Page 10
Tel Aviv University
- Tel Aviv University
- June 8, 2021
- One response
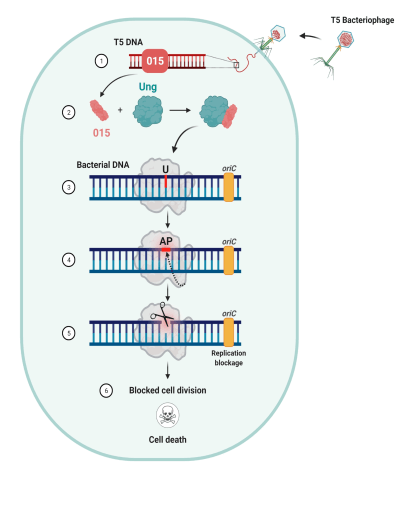
Researchers from Tel Aviv University discovered a process in which a "good" virus manages to selectively destroy the DNA of the "bad" bacteria, thus stopping the reproduction of the bacteria. The discovery may help in the development of treatments against antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which cause infectious diseases
- Tel Aviv University
- June 6, 2021
- One response
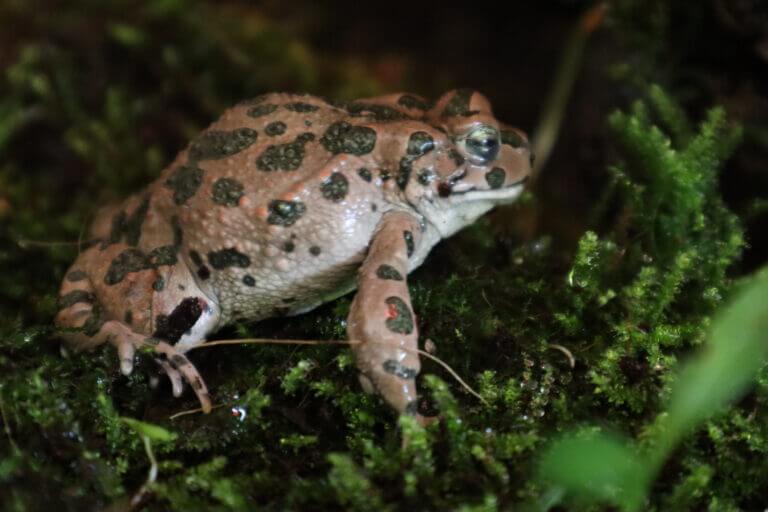
Large mammals give birth to a smaller number of offspring in each litter, so the risk of extinction increases. In amphibians, on the other hand, large females actually lay more eggs, so in amphibians it is precisely the smaller animals that are in danger of extinction
- Tel Aviv University
- June 6, 2021
- 2 תגובות
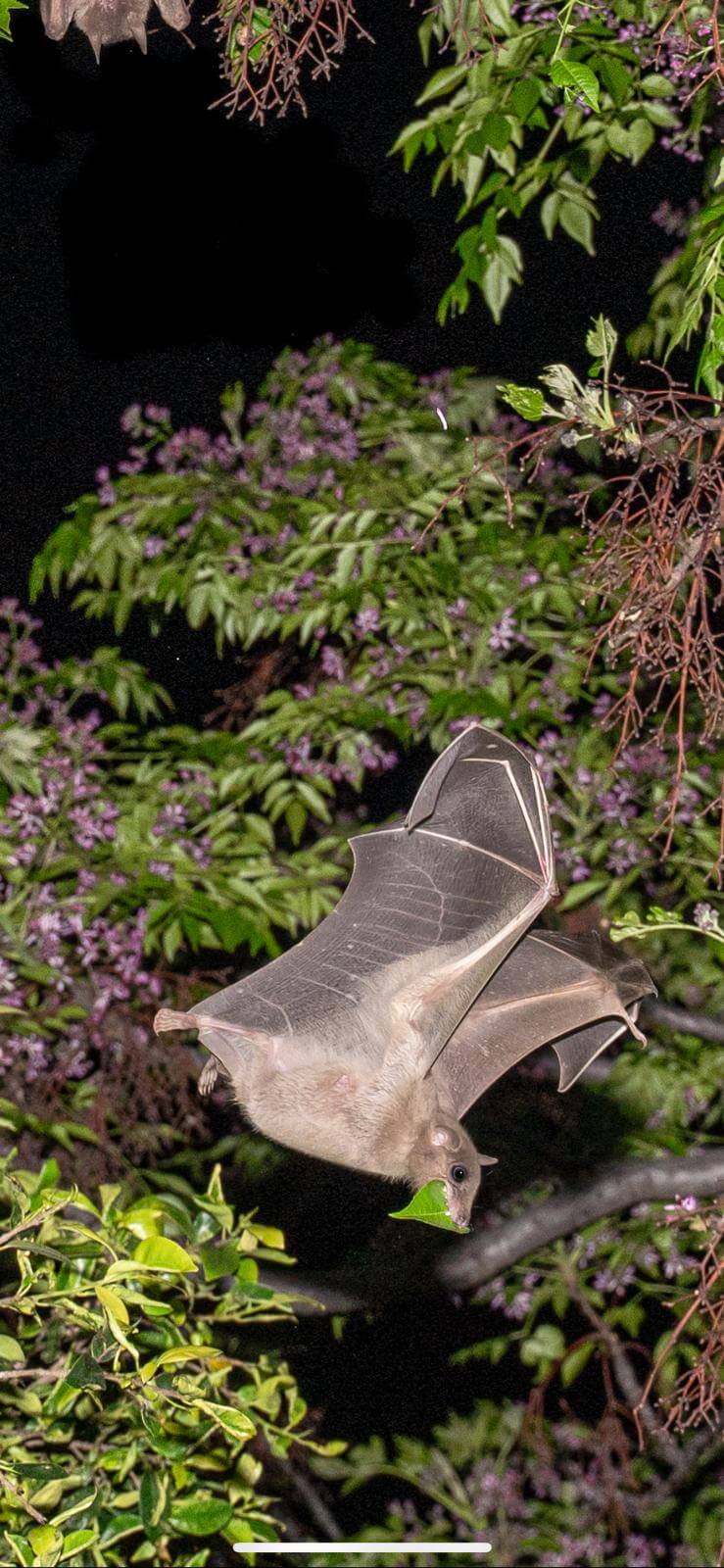
Sick bats also maintain "social distancing" and help prevent the outbreak of an epidemic
- Tel Aviv University
- May 30, 2021
- No comments
- Tel Aviv University
- May 27, 2021
- No comments
Bacterial resistance to antibiotics, intestinal bacteria
- Tel Aviv University
- May 25, 2021
- One response
- Tel Aviv University
- May 11, 2021
- 4 תגובות
Tel Aviv University launched a "smart material" into space - a folded polymer that unfolds to its original shape when heated
- Tel Aviv University
- May 10, 2021
- 2 תגובות
Researchers from Tel Aviv University have developed a product that protects the bone tissue and it will be registered as a new patent * The product is designed to prevent bone loss around orthopedic implants, dental implants and teeth
- Tel Aviv University
- May 9, 2021
- 2 תגובות
The researchers found that the activation process of stem cells in the brain responsible for the production of neurons (nerve cells) is not random but ordered and coordinated. According to them, the findings are of great importance for understanding the normal development of the brain. The findings may form the basis for the development of future treatments for brain cancer, for degenerative diseases of the brain such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, and for various brain injuries
- Tel Aviv University
- May 9, 2021
- 2 תגובות
- Tel Aviv University
- May 5, 2021
- 8 תגובות
- Tel Aviv University
- May 3, 2021
- 4 תגובות
In a first-of-its-kind project in space - Tel Aviv University will mediate between the two European Gaia spacecraft and NASA's Tess to enable easier and faster discovery of planets
- Tel Aviv University
- May 1, 2021
- No comments
In the Gulf of Eilat, an animal was discovered, which belongs to the mechanized system, can regenerate all its organs so that each piece knows exactly how to complete all the missing body systems and in a short time
- Tel Aviv University
- April 28, 2021
- No comments
The aim of the AI for Social Good program is to support research and collaborations in the fields of data science and artificial intelligence that can help and advance humanity in social issues that are on the agenda
- Tel Aviv University
- April 26, 2021
- 4 תגובות
- Tel Aviv University
- April 22, 2021
- No comments
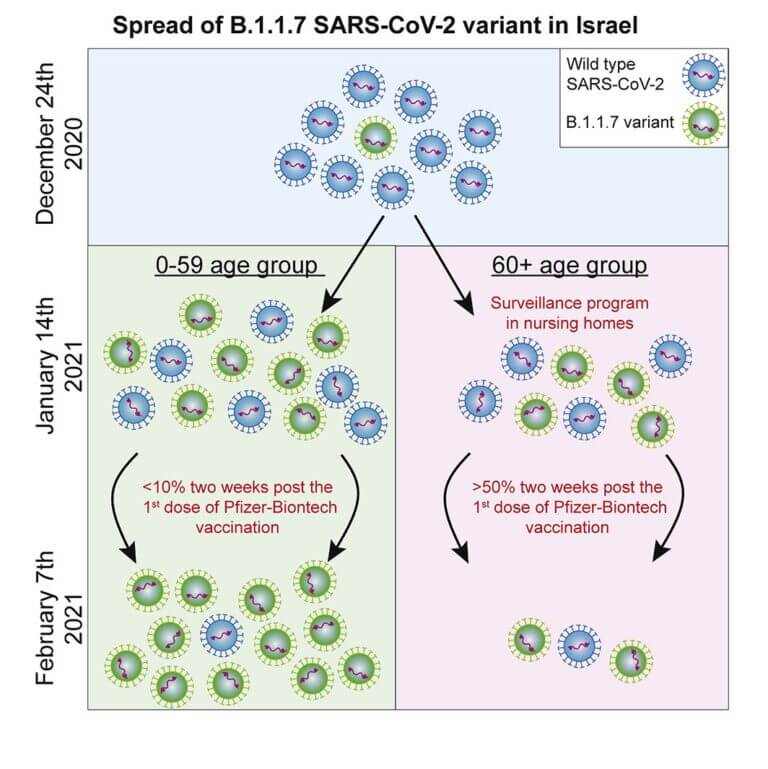
This is according to a study by Tel Aviv University that relied on data from about 300 corona tests performed on campus
- Tel Aviv University
- April 13, 2021
At the same time, the researchers make a reservation and say that at this stage it is not possible to accurately estimate the rate of decrease in the effectiveness of the vaccine. Their assessment is that the effectiveness of the vaccine does not decrease drastically, since there is no widespread spread of the South African variety and it is very rare in Israel
- Tel Aviv University
- April 12, 2021
- 2 תגובות
Researchers from Tel Aviv University have identified a failure in the brain's immune system that increases the division and spread of glioblastoma cancer cells instead of inhibiting them. Now they are looking for ways to turn the situation around
- Tel Aviv University
- April 6, 2021
This figure began to change in the Stone Age * Evidence of genetic changes and the appearance of unique stone tools for processing plants led the researchers to the conclusion that starting about 85 thousand years ago in Africa, and starting about 40 thousand years ago in Europe and Asia, there was a gradual increase in the consumption of plant food and a greater variety of the diet
- Tel Aviv University
- March 27, 2021
- 7 תגובות
The exodus from Egypt is the story around which Passover is celebrated, and it also symbolizes for us an exit from slavery to freedom, but is there any historical truth in the story?
- Tel Aviv University
- March 26, 2021
A new study by the Morris and Gabriela Goldschlager School of Dentistry states that increasing use of smartphones and social networks may lead to sleep problems, drowsiness and a feeling of fatigue during the day, and even teeth grinding and pain in the muscles of the mouth and jaw joints.
- Tel Aviv University
- March 16, 2021
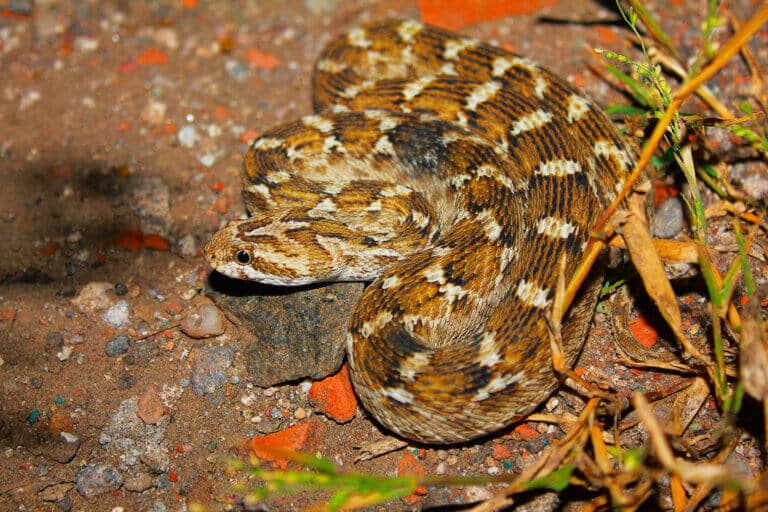
The World Health Organization strategic plan that aims to reduce by 50% the damage from snakebites by 2030. Researchers from Tel Aviv University are also members of the international group studying the field
- Tel Aviv University
- February 27, 2021
- Tel Aviv University
- February 4, 2021
- One response
- Tel Aviv University
- January 28, 2021
- No comments
Researchers from Tel Aviv University shed light on a 140-year-old mystery in an article published in Nature. The research shows for the first time how an abnormal number of chromosomes (aneploidy) - a unique feature of cancer cells that has been known to researchers for decades - can become a weak point of these cells. The research may in the future lead to the development of drugs that will take advantage of this weak point for targeted damage to cancer cells