Hayadan > James Webb Space Telescope
James Webb Space Telescope
- Avi Blizovsky
- May 1, 2024
- No comments
- Davidson Institute
- April 27, 2024
- 9 תגובות
James Webb Space Telescope observations of galaxies in the young universe revealed that the first light in space came from bright young stars
- Avi Blizovsky
- March 13, 2024
- No comments
This galaxy experienced a tumultuous and fast life: the star formation process worked quickly and suddenly ended, a situation that is not expected at such an early stage in the evolution of the universe. It is still unclear whether the "frozen" state of the galaxy is temporary or permanent, and what is the reason for the cessation of the star formation process
- Avi Blizovsky
- March 12, 2024
- 8 תגובות
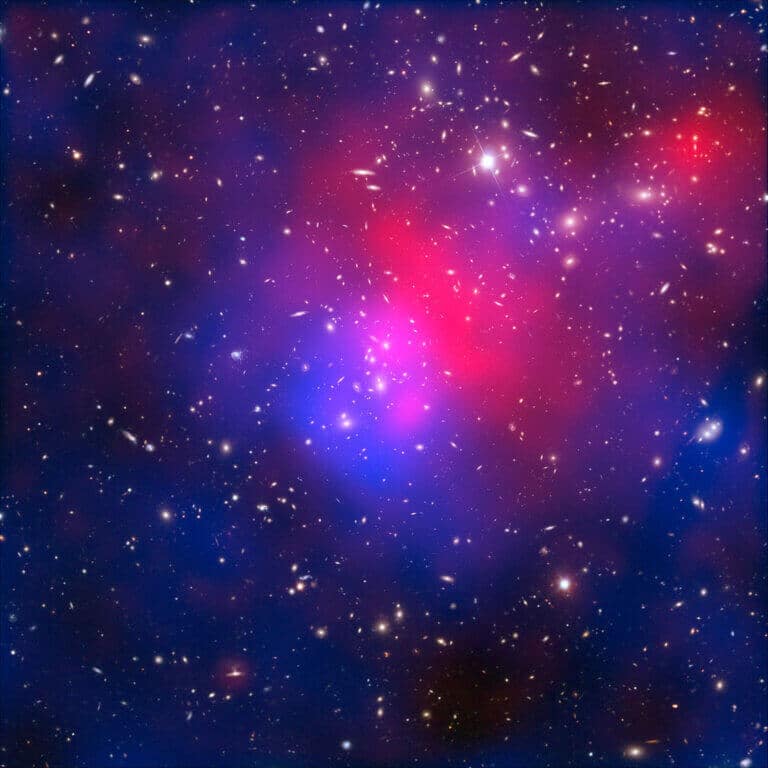
Webb's measurements provide new light on a decade-long mystery known as the Hubble voltage - the differences in the age of the universe between the Hubble observations and past observations that remain unexplained * Prof. Adam Ries, winner of the Nobel Prize in Physics for the discovery of dark energy heads the project
- Avi Blizovsky
- February 27, 2024
- One response
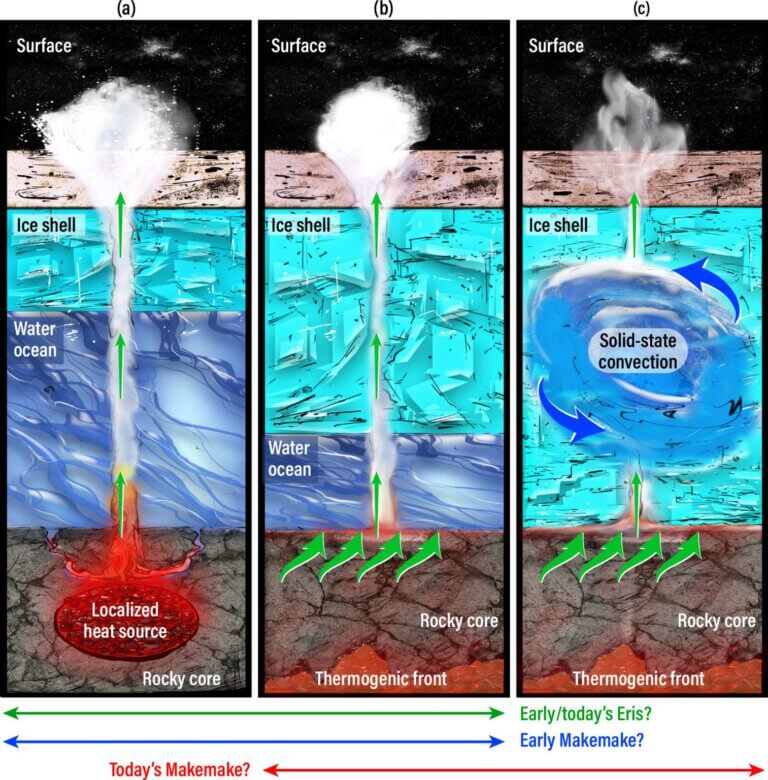
The Webb telescope has observed what appear to be young methane deposits on the surface of Eris and Maki Maki
- Avi Blizovsky
- January 31, 2024
- 3 תגובות
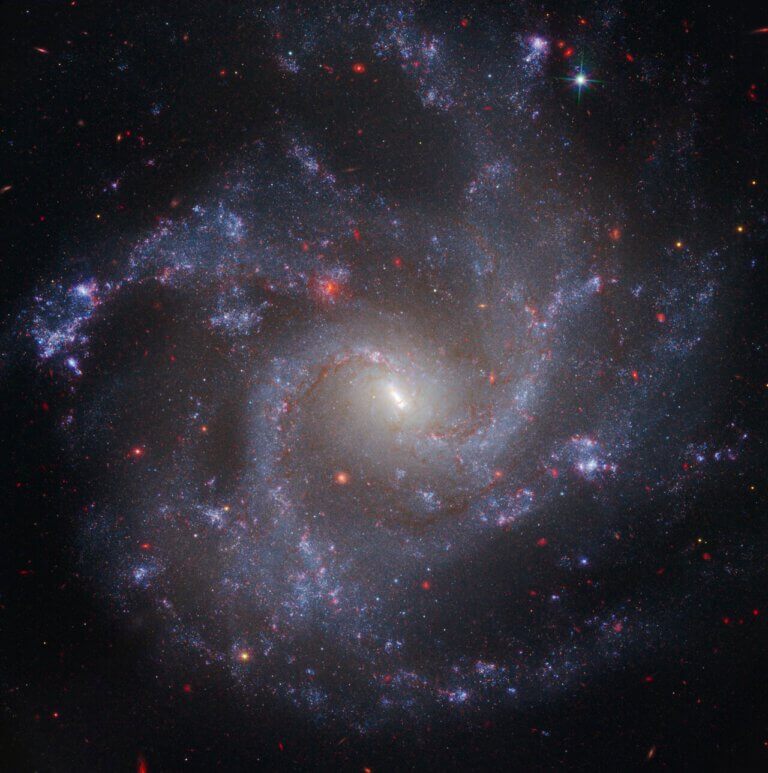
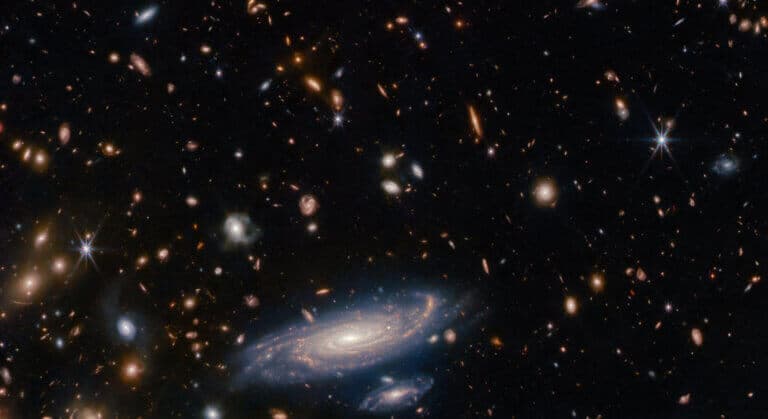
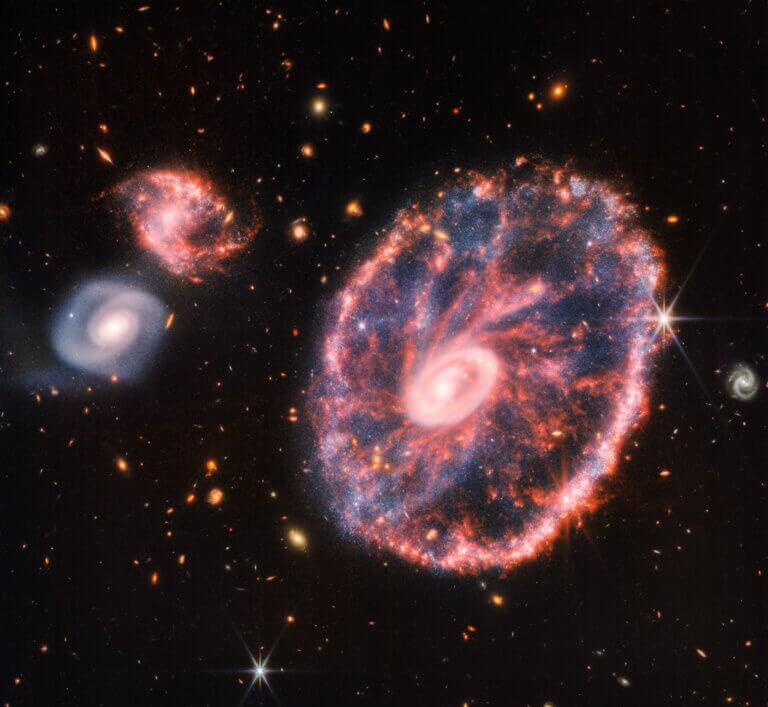
These are relatively close galaxies that face the Earth. The research reveals new details about the way galaxies are formed
- Avi Blizovsky
- January 23, 2024
- 4 תגובות
The first galaxies were much less developed than the spiral and spherical galaxies that exist today, which are actually the result of mergers, both because of the stage of development but also because of the conditions that prevailed at the time
- Avi Blizovsky
- January 16, 2024
- No comments
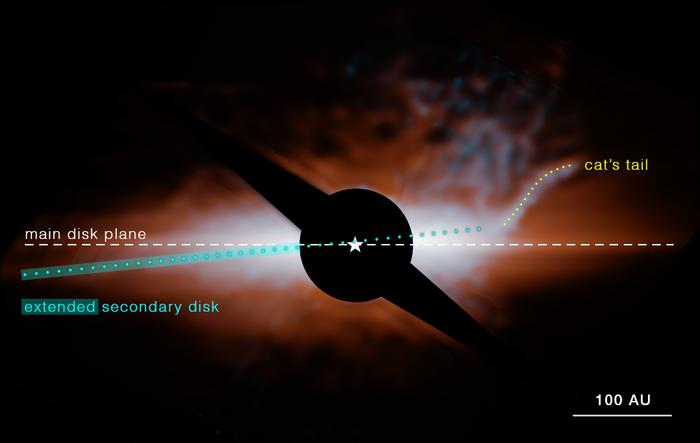
Beta Pictoris is a solar system in the making and relatively close so that the gas disks can be seen. It turns out that Webb was able to discover a structure that was not noticed in photographs with less sensitive instruments, thus he discovered a disk of gas tilted from our main disk and because of our vantage point it looks like a cat's tail
- Avi Blizovsky
- December 1, 2023
- 10 תגובות
- Avi Blizovsky
- November 5, 2023
- One response
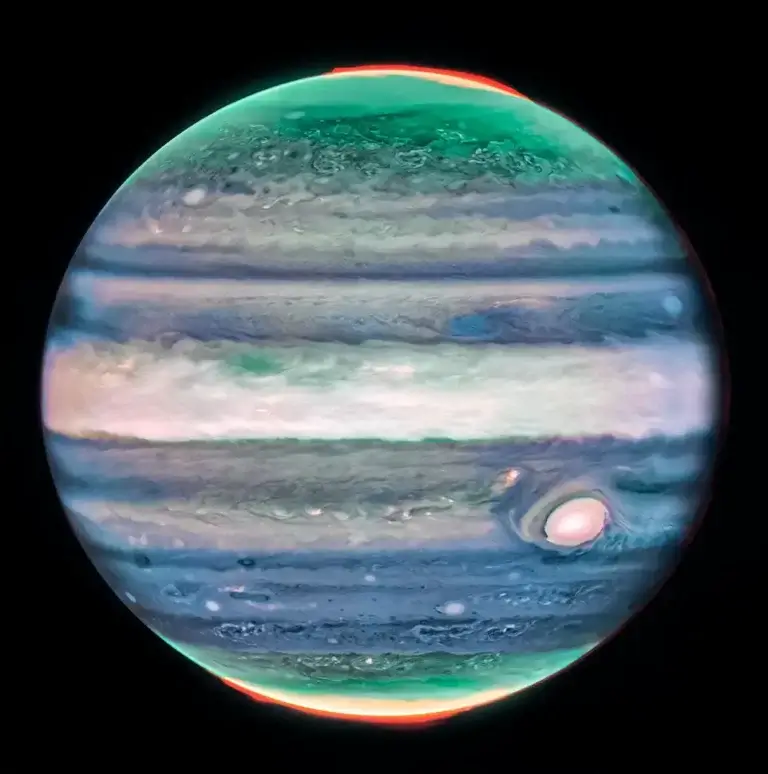
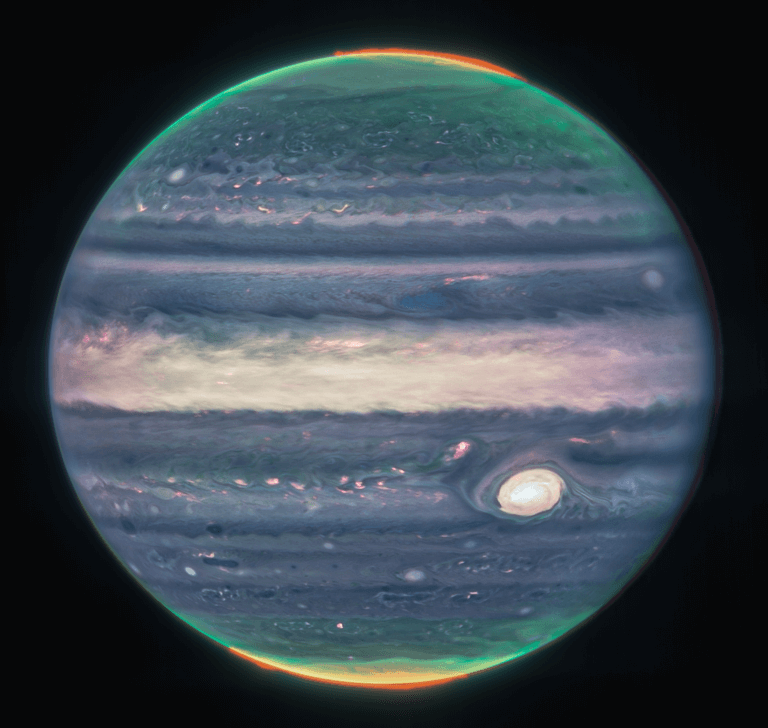
The James Webb Space Telescope discovered a previously unseen jet stream in Jupiter's atmosphere. Similar phenomena have been observed in Saturn, and both may be related to temperature variations in the atmospheres of the gas giants
- Dr. Moshe Nahamani
- November 1, 2023
- 3 תגובות
- Avi Blizovsky
- September 20, 2023
- 3 תגובות
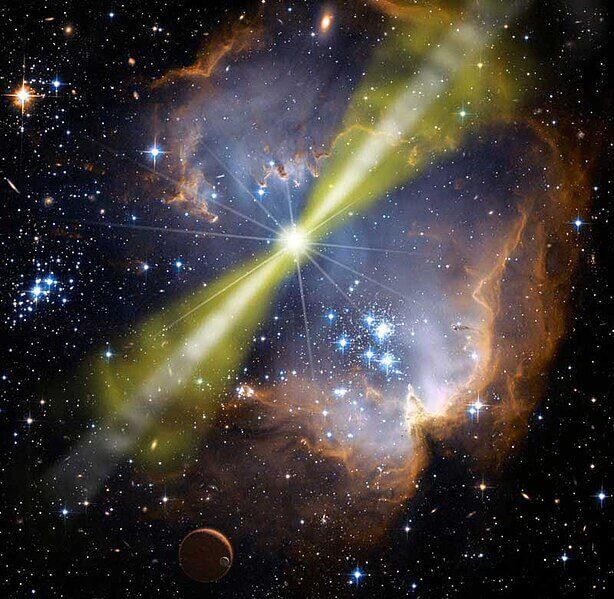
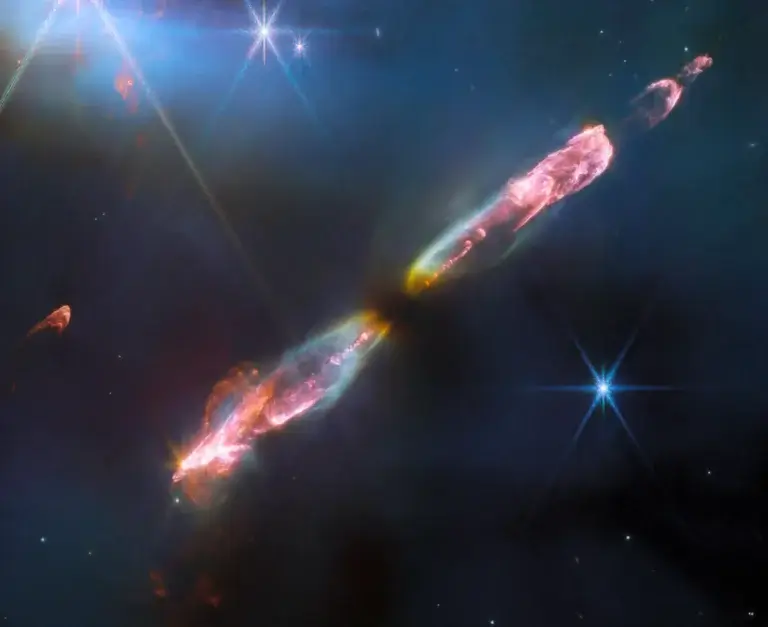
Herbig-harrows are luminous regions surrounding young stars. They form when stellar winds or jets of gas ejected from these stars create shock waves that collide at high speeds with nearby gas and dust.
- Avi Blizovsky
- August 24, 2023
- 3 תגובות
The Ring Nebula, formed by a star shedding its outer layers, is a classic example of a planetary nebula and is also relatively close to us.
- Avi Blizovsky
- June 14, 2023
- 5 תגובות
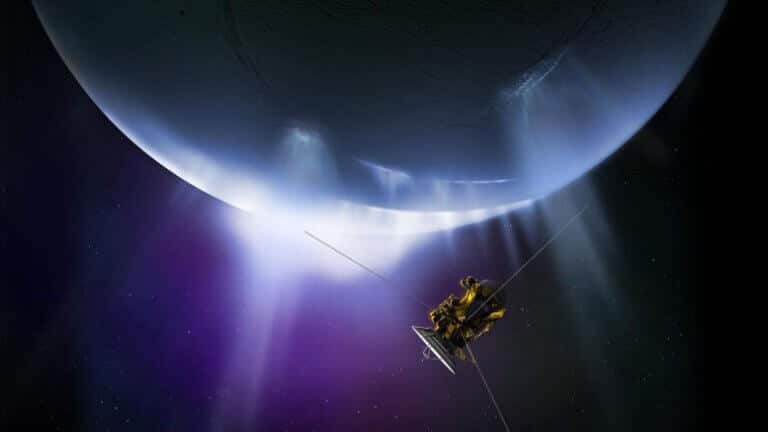
This is the first time that such an emission of water has been seen from such a great distance, and in addition, the web allows researchers a direct view, for the first time, of how this emission feeds the water supply of the entire system of Saturn and its rings
- Avi Blizovsky
- June 11, 2023
- 7 תגובות
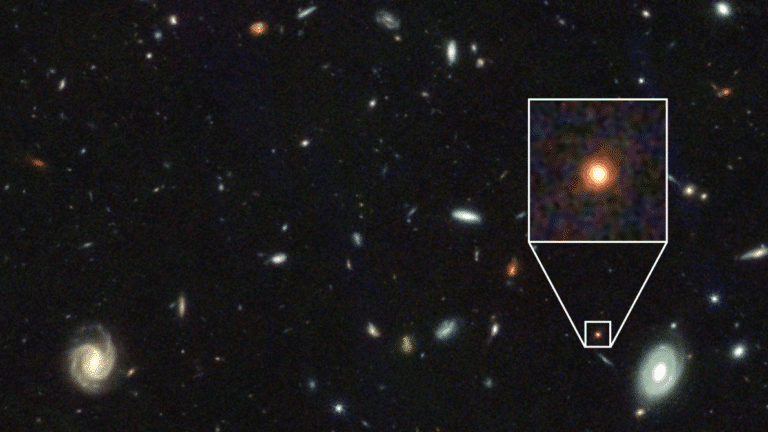
The galaxy is currently 25 billion light-years away, but when light began to travel from it to us about 12.5 billion years ago, it was much closer, because the universe is expanding
- Avi Blizovsky
- June 4, 2023
- 19 תגובות
The first findings from the James Webb space telescope hinted at galaxies so early and massive that they are somewhat inconsistent with our understanding of the formation of structure in the universe. A new study tries to deal with these contradictions
- Avi Blizovsky
- May 16, 2023
- 2 תגובות
The belts surround the hot young star, which can be seen with the unaided eye as the brightest star in the southern group Southern Pisces. The dust belts are fragments from the collisions of larger bodies, corresponding to asteroids and comets, and are often described as "fragment disks"
- Avi Blizovsky
- April 12, 2023
- 4 תגובות
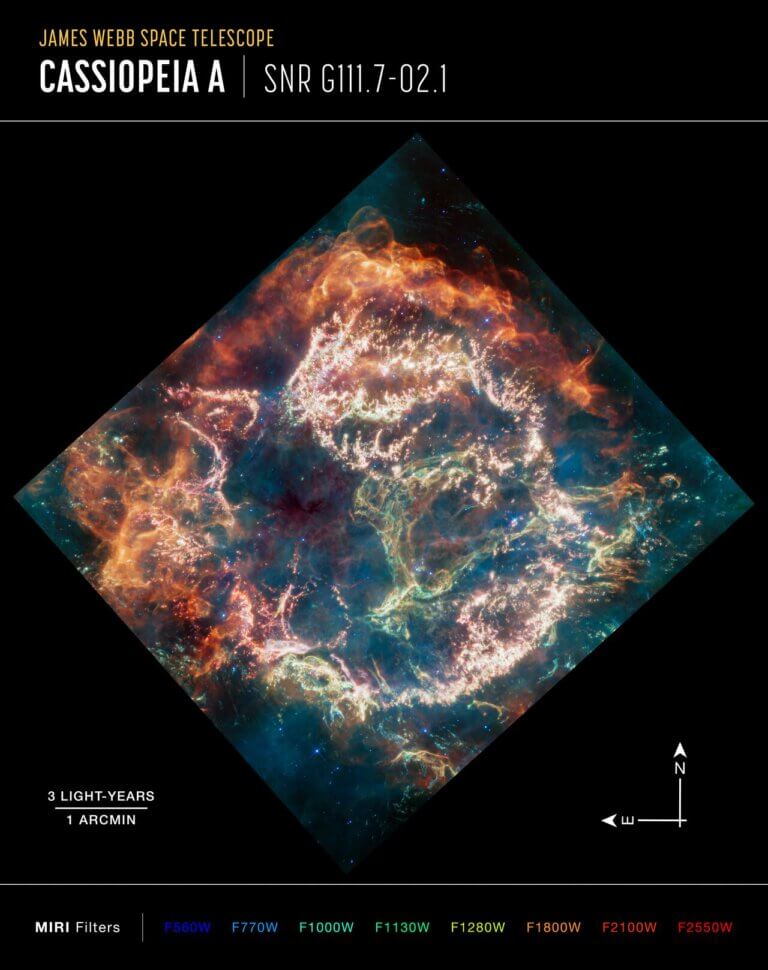
Webb recorded what remained after the death of a star only 11 thousand light years away from us. It is a relatively new supernova - only 350 years old
- Avi Blizovsky
- April 9, 2023
- 3 תגובות
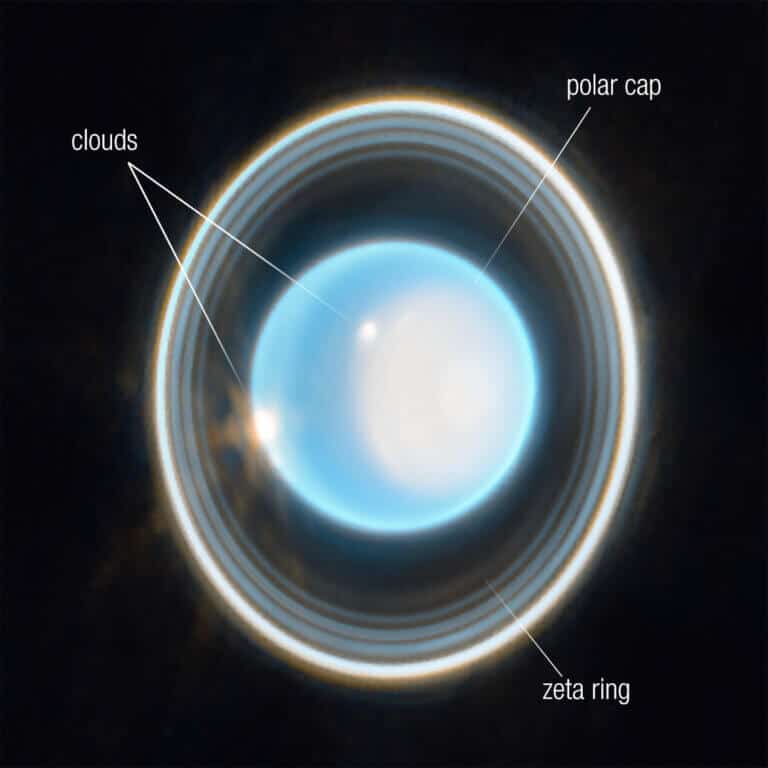
The Webb Space Telescope photographed in detail 11 of the rings surrounding Uranus-Uron
- Avi Blizovsky
- January 17, 2023
- No comments
Previous infrared studies of the NGC 346 nebula have focused on stellar embryos heavier than five to eight times the mass of our Sun. With the help of the Web, it is possible to reach even lighter protostars, as small as a tenth of our sun
- Avi Blizovsky
- January 13, 2023
- 2 תגובות
However, the conditions there are more reminiscent of Venus than Earth. It orbits a red dwarf in an orbit that lasts only two days * Webb was able to confirm the existence of the planet after only two orbits
- Avi Blizovsky
- November 18, 2022
- 9 תגובות
One of these galaxies is observed as it appeared about 300 million years after the Big Bang and shines much brighter than expected. This figure now makes researchers estimate that the first galaxies were formed 100 million years after the Big Bang. "It's like an archaeological dig, when you suddenly find a lost city or something you didn't know about," said one of the researchers
- Avi Blizovsky
- October 21, 2022
- No comments
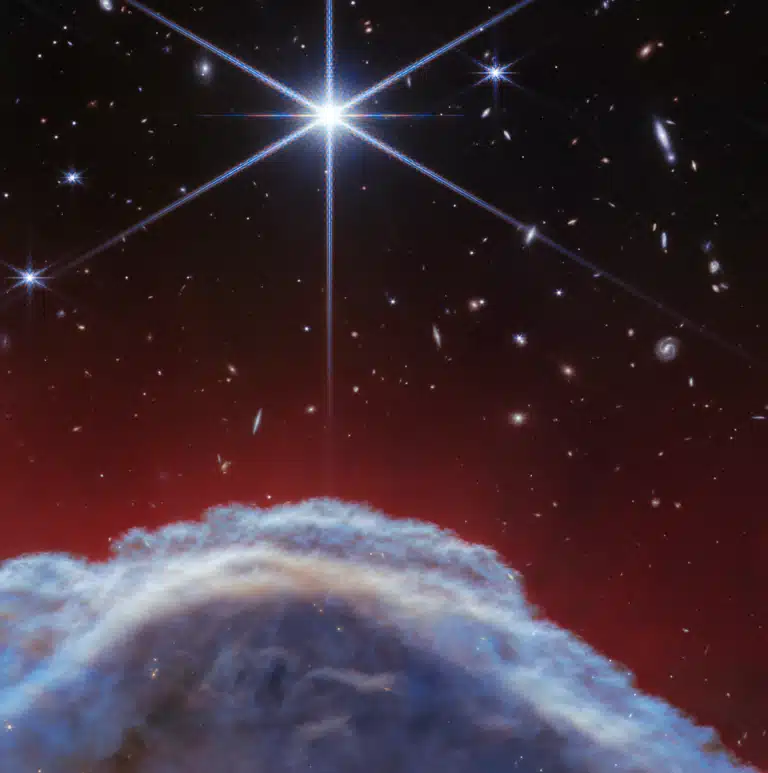
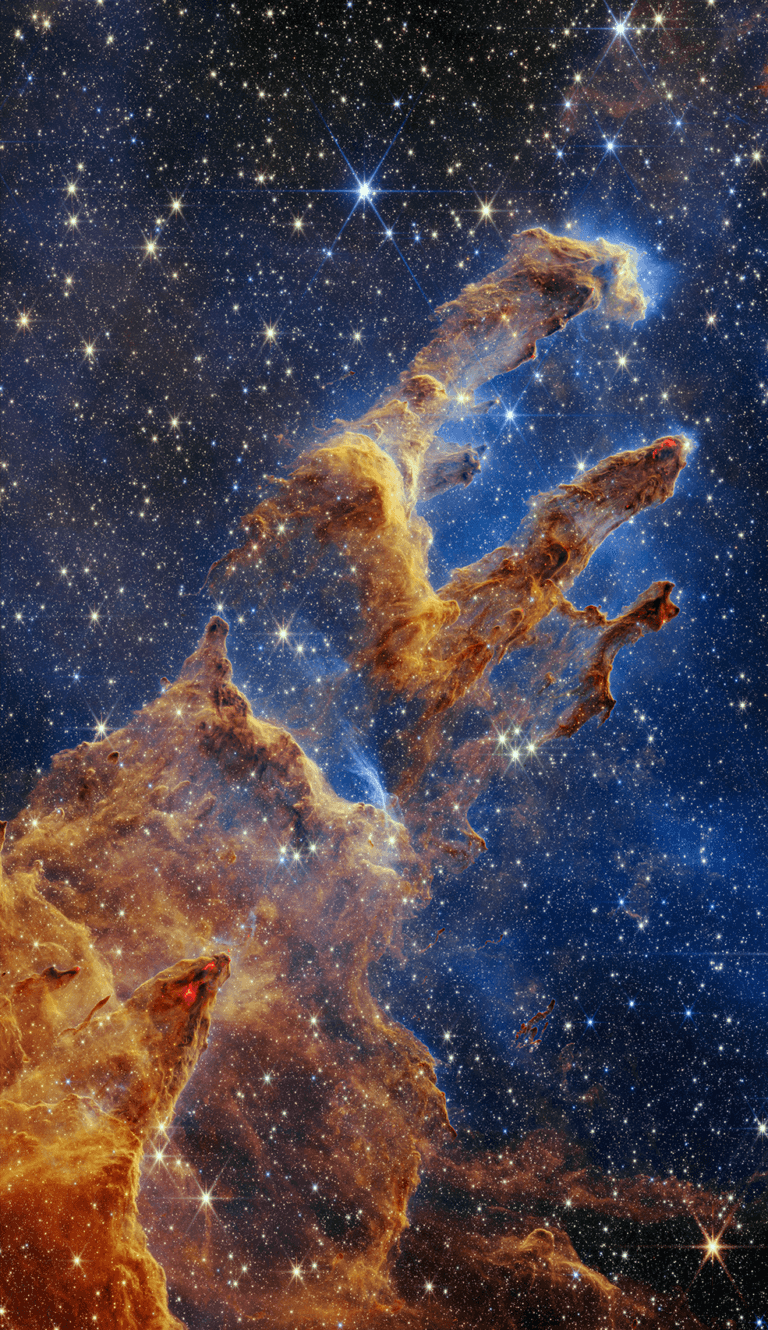
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope captured a rich and highly detailed view of the "Pillars of Creation." A region where new stars form within dense clouds of gas and dust that was previously captured in an iconic image by the Hubble Space Telescope at the start of its operation and returned to after upgrades, along with Strong landmasses
- Avi Blizovsky
- August 24, 2022
- One response
- Avi Blizovsky
- August 7, 2022
- 7 תגובות
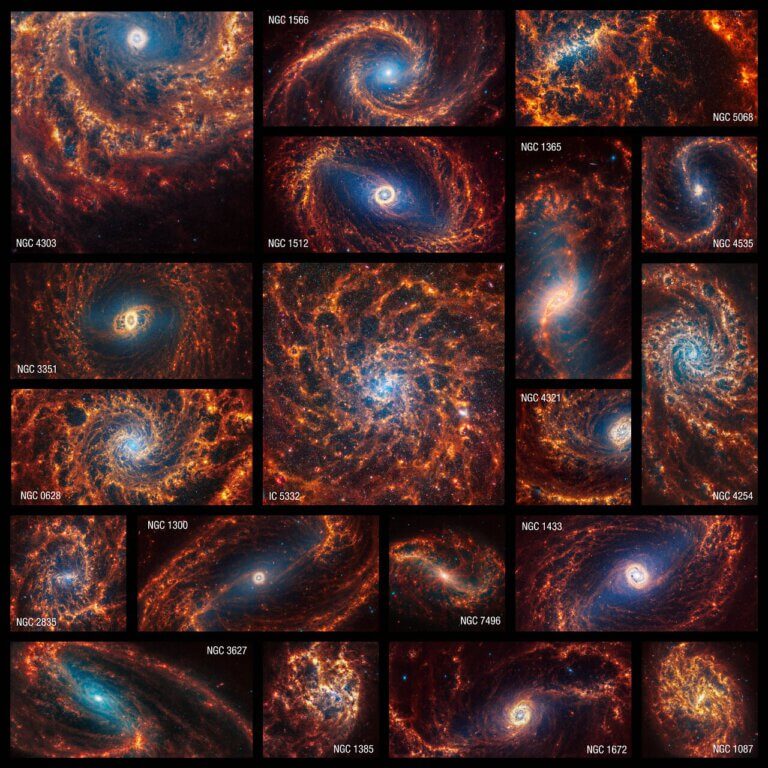
Webb's instruments reveal new details about star formation