This is according to a survey of research and development in government institutes, institutions and research units: 2009 published this week by the Central Bureau of Statistics • 2,755 employees were employed in research and development in research institutes, of which 1,702 are academics; 1,174 women were employed in R&D
In 1976, the Central Bureau of Statistics, in collaboration with the National Research and Development Council, conducted a survey of "research inputs and development in research institutes". Since then, no similar survey has been conducted.
A survey of research and development in institutes, institutions and research units for 2009 was conducted by the Central Bureau of Statistics,
He too, with the cooperation and funding of the National Research and Development Council (NRDC) under the Ministry of Science and Technology.
The purpose of the survey was to obtain a comprehensive picture of the R&D activity of government research institutes, private and public non-profits in Israel that will help to compile accurate statistics in the field of R&D activity and to calculate the national expenditure for research and civilian development, especially in the field of public R&D.
The survey included 104 government institutes, private non-profits and public non-profits whose main activity is research and development.
In order to get a comprehensive picture of the activity taking place in the institutes, institutions and research units, information is also collected on expenses and income for any other activity carried out in them, in addition to expenses and income for research and development activities.
The survey findings do not include security R&D.
Distribution of expenses
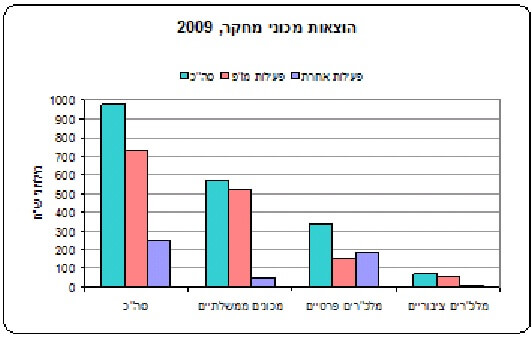
The total expenses of government institutes, institutions and research units (hereafter research institutes) for 2009 amounted to NIS 975.9 million. 728.9 million NIS was earmarked for research and development, of which 520.9 million NIS (71.5%) in government institutes, 148.2 million NIS (20.3%) in private non-profits and 59.8 million NIS (8.2%) in public non-profits .
The expenses for self-execution of R&D amounted to 648.5 million NIS. More than half of the expenses - 56%, were directed to wages, 40% were used for the consumption of intermediate goods and 4% for investments.
70% of the self-execution was concentrated in the government institutes, 22% was carried out by private non-profits and 8% by public non-profits.
The distribution of the execution by type of research shows that 61% was carried out in applied research, 21% was carried out in development and 18% in basic research.
The distribution by scientific field shows that most of the R&D activity was carried out in agricultural sciences (40%) and social sciences (28%).
9% of the execution was directed to political systems and processes and 7% to the environment.
56% of the scope of R&D activity in government institutes was in agricultural sciences, which were mainly carried out in the Agricultural Research Administration. In private non-profits, the largest scope of R&D activity was carried out in the social sciences (59%) and in public non-profits - in the humanities (50%).
The findings of the distribution of R&D expenditure according to socio-economic goal, in accordance with the goals established according to international definitions, show that a major part of the execution (38%) was directed to agriculture, forestry and fishing. In government institutes, 53% of the implementation was directed to agriculture, forestry and fishing, in private non-profits more R&D was carried out in political systems and processes (26%) and in public non-profits - in education (34%).
International comparison with OECD countries
The share of the government sector (including government offices and institutes, public non-profits, local authorities and national institutions) in the national expenditure on R&D in Israel in 2009 (3.8%) is lower than the median of the OECD countries (12.5%) on the other hand the expenditures for carrying out R&D In the private non-profit sector in Israel (3.2%), higher than the median in the OECD countries (1.0%)
R&D shopping expenses
Expenditures for purchasing R&D, for conducting research and development for the research institutes by external parties, amounted in 2009 to 74 million NIS.
63% of the R&D was carried out by the business sector, 14% by the higher education sector, 14% by private non-profits, 4% by the government sector and 3% by operators from abroad.
The distribution of R&D purchases in each of the groups of institutes shows that the majority of R&D purchases were from the business sector: in government institutes (67%) and private non-profits (50%). On the other hand, most of the R&D was bought in public non-profits from the higher education sector (74%).
Current transfers
The institutes' support for R&D through current transfers amounted to 6.4 million NIS.
Most of the funding was directed to the higher education sector - 64%.
The distribution of current transfers in the groups of institutes is not uniform: 86% of the transfers of government institutes and 98% of the transfers of private non-profits were directed to the higher education sector, while 90% of the current transfers of public non-profits were directed to households, through scholarships for individuals.
Distribution of income
The total revenues of research institutes in 2009 amounted to NIS 931.7 million.
The revenues for research and development activity amounted to 701.6 million NIS.
NIS 424.9 million (61%) was received from government support and allowance, NIS 118.1 million (17%) from sales of
Services, contracts and research grants in Israel, 82.2 million NIS (12%) were funded from abroad, 39.6 million NIS (6%) from donations and internal funds, 14.6 million NIS (2%) from funds
Binationality 11.1 million NIS (1%) from royalties, patents and concessions and 11.1 million NIS (1%) from other factors.
In the distribution of revenues by operating factor, it appears that 77% of the R&D in government institutes was financed by support and allowance
government and 13% through sales of services, contracts and research grants in Israel. In public non-profits, 71% of the R&D was financed by government support and allowance and sales of services, contracts and research grants in Israel financed 26% of it.
48% of the R&D in private non-profits was financed by financiers from abroad, 24% was financed by sales of services, contracts and research grants in Israel, and only 2% was financed by government support and allowance.
Funding through research contracts and research grants
The financing by contracts and grants from Israel and abroad amounted in 2009 to 142.8 million NIS. 36% of the R&D in research institutes was funded through research contracts and research grants from the government sector, 35% from the business sector, 17% was funded through research contracts and research grants from foreign funders and 6.5% from bi-national foundations.
Human Resources
In 2009, 2,755 people were employed in research and development in research institutes and the full-time positions amounted to 2,212.
61% of the employed were academics - 27% of them with a PhD, 7% engineers and technicians, 5% with secondary education, 4% with post-secondary education and 23% with other education (in government institutes this group included students working with scholarship funding).
66% of the employed worked in government institutes, 28% in non-profits
private and 6% in public non-profits.
1,174 women were employed in research and development, 65% of them academics.
66% of the women were employed in R&D in government institutes, 31% of them in private non-profits and 3% in public non-profits.
Personnel in R&D according to research cooperation in the research institutes in Israel and abroad
Part of the R&D activity is carried out by the cooperation of the research institutes with research bodies in Israel and abroad. The collaboration is manifested by writing a joint study. Sharing created for the purpose of consultation or guidance only is not considered research collaboration.
In 2009, the research institutes carried out 688 research collaborations in Israel and abroad. 64% of them were carried out in institutes
governmental, 21% in private non-profits and 15% in non-profits
public.
The expenses for research cooperation amounted to NIS 265.7 million. 86% of them were performed in government institutes, 8%
in public non-profits and 6% in private non-profits.
491 collaborations were carried out with entities in Israel. 39% of them were done with public or government research institutes and 27% with universities.
177 collaborations were carried out with entities abroad. 62% of them were carried out with national or international research institutes.
Tutoring students and doctoral students
In 2009, research institute researchers guided 56 postdoctoral students and 422 students, of which 254 were master's degree students and 168 were doctoral students.
98% of the master's degree students and 95% of the PhD students studied at universities in Israel and 73%
Most of the doctoral students were from Israel.
Geographical distribution of R&D activity in Israel
The classification into districts shows how R&D activity is distributed in Israel. The division includes six districts: Jerusalem, North, Haifa, Center, Tel Aviv, South. In the division into districts, the region of Judea and Samaria was also included, which was classified in the central district. The classification of all institutes is done according to their main address.
The geographical distribution of research and development expenditure shows that 39% of it was carried out in the Central District, 23% in the Jerusalem District, 21% in the Tel Aviv District, 12% in the Haifa District, 4% in the Northern District and 1% in the Southern District.
The distribution of expenditure by operating factor shows that the highest expenditure of government institutes was in the Central District (51%), the highest expenditure of private non-profits - in the Jerusalem District (50%) and of public non-profits - in the North District (50%).
Geographical distribution of the workforce in R&D:
Over half of those employed in R&D (60%) were in the Central District. 23% were employed in the Jerusalem district, 9% were employed in the Haifa district, 7% in the Tel Aviv district, about 1% in the southern district, and the lowest rate of employed in R&D was in the northern district: less than 1%. 57% of the women employed in R&D were in the Central District and 30% of them - in the Jerusalem District.
The distribution of the employed according to education shows that the highest proportion of academics was in the Central District (48%) and the Jerusalem District (30%).
83.6% of those employed in R&D in government institutes were in the Central District. A similar rate is also found among the women employed in R&D in government institutes - 81.7%. Private non-profits had the highest proportion of employed people (50.4%) and of women (50.2%) in the Jerusalem district. Also in public non-profits was the high proportion of employed (57.1%) and women (67.5%) in the Jerusalem district.
Settings
Expenses for self-execution - include expenses for carrying out R&D - salary, current purchases and investments (not including current transfers and capital and do not include expenses for buying R&D)
Expenses for purchasing R&D - expenses for purchasing R&D, for carrying out R&D for the research institutes by external parties.

One response
Why does it take two years for the data to be published?