The resolution of the satellite images from an altitude of 500 kilometers will be lower than 70 centimeters. More details - in the article
Note: The materials were prepared before Last night's successful launch of the Ofek 9 satellite (Ofeq 9),
The Comet satellite launcher:
The increasing use of small satellites for the purposes of remote sensing, observation and communication, provided an incentive for the State of Israel to develop the ability to launch satellites through an air industry - the Melam plant.
The Shavit satellite launcher is designed for launching and placing satellites in space in low orbits (orbits between 200 and 500 km above the Earth's surface).
The Shavit satellite launcher is a three-stage launcher that uses solid rocket engines made by TAS and Rafael. The launcher is about 20 meters tall and weighs about 30 tons.
The Comet launcher has been in use since 1988 when the first Horizon satellite was placed in space. Since then the launcher has been improved and capabilities have been added to launch advanced satellites. The Comet launcher successfully launched the Ofek 7 satellite on June 11, 2009.
Due to the geographical location of the State of Israel in the eastern basin of the Mediterranean Sea, the satellites are launched towards the west.
The launch to the west, against the direction of the Earth's rotation, is carried out at the expense of the maximum weight of the satellite that can be placed in space, but the high efficiency of the launcher and its coordinated combination with the satellite compensates for this.
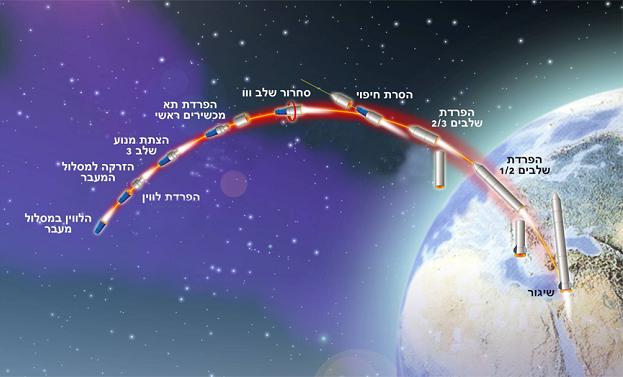
Launch process:
The process of preparing for the launch is carried out from a dedicated car that controls the satellite launcher and updates through communication the control center where the experts sit who analyze the data received from the launcher and confirm the execution of the launch.
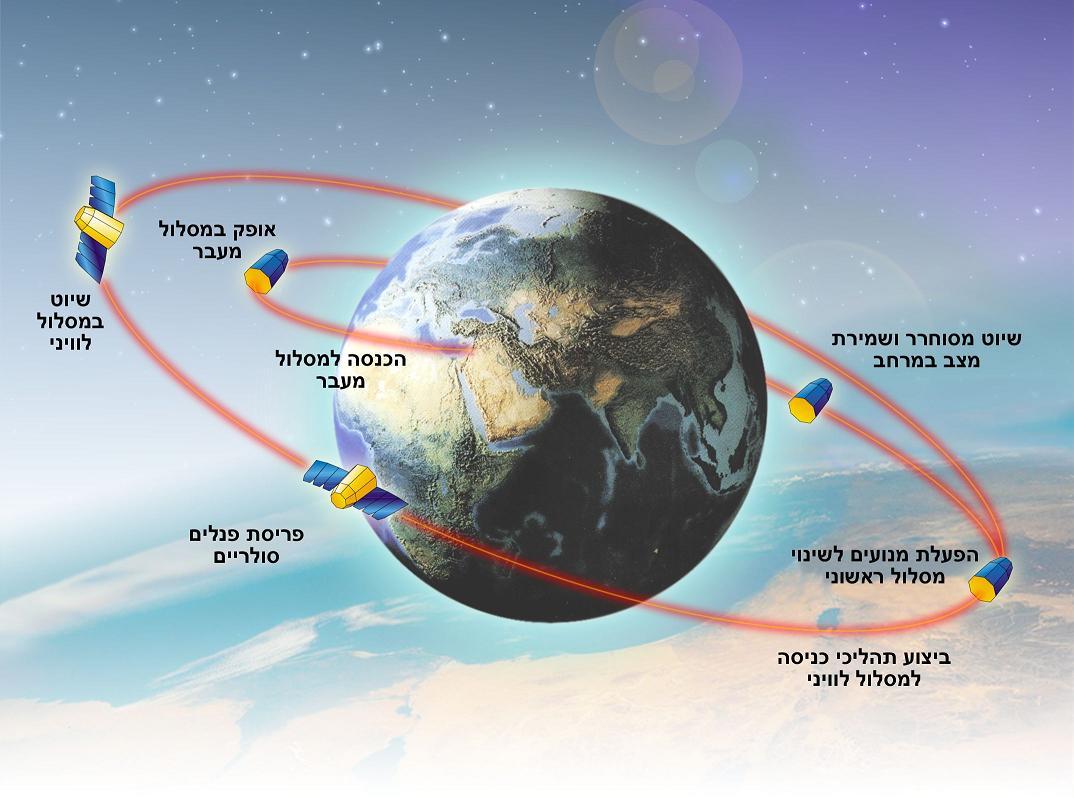
Shortly after the end of the engine operation of the first two stages, the launcher left the atmosphere surrounding the Earth and entered outer space. The third stage of the launcher continued with an unpowered cruise, in which the covering protecting the satellite was removed, and the satellite was exposed to the conditions of space for the first time. During the continued cruise, the launcher spins for stabilization and the main instrument compartment will be separated from it in order to accelerate only the necessary to the final orbit. At a height of 250 km above the earth's surface, the third stage engine was ignited, which gave the launcher the required speed and would place the satellite in the planned orbit. At this point, the satellite was separated from the launcher and began its independent function in space.

- Weight: about 300 kg
- Height: 2.3 meters
- Width with wings spread: 3.6 meters
- Diameter with closed wings: 1.2 meters
- Lifespan: over 4 years
- Performance and data: Ofek 9
- attribute value
- Resolution @ 500 km is better than 70 cm
- Scanning bandwidth about 7 km
- Accuracy of locating objects in the image
- (without control points) 20 meters

28 תגובות
On the 13th (Adi) Kazakhstan launched commercial satellites with Russian rockets,
On the other hand, to the best of my memory, India launched a military radar satellite (TECSAR)
In collaboration with the Indians - perhaps because it was too heavy.
From what I know, if we launch the comet towards the east, it will be able to carry 1 ton and not just 500 kg, right?
Nun:
I didn't know this sentence until I saw your comment and was looking for a parable to demonstrate its tautologies.
It is no coincidence that in your "explanation" you did not quote everything you wrote in the original because it is clear that you did so, every reader would understand why I wrote what I wrote.
Rothschild:
I understand you were looking for an opportunity to use the sentence with the fish…
I wrote that "not only is it due to security/political reasons", and it is also a little easier (politically/security) to "launch a satellite" than to test intercontinental missiles.
It's not Horizon 9 but Horizon 8
Wow, how many ultra-Orthodox worked in the development of the Ofek 9 satellite, later they will say that they are parasites and the like...
to me
Is your calculation correct?
The Earth moves eastward in the equatorial region at a rotational speed of 40,000 km per 24 hours, which is less than half a kilometer per second. Since satellites move at a speed of 8 km per second at these altitudes, then ours passes at a speed of 8.5 km per second over a point on the Earth and the others, at a speed of 7.5 km per second. It will not create differences of 15 vs. 10 but differences of 11 or 12 vs. 10. Just a calculation.
Shabbat Shalom
Sabdarmish Yehuda
Nun:
Very logical: not for security reasons but to be able to launch a warhead anywhere in the world.
It's kind of like saying you don't eat fish - not because of the taste but because it doesn't taste good to you.
The desire to create a launch system for satellites not only stems from security/political reasons of dependence on foreign launch systems, but also to develop the missile industry, after all what launches a satellite today can launch a warhead to any point in the world tomorrow.
Maybe I wasn't clear enough in the previous response:
Ofek passes over the same point on the Earth 15 times a day, compared to 9-10 that any other satellite passes.
Anonymous 17, the R-B-E resolution is better than 70 cm. 70 cm is the limit of commercial satellites if I'm not mistaken.
Ami (and others), from an interview with Prof. Haim Ashad (head of the space program) it appears that we developed the independent launch capabilities so as not to be dependent on external factors. It is a strategic decision to be able to launch satellites on our own regardless of the political situation, given the importance that the space program represents to Israel's security.
In addition to this, there is an apparent advantage to launching satellites to the West. Israel is the only country that launches to the west, so its satellites orbit the Earth against the direction of its rotation, which means that relative to a fixed point on Earth, they are 1.5 times faster than any other satellite. Ofek completes 15 rotations a day around Earth, compared to 9-10 rotations completed by American, Russian, etc. satellites.
Sorry for the ignorance, but what does it mean that the resolution will be smaller than 70 centimeters?
Each pixel in the image will be 70*70?
A. No matter how much the satellite costs
B. If they launched the satellite, then the people in TAA need it, it's not boring and they wouldn't develop and launch a satellite for nothing
third. Because of Section B, we have to invest in the development and launch of a satellite and comments like "How much does it cost us?" Evidence of ignorance
d. They launch from Israel because if we launch from another country they can reveal the technology in the assembly of the rocket and mainly because we need independence in launching satellites and not be dependent on other countries.
God. We are the only country in the world that launches to the west so that the missile doesn't fall in Arab countries and they will steal the technology but like everything else in our country, courage turned out sweet and because necessity is the father of invention Israel is the number 1 country in the world in the development of small and lightweight satellites that perform better than larger satellites And all the other powers far behind our tail.
What a spoon for the Iranians. They don't have to try. We tell them everything.
to my people,
A. Accuracy of 20 meters, I think it means the exact location of an object in the picture, without additional help.
B. The question is actually, what is burning to launch another satellite? Do you want more accurate intelligence on the flotilla of girls from Lebanon?
Ami,
There was a time when we used to launch from Baikonur (Kazakhstan I think). I assume that Israel wants to achieve full independence through launches (security reasons perhaps?).
11 is right.
Although it is not clear why it cannot be launched from another location. If it comes at the expense of weight (equipment) then just ship from Europe! or USA or any other place.
I just didn't understand the difference between a resolution of 70 cm and the accuracy of locating objects in a 20 meter image
Can someone explain the second part?
to 10 so that it does not fall over Arab countries in the event of a malfunction.
If I'm not mistaken, Israel is the only country that launches satellites to the west and not to the east.
Why not launch from the sea, to the east?
It is more accurate to write "due to the geopolitical location" instead of "due to the geographic location"
And I will continue with the analogy to his situation, we are chasing after Iran while we were so far away that we did not notice the growing "legal" Arab majority, it would be ironic that after all our superiority in wars we would lose our country not in war but in elections.
ZOOM OUT
It is said that he films so close that he films the screen in the control room that projects his footage.
Think about it deeply
Admit that it is itchy to fit the grays
To Moshe's suggestion, Israel produces airplanes, I mean of course unmanned aerial vehicles.
It has already been published about the biggest ones (and not just drones).
Is it worth it for us to develop and produce a manned fighter jet... in the quantities we need it is not worth it on the face of it. They won't buy it from us. On the other hand, newspapers buy a lot from us.
Aircraft auxiliary systems, radars, control systems, we are definitely at the forefront of the world.
The issue of the submarines, for armies, seems to be the direction in which everyone is heading.
Will such UAVs be able to perform any task that a manned aircraft currently performs? At least the Rabbi and with higher efficiency.
Yes Haim, what are you implying? And what is it about, share with us?…
Pay attention to the second picture, the earth on the background of the earth, funny, isn't it?!
Kudos to the country!!! (Agree with Moshe)
Chaim?... What are you implying..?
It just proves!! Israel should rely only on itself in technologies !! and not be dependent on other countries
There are excellent engineers here!!
Airplanes should also be developed in Israel and not be dependent on others!
And it doesn't say about all the strange helicopters and planes that flew to them in the Hazor area
Or about the beam of light that came out of the cloud after the "launch"...
It just doesn't say how much it costs us..