The earthquake that caused the giant waves was so intense - with the power of a million atomic bombs according to experts - and it caused the Earth to wobble slightly from its orbit. It is estimated that islands in Indonesia have also moved slightly to the side from their previous location
If you feel like the earth is spinning faster, maybe it's because of the tsunami
6/1/2005
It is possible that the deadly earthquake that hit Southeast Asia permanently accelerated the speed of the Earth's rotation - thereby shortening the length of the day by a fraction of a second - and even caused the planet to wobble on its axis.
The hypothesis was put forward by Richard Gross, a geophysicist from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. Gross believes that a mass shift toward the Earth's core during last Sunday's rumble increased the Earth's rotation speed by three microseconds (millionths of a second), tilting it on its axis about 2.5 centimeters.
When a huge tectonic plate on the floor of the Indian Ocean is pushed under the edge of another plate, "the result is that the Earth becomes a little more compressed, and therefore its rotation is accelerated," Gross said.
According to him, the changes that his model predicts are probably too small to be picked up by a network of global positioning satellites, which regularly measures changes in the Earth's rotation. But he added that the data from the satellite network may reveal the slight wobble in the Earth's axis.
The Earth's poles circle as it rotates in an orbit whose range of deviation is about ten meters, so an additional 2.5 centimeters of fluctuation is not likely to result in long-term changes, Gross said. According to him, "The Earth is used to changes in its rotation. The rotation is not that accurate. The Earth sometimes slows down anyway and changes the speed of rotation."
As these tiny deviations add up, planetary experts add a second to the end of the year. This has not been done for many years.
Scientists have long speculated that changes in the Earth's surface, such as fluctuations in tides, groundwater and weather, could affect the rotation of the globe. So far they have had no precise measurements to prove this, said Hiro Kenmori, a seismologist at the California Institute of Technology. "Even a very large event has a tiny effect," Kenmori said. "It is very difficult to significantly change the rotation speed of the Earth."
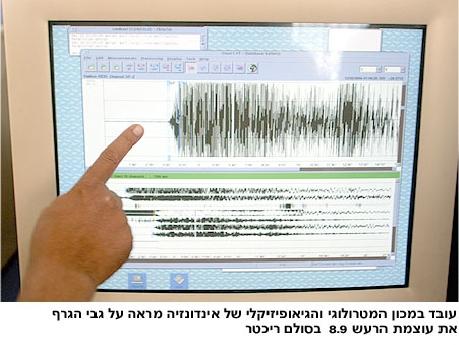
The earthquake affected the rotation of the earth
By: Walla system!
(The update as of this hour is that the number of dead has exceeded the enormous number of 120 thousand)
31/12/2004

the center of the noise. The friction between the tectonic plates erupted along 1,200 km (Map: "Haaretz")
Scientists believe that the intensity of the noise in Asia is equivalent to the simultaneous explosion of a million atomic bombs. According to estimates, the height difference between the tectonic plates that caused the earthquake reaches up to 18 meters
Scientists describe the strong earthquake in the Sumatra region on Sunday as a "mega-motion" - a term reserved for the strongest known movements of the earth's crust. However, even this nickname fails to describe the tremendous intensities of the earthquake, which triggered tsunami waves all over the Indian Ocean.
According to scientists, despite its almost unimaginable power, the earthquake was not unexpected. Sumatra is one of the most earthquake-prone places in the world, due to the fact that it sits at the junction of several tectonic plates - the Indian, the Burmese and the Australian - that rub against each other. The enormous pressure that is released in the single moment of the earthquake, has built up over decades.
"These areas of contact between the tectonic plates are the places where the largest earthquakes occur," geologist Kerry Seay of the California Institute of Technology told the AP news agency. "The earthquake was one of the strongest in the region in the last 200 years."
how strong According to some estimates, it was comparable to detonating a million atomic bombs at the same time. Si and other scientists believe that the earthquake also affected the rotation of the Earth on its axis. "It caused the earth to shake a little, but it will not cause the earth to completely overturn," said Si.
The scientists are trying to guess what change was caused to Sumatra's coastline following the earthquake, but at this stage the floods and extensive damage are being prevented instead of making precise measurements. Under the ocean, the scientists say, there is a chance that the edges of the tectonic plates of the earth's crust have moved vertically, up to a gap of about 18 meters between each other. However, according to them, even such a large movement is not expected to change the sea water level significantly. If Sumatra's coastline recedes or advances a little, the scientists say, it won't be more than a few meters.
"The tides will be only slightly higher or lower than they have been so far," says geophysicist Paul Earley. On the other hand, he adds, the surface of the land in North Sumatra may change noticeably to the eye. "When the section of land above the friction zone of the tectonic plates shakes towards the west - to the Indian Ocean - you can expect the land beneath it to sink," says Earley.
Constant tectonic pressure
Tsunami in Malaysia. The tsunami energy in the Indian Ocean caused waves in Mexico to be 2.5 meters high (Photo: Reuters) Seismologists say that the epicenter on Sunday was at a depth of about 9 km in the Indian Ocean, near the west coast of Sumatra, about 240 km south of the city Banda Aceh at the northern tip of the island. Pressed from many directions, the pressure between the Indian and Burmese plates - located to the northeast of the Indian - along the coast of Sumatra is created.
The edges of the plates rubbed against each other for about 1,200 km, in a line known as the Sunda Trench. The earthquake began far from the coast, then zigzagged towards the island, under Banda Aceh at its northern end, and from there the collision between the plates continued northward, under the Andaman Islands and almost to the coast of Myanmar (Burma).
To complicate matters further, the Indian and Australian plates, which meet in this area, continue to slide steadily towards the northeast, contrary to the direction of the Burmese plate. The strongest recent earthquake in the region occurred in 2000, with a magnitude of 8 on the Richter scale, and it killed at least 103 people and injured about 2,000. Huge earthquakes also occurred in 1797, 1833 and 1861.
Similar to the earthquakes at the point of friction between the tectonic plates in California, the quake caused one plate to slide past the other. It is this movement at the bottom of the sea that "moved" the ocean and caused the giant waves (tsunami). According to the Hawaii Tsunami Warning and Prediction Center, some of the wave energy from the Indian Ocean reached the Pacific Ocean on Monday. In Mexico, the height of the waves increased due to the noise by about 2.5 meters, in San Diego the height of the waves was felt by several tens of centimeters, in New Zealand and Chile a certain change in the height of the waves was reported and in Hawaii almost no change was observed.
29/12/2004
Did we shake? The intense earthquake that caused the large tsunami waves to hit the coasts of Southeast Asia apparently caused the Earth to oscillate in space and some islands in Indonesia to move a few tens of meters from where they were before, American geophysicists claim today (Tuesday).
According to measurements, the earthquake had a magnitude of 9 on the Richter scale - the strongest recorded in 40 years and the fifth strongest since 1900. Some experts compared the force of the noise to the explosion of a million atomic bombs.
Ken Hadnat, of the US Geological Survey, told AFP that the earthquake caused the Earth to wobble on its axis. "We are registering slight changes in the movement of the earth and I assume that the earth moved relative to its axis when the earthquake occurred, because of the large amount of energy that was released and because of the sharp changes in mass in that area."
Another expert, Kerry C. from the California Institute of Technology, agreed with Danat's opinion, "but this is not something that will change the world", he emphasized.
Italy's National Geophysical Institute, Enzo Bucci, told the AP news agency that the earthquake caused a disruption in the Earth's rotation.
Sam Friedman, a professor of civil engineering at the Technion, believes that it does not make sense for the earth to move from its place. "There were stronger tremors and we don't know that they caused such disturbances, but in any case the term used by the researcher means oscillation, not necessarily a permanent change in trajectory. It may be rocking, but taking the Earth out of orbit - it doesn't make sense."
Dr. Rami Hofstadter, Director of the Seismological Division at the Geophysical Institute, from the Seismological Division at the Geophysical Institute, also believes that the oscillation will not have a long-term effect: "It is true that when there are strong earthquakes, the earth seems to shake, but this does not have a long-term effect. If after every earthquake the earth would randomly change its course, we would have been lost in space a long time ago... it is impossible to divert the earth from its course."
The islands moved
The Danat also said that the intense intensity of the noise slightly changed the map of Asia. "According to models, some islands in the southwest of Sumatra (part of Indonesia) moved about 20 meters to the side. He also says that it is possible that the northern end of Sumatra was also shifted from its place by about 36 meters.
Another expert, Stuart Sipkin, disagrees. He believes that what happened is that the plates that make up the Earth's crust went under one another, which caused one of them to be pushed upwards. "In such a case... the movement of the islands was up and not to the side, and they rose slightly from their previous height in relation to sea level...".
Friedman from the Technion is surprised by the data: "Until today there are no known cases in which islands moved by 20 meters. In the past, cases of displacement of 10 and even 12 meters were recorded. This probably indicates that the intensity of the earthquake did reach 9 on the Richter scale and not 8.9, because only if you include this intensity in the calculation, you can get a displacement that may reach 20 meters."
What is your reaction as a geologist to the words of your colleagues from the US Geological Survey (USGS) about the shaking of the earth in its orbit?
Dr. Hofstadter: "It is true that when there are strong earthquakes, the earth seems to shake, but this has no long-term effect. If after every earthquake the earth would randomly change its course we would long ago be lost in space.
It is a closed system and if there is a mechanical torque in one direction, there is an immediate reaction to conserve the torque in the other direction. We must maintain the energy and the torque. These are basic laws of physics. Following earthquakes with a magnitude of 8 or higher on the Richter scale, waves are created that run inside the entire earth and circle it several times. This is a well-known phenomenon that was already measured decades ago. Like a thread that encircles the whole earth. When you hit it on one side because it is strong enough there will be movement in the rubber, the movement will make several laps. After a few laps the humans don't feel anything but the seismometers measure these phenomena for several days. I assume that the experts are referring to these shocks. In any case, it is impossible to divert the earth from its course."
"You require conservation of angular momentum and linear momentum. In such a tremor - one block went up and one block went down. The division is different but the total remains the same otherwise you have a problem with maintaining momentum. I haven't done an estimate but let's say I move a huge plate, and the earth spins like Porphyra. It has angular momentum. You're spoiling a certain palette within that purple. It is a small part of the earth. The question is how much you cause the angular momentum to change. It is believed that this is not bad because most of the angular momentum is inside the center of the Earth. The main mass of the Earth is there. It may be a fraction of a very small percentage. Only in the last century there have been several large earthquakes and if the Earth had been moved by any such earthquake, it would have long since gone out of its orbit. People have been dealing with this problem, and from time to time they try to check it.”
Can't supercomputers help with these calculations?
They can but you need to properly design the software. There are many things that computing power should be used for. For example, the rift (Syrian-African rift, AB) is an active area. Let's place equipment next to it and catch the tremor very close and build a warning system. By the time the wave reaches Tel Aviv or Jerusalem we will gain a few seconds. You need very fast computing power. The problem is how to build a correct system without false alarms. Such things were built all over the world - in Taiwan, in Mexico City. These few seconds will allow people to leave their homes with a message on radio and television and thus reduce the number of casualties. Things were done, even good things, and you can definitely learn from them. It's something that goes on with us and we debate it all the time.
How does the tsunami warning system work?
"You can build a simple warning system - activate many seismometers on the shores of the Pacific Ocean and on the islands within it, and as soon as you detect a strong earthquake, you send alerts to everyone. It is impossible to know in advance what the intensity of the tsunami will be, but it is better to be warned and be fooled than not to be warned and suffer damages. In this case there is a much larger time span. If the wave speed of the tsunami is a thousand km/h. There is an hour until he reaches you. There were cases of even 2,000 kilometers. But let's say it's an hour. Calculate the seismic wave from one side of the ocean I know what is happening. I have at least 20 minutes to inform the whole world - there was an earthquake, stay away. It's not that difficult to go half a kilometer away. Such an alert would have saved many lives. The system is currently working in the Pacific Ocean. It is certainly not ideal and perfect, but quite sufficient. As it works in the Pacific Ocean it can be done in other parts of the world. Need money and not even a lot of money.
What exactly needs to be established?
It is necessary to establish 2-3 centers that will calculate automatic localization. Even if the calculation is rough and there is an error of 5 kilometers in the exact location of the earthquake, it is not bad because it is more important to warn about the tsunami. I would connect systems around the entire Indian Ocean in all the countries, Thailand, Burma, India, Ceylon, Africa and arrange a system that as soon as it detects it immediately sends a warning to everyone. Of course, a human brain is needed to decode these messages and send an immediate warning to the local broadcasting stations. This requires work and money, but the cost is negligible compared to the damage caused.
Prof. Sam Friedman, from the Faculty of Civil Engineering at the Technion. What do you think of the things the USGS man said to the French news agency?
Prof. Friedman: "There were stronger tremors and we don't know that they caused such disturbances, but in any case the term used by the researcher, rattled, means swaying, not necessarily a permanent change in trajectory. It may be rocking, but taking the Earth out of orbit doesn't make sense."
Is it related to the fact that the earth happens to be at the closest point to the sun at this time of the year?
Do not believe.
What boards are these?
Broadly speaking, this is the collision of the Indo-Australian plate and the Eurasian plate, the Indo-Australian plate is the one that penetrates under the Eurasian plate and in another part of it causes the Himalayan mountains to rise.
They knew about islands that moved 20 meters
It seems to me that the displacement estimate of 20 m here is exaggerated, since the main displacements in this earthquake (as a result of the fracture mechanism) were vertical, not horizontal. It is possible that there was an uplift of the island, but it is hard to believe that there was a horizontal displacement of 20 m.
From my data, in earthquakes to this day there are no known cases where islands moved by 20 meters. In the past, there have been cases of displacement of 10 meters. This probably indicates that the intensity of the earthquake did reach 9 on the Richter scale and not 8.9, because only if you include this intensity in the calculation can you get a displacement that may reach 20 meters.
We are already talking about 50 thousand dead. How does it measure up historically?
There have been more difficult cases. In an earthquake that occurred in China in 1976, although with a lower magnitude, 7.8, an entire city of TANGSHAN was destroyed. In China it is hard to know if it is accurate or not, but the estimate of the number of dead was 700 thousand. In 1908 there was a strong earthquake in Italy - 83 thousand dead. In 1923 in Japan magnitude 7.9 - killed 99 thousand. Also in India, there was a historically strong earthquake around the year 900 which is estimated to have killed 180 people. In 1819 there was a strong earthquake in India but only 1,500 people were killed. I have here a newspaper from 1934, a few days after another earthquake - THE GREAT INDIAN EARTHQUACKE and they talk about an order of magnitude of ten thousand dead. In Bam, Iran, about two years ago, in the last big earthquake so far, there were over 10,000 dead.
