This is what two Australian scientists who study tachyons claim
Dr. Gali Weinstein
Einstein's special theory of relativity provides an accurate description of natural phenomena on the condition that the relative speed of bodies in nature cannot equal or even exceed the speed of light.
In the special theory of relativity there are two well-known equations: the first is an equation for the relative mass of the body which is proportional to its rest mass (the faster a body moves, the greater its relative mass) and the second is Einstein's famous equation: E = mc^2. According to this last equation, matter moving at the speed of light would require infinite mass and an infinite amount of energy to reach the speed of light. Both of these equations are valid for relative velocities that are smaller than the speed of light, so they show singular behavior - that is, they break down - when the relative velocity is equal to the speed of light.
Einstein claimed in 1907 that super-light speed is not possible because if we assume that the speed of the body relative to some system is higher than the speed of light, then we can always choose a speed so that the time is less than zero. As a result, it will be possible to examine a mechanism that can move the result before the cause. Although Einstein thought this situation contained no logical contradiction, it nevertheless fundamentally contradicts our experience. Einstein thought this so contradicted our experience that it was sufficient proof that relativistic speed cannot exceed the speed of light.
According to Einstein's special theory of relativity:
- No signal can exceed the speed of light - this is an argument against super-light speeds.
- It is not possible to accelerate a body to the speed of light and beyond the speed of light - the speed of light is an upper limit.
However, since Einstein expressed his strong opinion against supersonic speeds, many researchers have pondered the possibility of theories where such speeds could exist; We well remember the tachyons and the theories proposed in connection with the tachyons.
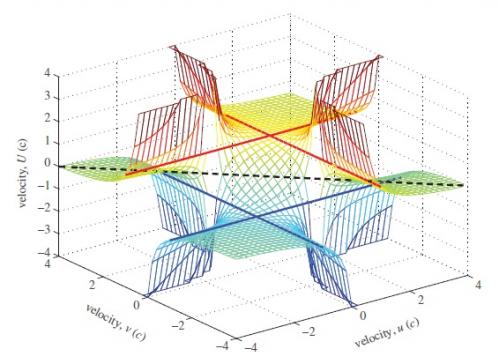
And here are two researchers from Australia, Prof. Jim Hill and dr Barry Cox from the School of Mathematics at the University of Adelaide propose a special theory of relativity that is valid for relative speeds that are higher than the speed of light; And in more detail their Torah applies to tachyon speeds: speeds less than infinity and greater than light.
The equations in special relativity are called Lorentz transformations (between inertial systems moving at constant and uniform speeds). The researchers' question was: What transformations between inertial systems will be valid for speeds that are greater than the speed of light and less than infinite speeds?
Both researchers are mathematicians and to write down the relativistic formalism in a simpler way they usually use the theory of bundles. Einstein's law of relativistic velocities is usually written in relativistic velocity space. Although Einstein wrote his theory of relativity with the help of reference systems, observers, clocks, rulers and thought experiments; But since Einstein's special theory of relativity mathematicians formulated it in a geometric and mathematical way. The formula that expresses the law of the addition of relative velocities is actually very complicated, especially if the two velocities are not in the same direction. Other researchers after Einstein began to interpret Einstein's law of the addition of velocities geometrically. They gave a non-Euclidean geometric interpretation to the theory of special relativity, while using the Minkowski space. The researchers discovered that the application of hyperbolic geometry in special relativity leads to interesting results. They linked the law of relativistic velocities and hyperbolic non-Euclidean space. This is a geometric approach to problem solving, an approach that Einstein did not use.
Using such an approach and defining a parameter that the Australian researchers call "pseudo-velocity", they were able to demonstrate that in their theory, mathematically, the law of relativistic addition of velocities is strangely applicable to speeds that are higher than the speed of light: if the two speeds in the equation are higher than that of light, the law of addition of velocities of The researchers still give the result that the total speed is lower than that of light. That is, one observer can measure a particle moving faster than light and relative to another observer the particle can appear to be moving at a speed smaller than light.
Also, it follows from the equation of the researchers' theory, that a spaceship that initially moves at a speed greater than the speed of light and accelerates faster and faster, will lose more and more mass, until at infinite speed the mass becomes zero.
The researchers' theory is interesting for the following reason: when they proposed the tachyons, objects whose speed is higher than that of light, their movement required complicated mathematics, such as imaginary masses and complex physics to ensure significant results. On the other hand, the researchers' theory stems from a mathematical model that does not require complicated mathematics and imaginary numbers.
The researchers' theory is a logical extension of Einstein's special theory of relativity, but it is valid for relative speeds that are higher than the speed of light. The new theory is consistent (compatible) and complementary to Einstein's theory of relativity and it also derives from the same mathematics as Einstein's. The researchers claim that their theory is valid for relativistic speeds that are higher than the speed of light. Let's say we live in a world where the lowest possible speed in a car is c (the speed of light) and the highest is infinite speed. This is not the world of Einstein's special theory of relativity, but a tachyon world, where new laws apply.
We in no way can know what exists in this tachyon world, because the theories of researchers like Einstein's theory of relativity show singular behavior (stop working) when the relative speed is exactly equal to the speed of light. This is an interesting point worth dwelling on. Let us imagine a world like that of Alice in Wonderland. There are two worlds: one of Alice and the other world of the mirror. These are two parallel worlds. In the story "Alice in the Looking Glass", Alice can jump from one world to another by crossing the mirror. Let's imagine that the mirror is the limit v = c, that is, the speed of light is called a singularity. The mirror splits the world into two: our world where everything moves at speeds lower than light and the world of tachyons where everything moves at speeds higher than light. In this state, a tachyon will never be able to jump through the mirror or through the singularity towards the world of speeds lower than light; Conversely, an ordinary particle would not be able to jump from our world towards the tachyon world.
From this, is it possible to exceed the speed of light and is what exists in the world beyond the singularity a different theory, a sort of daughter theory to private relativity or a sister theory to relativity? There are actually two questions here: the first, is it possible to cross the limit of the speed of light, the singularity. According to Einstein's special theory of relativity, the limit of the speed of light cannot be crossed: no signal can exceed the speed of light and no body can be accelerated to and beyond the speed of light. According to the theory of the researchers, which is a theory that applies to the world beyond the singularity, different things occur in this world than in Einstein's special theory of relativity, and therefore it is a theory that is not Einstein's special theory of relativity, but the researchers claim that it is consistent with it. what do you think?

95 תגובות
Moses
Today there is a hypothesis for what happened 13.8 billion years ago. The hypothesis comes from a good theory (explains the existing, predicts the future and can be refuted). The hypothesis is supported by diverse observations.
Your hypothesis contradicts all of this, and is also illogical. How could it be that the universe started small and empty? The material that exists today was created from what? and why?
Hubble's law shows that if a galaxy is twice as far away then it is moving away eight times as fast. If we don't assume that the speed of light is constant, then there is no reason to think that the universe at all started at a point.
It is not at all clear to me what you meant by your tensor.
Friends
I am aware that this argument between you took place five years ago and yet I would like to add my own.
Like Lemair, the cosmological constant in general and dark energy in particular appear to me to be artificial. Reminds me of the situation in physics before Einstein, when they added ether. But first I want to suggest another reason for the red formulation, which is not related to the cosmological constant.
The assumption of the evolution of the universe.
The universe was "born" in the big bang. In the beginning it was very small and empty, so time had no meaning. This is a 4D Euclidean universe. As the universe expanded, time became more significant and thus a XNUMX-dimensional space-time, the Minkowski universe, was created. When the first stars were formed the universe warped and warped and thus the Riemann universe was created. Everyone agrees that our universe today is expanding and expanding, but it is possible that in the future this expansion will stop and the universe will begin to contract. Some say that in that case time will go backwards. In any case, the properties of the universe will again change. I want to say that our universe is subject to evolutionary changes. If so, then universal constants, such as the speed of light, should also be affected by these evolutionary changes. In other words, the speed of light may have changed during the evolution of the universe. If we accept this assumption, then the distance to the distant galaxies, as known today, is not correct and therefore the size of the universe is also incorrect and the distances between the distant galaxies are incorrect. I know that experiments are being done today to test the existence of evolutionary changes of universal "constants" and the last word has not yet been said on the subject. Nevertheless, it is worthwhile, in my opinion, to discuss this possibility and try to examine its effect on redshift.
Assumption of the absence of evolution of the universe.
Suppose our universe was "born" crooked and distorted. I want to say that the curvature of the universe is not a result of large masses, but is an inherent property of the universe that can be described by an internal distortion tensor. what do you think?
Interesting article. But... the real extension of special relativity is not theoretical to a world faster than light but to apply the same principles that gave birth to relativity to the world of mathematics. The one who managed to do this is the English mathematician George Spencer Brown who published in 1969 the revolutionary book Laws of Shape. Laws of Form. The philosopher Wittgenstein already had the basic idea and it is to see the act of pointing at an object as a mathematical act for everything. The operation is called differentiation, it has a special notation, but if we just mark it right now as parentheses, then the formal system maintains two simple reduction laws ()=()() =(()) . An example of a simple exercise = (())=(()())
Normal logic is a special case of this system. The acceptance of the new mathematics by the scientific community will make it possible to better understand the paradoxes that exist in quantum theory today.
Spencer is approaching the age of 90 today and I hope that he will receive the proper recognition from the scientific establishment in his lifetime!
Thanks for the honesty (literally).
And on what, to the best of your knowledge, do the researchers base their hypothesis that the wavelength of a photon passing through space changes as a result of the stretching of space and in direct proportion to this stretching? (Alternatively, on what basis do they rule out the possibility that the cause of the expansion of space is a and the cause of the lengthening of the wave is b and that there is no correlation between these factors)?
Yes
deer,
The whole debate between us broke out here with your assertion that "as Nissim pointed out - your diagnosis as if there is a "real cause" for the red shift, but no "dark energy" is a very puzzling diagnosis".
In your current message you write:
"The cosmological redshift is due to the expansion of the space between two distant galaxies".
Can I understand from this that you agree with the opinion of the researchers that there is a "real cause" for the cosmological redshift, and this cause is the expansion of space, which causes the stretching of the photons passing through it?
Yes, or no (no pun intended)?.
In the event that the universe is indeed expanding in an accelerated manner, then it is doomed to the so-called "big rip", in which case all the atomic structures disintegrate into subatomic particles, since the connection between them is weaker than the dark energy that accelerates the universe.
Meyer,
My education in physics is also not based on entries in Wikipedia, but in my experience, Wikipedia is not wrong for the most part, at most it is inaccurate. The cosmological red shift is due to the expansion of the space between two distant galaxies and thus it creates exactly the Doppler effect - the slowing down of the arrival rate of photons and the lowering of their frequency due to the change in the distance between the source and the observer.
The expansion of the universe was predicted and confirmed experimentally even before it was thought that there was "dark energy" in the world and it does not require its existence. According to the theory of relativity there are three possible models for the universe (Friedman solutions to the field equation) - all three assume an unstable universe, that is, a universe that at least in some of the phases and in 2 of the three solutions in all of them, is in the process of expansion - the expansion of the universe in the way that Hubble accelerated is explained in an excellent way in the theory which existed even before the experiment confirmed it.
The problem is that none of the models explain accelerated expansion in the absence of a cosmological constant, you can add the same cosmological constant or dark energy and then the models explain the accelerated expansion. The problem of adding a cosmological constant is that adding it does not contradict anything, but it seems artificial, it does not relate to anything we know other than it and it is not clear where its size comes from (referring to fine tuning that Perlmutter mentioned in his article).
Obviously, as of today, not enough is known to say that everything is understood,
On the other hand, it is clear that as of today:
1. Most physicists accept the model called lambdaCDM according to which the universe contains a cosmological constant and is the cause of its accelerated expansion:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lambda-CDM_model
2. The cosmological red shift results from the expansion of the space between the galaxies, it is quantitatively calculated according to the theory of general relativity and in particular by the Doppler shift.
deer,
My education in physics is not based on Wikipedia entries, and my reading comprehension in English is at the level of a native speaker.
I repeat: there is nothing to do between cosmological redshift and the Doppler effect.
In cosmological redshift, the light leaves a galaxy that is at rest relative to the galaxy that the light will reach in the future, and it arrives at a galaxy that is also at rest relative to the galaxy from which the light was emitted in the past. Its wavelength is redshifted for the millions and/or billions of years in between and the million dollar question is "why". One thing is clear: it is redshifted not as a result of a relative velocity between the galaxies, and this is in contrast to the Doppler effect caused by a relative velocity between the source and the target. If the meaning of this difference is not clear to you, I will bother to look for you a link to one of Hubble's own articles, or of someone who quotes his words.
According to the researchers, it is highly improbable that the cosmological constant is the cause of the expansion of the universe. (See for example the last two paragraphs on page 57 of Perlmutter's article to which I referred in response to Olly Yes's request).
Therefore, although I am not a follower of the theory of relativity you have nothing to complain about me on this point, and you should direct all your complaints to those who are looking for dark energy.
Meyer,
Tell me, are you serious?
There is no connection between redshift and Doppler effect and that is indisputable?
Read this (in Hebrew, may it be convenient...):
http://he.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D7%94%D7%99%D7%A1%D7%98_%D7%9C%D7%90%D7%93%D7%95%D7%9D
And as for the derivation of the Doppler effect for light from the theory of relativity, it is explicitly written about the Doppler effect:
"The Doppler effect in electromagnetic waves is formulated differently because the speed of electromagnetic waves is the speed of light, which is a constant speed in any system. The formulation of the Doppler effect in this case is based on the special theory of relativity, but the result is similar to the result in sound waves."
The redshift seen from distant galaxies behaves exactly as expected from the Doppler effect and therefore the claim that the effect is not true is the claim that the theory of relativity is wrong.
And as for the cosmological constant:
Einstein gave it up and rightly so because it seems to be something strange that has no explanation as of now, and even so it is compatible with the theory of relativity unlike for example your proposal to replace the Doppler effect. The theory of relativity assumes that the world behaves according to a certain symmetry (Lorentz invariant theory), the cosmological constant is the only way to add something to Einstein's field equation in a way that does not damage this symmetry - if you want to add something else, you are basically claiming that Lorentz symmetry does not hold - maybe you You're right, but you'll have to find good reasons for it.
Ehud, here is the question in detail:
If you photograph the sky with a high resolution camera with the moon in the center from the earth (384,000 km), it will occupy a small part of the image and you will hardly notice the details. If you use the exact same camera and photograph the sky at a distance of 384 km from the moon, it will fill almost the entire image and you will notice many details. Same as above if you use zoom.
In my understanding, if you take a picture of the moon with the same camera that passes by KDA at such a high speed that the longitudinal contraction will be 1000:1, you will see the same size and details of the moon in the picture as if you took a picture from a distance of 384 km or if you used zoom. (The camera is activated only when it "touches" its sister stationary on the ground).
Am I wrong? where? And if indeed I'm wrong, what exactly is the length contraction?
Israel
Again your example (from the brochure) is not related to your question about the moon
to which I answered you. In the example there are two systems: the laboratory system
and the particle system when the comparison is between the systems regarding how
The movement of the particle is seen in the question about the moon, it is about what is its shape
The moon as it appears from two different systems.
Dear friends, thank you very much for the articles, I have not read yet, I will read for the next week.
In the meantime, enjoy the weekend and continue to argue patiently (-:
deer,
Further to my answer to miracles:
Cosmological redshift - it has nothing to do with the Doppler phenomenon, and this is agreed upon by all those involved in the field without exception.
Relativity does not predict cosmological redshift.
The theory of relativity allows for a cosmological constant, but the father of this theory preferred to get rid of this forced invention in itself and considered it an embarrassing mistake.
Just as a reminder: Einstein invented the cosmological constant to explain why the universe is stable and does not collapse in on itself as a result of its own gravity. When Hubble discovered the redshift and it became clear that the universe was actually unstable, Einstein was very happy to get rid of this ugly invention of his.
From the reasons I wrote in my answer to the miracles, there is no reason to put this invention back in the back door just because someone (Hubble) once said something that seemed right at the time, and someone else (Perlmutter and Co.) adheres to it as a Sinaitic Torah.
Relativity works fine even without a cosmological constant, and if so why do you find that my suggestion to give it up means giving up relativity? You don't have to throw out the bath with the baby.
Miracles,
I understand very well what Hubble saw and you are wrong that he did not guess. If you continue to insist and are too lazy to look for Hubble's explanation of the source of the cosmological redshift (which by all accounts is not a Doppler phenomenon), I will bother to look for the exact quote of his words for you.
Hubble claimed that cosmological redshift is due to the expansion of space. Space stretches and along with it the wavelength of the light passing through it stretches. It is a guess, since it is not accompanied by a physical explanation, and an experiment cannot be conducted to disprove it.
Now, as long as the redshift was linear with distance, this Hubble guess is nice, neutral, and harmless. Once it was discovered that this was not the case, the right thing was to doubt this guess and try to find another explanation, which does not involve the expansion of the universe with the cosmological redshift.
In fact, two curves can be drawn:
One curve will describe the expansion of space as a function of time as we would expect from a big bang without a cosmological constant, the other curve will describe the expansion of the wavelength as a function of time according to the findings of Perlmutter et al.
The curves will overlap and be linear in relatively short distance ranges (approximately up to a redshift of 0.1)
and will begin to separate from each other at longer distances.
What did Perlmutter and Co. do? Since, according to Hubble, the curves must overlap (the rate of expansion of space is equal to the rate of lengthening of the wavelength), they "matched" the curves to each other by assuming that the expansion of the universe is accelerating in the last 7 billion years.
My argument is that the curves should not be adjusted to each other, since no one has really proven that there is a connection between the expansion of space and the decay of the wavelength of a photon traveling through space.
It is possible that the lengthening of the wavelength is due to a physical reason that has nothing, not even half of it, to do with the expansion of the universe.
I repeat and emphasize: I did not say that Hubble was wrong. I said it was stupid to stick to his guess as a Messianic theory, after new findings were discovered that do not fit with a conventional big bang with no cosmological constant and no dark energy.
Furthermore, I contend that Hubble himself would have said what I am saying if he had been alive when the supernova polls were published in 1998.
skeptic,
Where did you get the impression that I deny the big bang?
And also regarding the consensus - I do not deny. I only doubt the reasons I wrote and will continue to explain them in response to the words of Nissim and Zvi.
Meyer,
As Nissim pointed out - your diagnosis as if there is a "real cause" for the red shift, but no "dark energy" is a very puzzling diagnosis.
The red shift as a result of moving away can be obtained even from relatively simple considerations of special relativity, and its extension is given in the framework of general relativity.
General relativity is a fairly successful theory that has been tested in a large number of tests and so far no places where it is wrong have been discovered. General relativity allows for a "cosmological constant" - an energy of the void that will create an accelerated expansion - so far the dark energy behaves completely like that cosmological constant so that mathematically, the dark energy does not contradict anything, its problem is that so far we have no idea where it comes from physically and why It is smaller by 120 orders of magnitude than a naive calculation would suggest.
What you are saying is something like this:
I don't believe there is dark energy even though it doesn't fundamentally contradict what we know about the world, because we still don't know enough to tell me about it. Instead, I prefer not to believe that the redshift is proportional to the speed difference (actually - I don't believe in general relativity) - in my opinion there is something else (which of course I don't know what it is) and it is the cause of the redshift.
In the bottom line, you are proposing to throw out an old proven and logical theory, because scientists today still do not know everything about something very weak that was first discovered 15 years ago.
In my opinion, it is possible that one day they will discover that general relativity is wrong - it is more correct to say that it is not accurate within certain limits, but I am quite sure that one of the last things that will hurt is Doppler shift!
Meir
Hubble saw in the observations that there is a linear relationship between the distance to the galaxy and the speed of its retreat. He didn't try to explain why it was and what it meant. He was an astronomer, not a cosmologist. Unlike you, he didn't guess anything.
Are you willing to explain why you claim that Hubble is wrong?
And your weird paragraph about "real factor" vs. "dark energy" is just weird. It is clear to science that there is a serious problem here - after all, there is an inaccuracy of 120 orders of magnitude!!!! That's what science says, not some blather on a blog……
And again... “The baseless premise of grief” … investigate before you slander …..
maybe yes …
There are a large number of articles, for example search Harvard: http://www.cfa.harvard.edu/supernova/HighZ.html
Cornell also has several famous articles on the subject.
Meir
Be careful not to deny the "consensus" of distant cosmology (including the Big Bang).
The website owner denounces every "consensus denier" as if he has unfair interests to deny, as if he is funded by the enemies of science, etc.
maybe yes,
Get a link to a popular article by Saul Perlmutter:
www-supernova.lbl.gov/PhysicsTodayArticle.pdf
It all starts with the fact that in short ranges the luminosity of type Ia supernovae decays as a more or less linear function of the square of the distance if it is assumed that the rate of expansion of that space is constant, but in ranges of about 7 billion years the decay increases beyond what is expected from the expansion of space at a constant rate. From this, the researchers concluded that the expansion of space is at an increasing rate in the last 7 billion years, which causes the light emitted from distant supernovae to travel a longer distance in space and appear to our eyes with a weaker intensity.
Personally, I am clear that this awarding of the Nobel Prize will turn out to be a sad joke, because at its core it relies on Edwin Hubble's physically baseless conjecture that cosmological redshift results from the fact that a light wave is "stretched" as a result of the stretching of the space through which it passes. The researchers adopted this guess only because they could not find a more reasonable explanation (and of course thanks to the fact that his father is Edwin Hubble, a respected researcher whose respect and right to make guesses I do not disrespect).
But decades later, after the baseless guess had already settled without justification, came the surprising results of the Ia supernova surveys. Instead of going back and in light of the strange findings to re-examine the baseless premise of the mourning and challenge it, the researchers continued as if it was a teaching to Moses of Sinai. From here to the conclusion of "dark energy" the road is short.
In conclusion, the researchers replaced a cow with a donkey: instead of the million dollar question being "what is the real cause of cosmological redshift", they seriously ask "what is the mysterious dark energy", a question without scientific value as long as there is no answer to the previous question, but valuable for the purpose of receiving prizes and research grants.
This is how science works (at least for now).
sympathetic.
On page 12 below it is stated that due to the shortening of the length the distance of 20 cm that the particle travels is only 3 cm for him. On page 13 there is a picture that illustrates my point: in the picture on the right we see the path that the particle takes as the radius of a circle whose size is 20 cm. In the picture on the left we see that the radius perpendicular to the direction of the particle's movement remains 20 cm while the component along the vertical has been reduced to 3 cm.
This is also the explanation given for the lengthening of time: the particle travels only 3 cm in its frame of reference, but for our assumptions, the distance is 20 cm.
Israel
I'm sorry, I don't understand what you're talking about. The example from the brochure
What you brought is not related at all. This is about the decay of a particle
in the laboratory system and the particle system. This example has nothing to do with it
How would a certain object be seen by two observers moving one
in relation to the second.
Thanks Robbie, but it doesn't help me, I'm looking for the m-m-c-a-y-m that brought us to the conclusion that the speed of expansion of the universe is accelerating, not the claim/conclusion, but the findings.
Miracles, I'm not lazy at all, I looked for Perlmutter's article, but it's not open on the Internet.
There is an option - maybe - if you sign up for a site that Perlmutter is connected to, but registering for a site for one article doesn't seem relevant until I check other options.
Can you link me to the article I'm looking for?
maybe yes ….
Perlmutter, Schmidt and Rice received the Nobel Prize in Physics a year ago for this discovery.
You are so lazy………..
Read on Wikipedia about the expansion of the universe: http://he.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D7%94%D7%AA%D7%A4%D7%A9%D7%98%D7%95%D7%AA_%D7%94%D7%99%D7%A7%D7%95%D7%9D
In general, there are many articles on the Internet about the subject
Friends, I tried to find an article that presents the findings based on which they determined that the universe is accelerating, I couldn't find it.
Can anyone explain or provide the evidence that the speed of expansion of the universe is accelerating?
sympathetic.
If you look at a full moon, you can measure the angle formed between the central perpendicular connecting you and the moon and the shank connecting you to the circumference.
In my understanding, for an observer who will pass by you at a relative speed, the diameter of the moon will remain as it was, while the length of the vertical will be shortened. Therefore, the viewer will measure a larger angle between the vertical and the shank that connects it to the circumference.
See also pp. 12-13 b
http://www-d0.fnal.gov/~aharel/about/Harel_SR.pdf
If the moon was large enough or the speed was high enough, it would fill almost the entire field of view of the observer.
Israel
The shortened distance is in a given inertial system. That is
A person passing in a spaceship past the stationary observer will see his own spaceship
As longer than the length of the spaceship as measured by me
The astronaut inside her. You keep insisting on asking the mother
The distance between a stationary viewer and a moving viewer will be shortened. First this
is not a measurable quantity, the question is the distance in what time and can be defined here
different times and secondly it is not the distance that changes its length according to
The private relationship.
questionnaire
According to my understanding, the speed of light is constant in inertial systems
That is, systems that differ from each other at a constant speed. in the moment
That you are talking about effects of general relativity you must define
Restores speed because space is curved. you can set
Speeds in small areas where it can be assumed that this is the case
in a flat Minkowski space in which relations can be used
Private but you must define how you glue everything together
these spaces.
Ehud, thanks for all the answers.
And it is impossible without another question: to my understanding, distance shortens with the direction of movement of the viewer, but not in the direction perpendicular to it.
Therefore, if an observer at rest observes a distant straight line perpendicular to it, he will see it as having a length of L and its distance from it as D.
The question: If one observes the one passing by the first one at a speed close to that of light in the straight direction, one will still see the straight line with length L (perpendicular, not changing) but the distance from it as much smaller than D (shortened due to the speed).
And when I say "seeing" I don't mean measurement through calculations, but actual sight, with the eyes.
a question :
Does gravitational acceleration affect the speed of light? The question is derived from the NASA exercise
It makes sense to speed up the speed of a spaceship and puts it into orbit around say Saturn
And from there it is sent on at a higher speed than it arrived.
Although gravitational attenuation is the name of the observation, the meaning is whether the light is affected by the force of gravity
that can speed up or slow down his speed?
And another similar question, as light cannot escape from a black hole, is light on its way to the black hole
Can't accelerate beyond the speed of light?
I'd love to understand.
Thanks.
Israel and miracles
I think the intensity of the source does not depend on the speed of the source relative to the viewer. effect
Doppler will indeed change the frequency and this is equivalent to a change in the energy of the photons
that the source emits but on the other hand the relative lengthening of time will cancel out in my opinion
The first effect. The basic question is whether the power of the source is relative invariant
And I believe so, because it is a 4-dimensional integration over time and space. integral
4 dimensional is Lorentz invariant.
From the article it becomes clear that as the speed increases towards infinity, the mass decreases towards zero.
It is also interesting if the body lengthens as the speed increases since everything is the opposite in this theory.
Avi Blizanevsky, congratulations!
Yair
There are many, many differences. Sound is not a movement of particles. He is a wave in the middle, and in the light there is no middle. This is the important difference, which makes the speed of light independent of the frame of reference. In the context of sound there is a speed of the source compared to the medium, i.e. absolute speed.
The singular point in the speed of sound is due to the fact that the particles of the medium are not enough to move sideways, therefore there is a high pressure at the front of the movement. In the light of the source it does not "move" the middle to the side, because there is no middle.
In practice, when a plane passes the speed of sound, nothing special happens, because the parts of the plane pass the speed of sound at different times, this is because there is an uneven flow in the space of the air.
a question:
What is the difference between passing the speed of sound and the speed of light?
Changing the speed of a liquid so that it exceeds the speed of sound is not simple, and there are unique and opposite phenomena than a liquid with a speed lower than the speed of sound. And there is also a singular point where the speed of the liquid is equal to the speed of sound.
If the phenomena are similar, why is it possible to pass the speed of sound but not the speed of light?
Boaz
The acceleration of galaxies has nothing to do with Hubble. He actually thought that the galaxies were slowing down.
The galaxies have long passed the speed of light (as far as I know) and there is no problem here. The galaxies themselves are not accelerating - it is the space that is expanding at an accelerating speed.
And what will happen is that in the future the universe will be a very dark place. We will see a completely different universe, and moreover, we will never be able to know that what we see is the whole universe.
Now imagine that a cosmologist in the future will claim that there are galaxies that move away faster than the speed of light and cannot be seen - all the philologists will say that this is not a theory at all because it cannot be disproved....
Miracles.
Well, Shawn. Consent is an important thing.
Let's hope that Ehud will agree with my summary, or come up with another explanation.
Good night from Los Angeles.
According to Hubble, galaxies are accelerating outwards.
When will this acceleration reach and exceed the speed of light and what will happen to the universe then, if at all?
Israel
In the example I showed that the distance to the body does not depend on its speed. You claimed that the theory of relativity claims otherwise. that's it.
And again - the intensity will not be the same, because the energy of each photon definitely depends on the speed of the source. What I'm saying is that the distance doesn't matter, but the direction of the speed certainly does.
And regarding my photon - yes, we say exactly the same thing. What I tried to show is that the distance to a photon does not depend on its speed.
And regarding your photon:
From his vantage point, the distance is 0, not 4.3 light years. If a spacecraft flies at a speed close to the speed of light, the distance for it is shorter than 4.3 light years, and tends to 0 as its speed tends to the speed of light.
sympathetic.
I'm not looking for paradoxes, just answers to questions. Actually your answer solves my question. I just want to make sure I understand correctly:
If a source of electromagnetic waves has a constant power, then at some point in the universe that is at rest relative to the source (a spaceship for example), any two or more meters that pass each other will measure the same intensity as the signal received from the source, and it does not matter what their speed is relative to the source.
In fact, if they know the strength and frequency of the source, they will be able to deduce by measuring the signal and Doppler what is the distance of the point to the source, and hence the amount of time that has passed since the signal was transmitted until it reached that particular point, a time that all the surveyors can agree on, regardless of their instantaneous speed or their history .
I understand it right?
Miracles, maybe I missed something.
Can you show me where I didn't refer to your example or something you said?
Israel Shapira
1. It's a shame you didn't try to understand my example. Maybe she's wrong, but your non-attention doesn't contribute anything to the conversation.
2. Too bad you didn't try to understand your example! She never says that the distance is getting shorter. What she does is explain the twin paradox (which of course is not a paradox at all).
I'll give you an even simpler example, please consider it, okay?
A photon that leaves Alpha Centauri towards us travels at the speed of light. And yet the distance to it is the same as the distance to the star in question - about 4.3 light years. After all, the time of his arrival is 4.3 years. Of course - in the world of the photon, time is simply 0.
If you don't see anything wrong with my example you should get it - that's how it works...
Israel
You forget the dimension of time and only consider distance. What is the strength of a source? A number
The particles it emits per unit volume per unit time. Because what is kept in the relationship
It is the four volume (space full of time) after all the strength of the source will not change as a result
His movement on the shortening of space will be compensated by the lengthening of time. These paradoxes are old
Almost like relativity, do you expect to find something new that hasn't been thought of?
and apply the logic that mathematics gives us
Cause and effect does not make sense according to our logic
But our logic is limited to the senses
"I don't think the distance is getting shorter, from the example I gave."
But according to relativity he is. The solution of the twin paradox in the framework of special relativity speaks of the fact that the distance traveled by the moving twin is small because of its motion.
And hence my question: what happens to the strength of radio signals received by a remote receiver? After all, they are inverse to the distance squared. So if the distance is shortened, doesn't this require that they be received at a higher intensity?
I don't think the distance is getting shorter, from the example I gave.
A body shortens both when it approaches and when it moves away.
I really don't have any idea what is happening that the body is getting shorter - after all, the distance to the two ends then probably changes...
I'll think about it tomorrow 🙂
Let's say so.
So what about the shortening of the distance? Exists or does not exist?
After all, according to relativity, the distance to moving objects is smaller than to a stationary object, isn't it?
Now I understand your mistake.
Describe to you 2 objects. One is closer and moves away by 0.9c and the other is further away and moves closer by 0.9c. And describe to you a third object that is in the middle of the distance between them.
What will happen when the two moving objects pass the fixed object?
All three will show us at the same distance - won't they?
"The distance to the object does not depend on the speed of the object. Don't you agree if it is?”
I agree, brother, but Einstein, you understand..
After all, he claims that the distance shortens when the object moves relative to it, so who am I to question?
"Since this is the case, the length of the Milky Way will appear to him to be 12 orders of magnitude smaller (in the direction of progress) than it appears to an observer from the rest system of the galaxy, meaning that the length of the Milky Way will be equal to a million kilometers for him"
For our traveler who passed the first star in the Milky Way, the last star is only a million kilometers away, not a hundred thousand light years. That's why it will only take him 3 seconds to finish the Milky Way and move on, and not 100,000 years.
And we - here we come?
And what's the connection?
You asked if the intensity of a rapidly moving beam would change
The distance to the object does not depend on the speed of the object. Do you not agree if it?
Miracles.
See: http://ofer-megged.blogspot.com/2011/09/blog-post.html
"Let us observe an observer riding on a proton with an energy of 1021eV, passing by the Milky Way a little above the plane of the disk. In this orbit, gravity is negligible, and we are only left with the results of special relativity. In the resting system of the "proton vehicle", it will be the milky way that flies past it. Because of this, the length of the Milky Way will appear to him to be 12 orders of magnitude smaller (in the direction of progression) than it appears to an observer from the rest system of the galaxy, meaning that the length of the Milky Way will be exactly equal to a million kilometers for him. Moreover, our proton vehicle will see the Milky Way galaxy pass by at a speed that is for all intents and purposes equal to the speed of light (of course there is not, and never will be, full equality). Since light travels at about three hundred thousand kilometers per second, it will take a little more than three seconds to cross the galaxy, while the distance of forty kilometers (...) between the Earth and Alpha Centauri it will travel in a little more than one part of ten thousandths of a second... Obviously, during this blink of an eye We ourselves will age in four years and a bit, while the three seconds of crossing the entire galaxy will last for us no less than a hundred thousand whole years..."
The Doppler, as you mentioned, depends on the direction. However, the signal strength also depends on the inverse of the square of the distance, hence my question.
Do particles moving at high speed obey Maxwell's laws?
Israel
Mario Livio's explanation is exactly for the speed constants. The explanation shows that information comes from point to point regardless of the speed of the information generator. Imagine that both planes turn on a flashlight aimed at the viewer at the moment of the collision. Logic says that we will see the 2 lights at the same time. Otherwise - we will see the same event at different times, which makes no sense.
That's my understanding at least...
Regarding your second question. The distance to the radiation source does not depend on the speed of the source. The fact that the length of the source will be shortened (only in the radial direction) is not related to the distance to the source.
But - assuming that the source is moving in our direction - then there is an increase in energy, due to the Doppler effect. Alternatively, if the source moves away, then it will be smaller.
Note that the change in the length of the ray does not depend on the direction of the speed - a receding body and an approaching body will shorten to the same extent. But again - the distance to the body will not change at all.
sympathetic.
I am not disputing the second postulate, just asking if there is an explanation for it.
The mathematical equivalent of a postulate is an axiom. Besides being primary and not requiring proof, it must also be self-evident.
The fact that the speed of light is the same in every system contradicts Newtonian logic, and I was hoping that there might be a physical explanation for this.
Regarding the second question. In my understanding, from the point of view of a body moving at a relative speed relative to the Milky Way, the diameter of the galaxy will be shortened according to the Lorentz transformation. My question is whether, because of this shortening, the strength of a radio signal will also decay to a lesser extent, whose strength is known to be proportional to the distance squared.
Israel
The fact that the speed of light is constant in all reference systems has been established experimentally
Michelson Morley. The only reason to appeal against a Postvalt Fiscal is by me
An experiment that shows its violation. There is no point in saying that maybe the principle of uncertainty is not
Valid, maybe the second law of thermodynamics is wrong. In addition, a physical postulate
Accumulates more and more "power" or backup as the physics on which it is based
It is more complex and special relativity is the basis for field theories
quanta whose predictions have been verified with astonishing accuracy.
Regarding an experiment to measure the shortening of the distance. In an experiment it is much easier to measure time
And there is countless evidence of the lengthening of time in fast systems, whether it is
in cosmic radiation and whether it is a cosmic device. times. Ace, that the clocks on
The satellites undergo relativistic corrections of both special and general relativity.
Regarding the shortening of the length, I think you are confusing lengths. shortening
The length is about the system inside the spacecraft about the lengths inside the spacecraft
as measured by an outside observer.
Detractors will say that this is a mistake, but Plato also stated that the world is continuous, since in his opinion the speed of a thing is equal to the inverse ratio of its density, and therefore a universe that has points without density is a universe with infinite speed, something that he considered impossible.
Miracles.
See: http://he.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D7%AA%D7%95%D7%A8%D7%AA_%D7%94%D7%99%D7%97%D7%A1%D7%95%D7%AA_%D7%94%D7%A4%D7%A8%D7%98%D7%99%D7%AA
1. Postulate B of relativity: "The speed of light is constant for every observer, regardless of its relative speed in relation to the body that emitted the light, or its speed in relation to any other body".
2. The shortening of the length: "If a spaceship moves relative to the observer at half the speed of light, then when the observer looks at its length it is shortened by 13% compared to the length at rest, but those in the spaceship will not see any difference."
3. I believe that Mario Livio's explanation is that it is not possible to exceed the speed of light, not for the constancy of the speed of light in all reference systems. The same explanation holds for any other constant velocity in any system. If the speed of sound for example was constant in any frame of reference, according to the same explanation it would be the upper limit of speed, and it could not be exceeded.
4. I don't understand how the Michaelson-Morley experiment demonstrates the shortening of length. By the way, the Michelson-Morley experiment can be easily explained by the assumption that the speed of light is relative to the light source.
Israel Shapira
1. What is constant is not exactly the speed of light. The principle is, in fact, the maximum speed of information transfer. If this speed is not constant in all inertial axis systems, it can be shown that a contradiction is obtained. I read a beautiful example in Mario Livio: Imagine 2 planes - one coming at you at high speed and the other crossing its path. Imagine the two planes collide. If the speed of light of the approaching plane had connected to the speed of the plane then its light would have arrived earlier, and then we would not have witnessed the collision. Think of the meeting point at a distance X. Light from the perpendicular plane would arrive after X/c seconds but at this distance the light from the approaching plane (let's say at speed v) would arrive after only (X/(c+v seconds.
2. I think the Michelson-Morley experiment is exactly the evidence you are looking for.
3. I don't understand exactly what distance was shortened. I don't think there is a change in distance to the object itself.
Questions for those who understand:
1. Is there a physical explanation that is not a postulate for the strange phenomenon of the constancy of the speed of light in all reference systems?
2. Is there experimental evidence of the shortening of the length in relationships?
3. Is the strength of a distant source of electromagnetic radiation moving very close to the speed of light greater because of the shortening of the distance?
For example: a radio transmitter at a distance of one light hour from a receiver at rest receiving the signals with a strength of X, will the reception strength from an identical transmitter passing by the first one along the line connecting the two devices at a speed of 0.999999C be higher because of the shortening of the length?
*instead of:
which is formulated in trigo gossip terms
should be written:
which is formulated in standard Trigo terms
My impression is that the Australian HILL-COX mathematical model has nothing to do with physical reality, because the model does not describe measurable physical reality (and there are no proof-or-refutation experiments for it anyway).
It has long been known that there is a formal similarity between the functions SINUS COSINUS and their corresponding functions SINUSH and COSINUSH (Euler's formula is especially known which defines SINUS and COSINUS in a very similar way to the definition of SINUSH and COSINUSH). It is possible that the similarity between the two sets of functions (trigo vs. trigo-hyperbolic) is what made it possible to successfully develop a mathematical model for trigo-hyperbolic, a model that has many properties that are similar to the properties of the theory of relativity (which is formulated in trigo-gossip terms). Also the fact that in their model there is a time-like parameter that takes values above the light speed C, is a spicy matter that attracts attention. But imagination alone, as well as the piquant point of supersonic-like speed, are not enough, we need an affinity to a physical measuring system.
The topic of quantum gravity is not related to the article at all, but if it has already been brought up then... the problem
In writing a theory of quantum gravity it is twofold, technical and physical. Technical calculation of
Quantum corrections to general relativity yield infinite sizes. Also in the theory of electrodynamics
The quantum (which deals with the interaction between light and matter, i.e. atoms) infinite sizes were discovered but it turned out
Because you can eliminate the infinite sizes and get astonishingly accurate results. The mathematical process of eliminating the infinities from the Torah is called renormalization and it was Feynman, Tomanga and Schwinger (who won the Nobel Prize for their discovery) who found the way to eliminate the infinite sizes and the resulting Torah was incredibly accurate. The most accurate physical theory to date. Even in quantum gravitation, infinities are discovered that originate from quantum theory, only that they cannot be eliminated. In technical language they say that quantum gravity theory is not renormalizable. The physical reason for the infinities is that the quantum particle responsible for gravitation, the graviton, interacts with itself. While a photon does not "carry a charge" and therefore there is no direct interaction between photons, in gravitation the grouton is a "gravitational charge carrier" or in simple language two grouton attract each other.
Nte
The whole theory of evolution is less "mathematical". Evolution is an explanatory theory and not a mathematical model, like the theories of relativity for example. These predictions only show that there is "something" in the theory.
And to remind you, predictions of general relativity can also be interpreted on the basis of competing theories.
There are many attempts to disprove evolution, based on Darwin's own theorem, if a mechanism is found in a living being that cannot develop in a series of small steps, then the entire Torah fails." At the moment - there are none 🙂
One of the arguments against evolution is that we don't see it happening. This is simply not true - there are a number of examples nowadays where we see species forming before our eyes.
When I wrote above that the theory of general relativity was later formulated in a simpler way, the meaning is that more sophisticated mathematical tools were invented and therefore they made the theory of general relativity simpler, while the classical tensor formulation of the theory of general relativity is quite cumbersome but is relatively simple mathematics.
So thanks for the compliments...
The article is a report on the scientific news and also a discussion of the philosophy of physics. That's right, you understood the article correctly and excellently.
Therefore it is not popular science: the article is a discussion of the philosophy of physics. Avi Blizovsky brings the PhD writers to report to a standard of experts and my expertise is history and philosophy of the physics of special and general relativity.
In fact, the topics I raised in the article represent some of the problems that are asked in the philosophy of physics on the subject of movement at speed on Orit.
A distinction must be made between the classical special theory of relativity, which was formulated by Albert Einstein, and the later formulations. And also between the classical theory of general relativity that Einstein formulated and the later developments. I tried to convey in the article the differences between Einstein's special theory of relativity and the later developments.
Einstein formulated a special theory of relativity using high school level mathematics, maybe a little beyond, barely. The later developments are more interesting from a mathematical point of view because they already relied on Minkowski's four-dimensional formulation and geometric formulations, tensorial formulation, etc.
The classical theory of general relativity is also formulated with the help of fairly simple mathematical tools: indeed tensors, but later it was formulated in a simpler way, even during Einstein's lifetime and he accepted these formulations.
Regarding string theory, quantum gravity. Is string theory quantum gravity? Today many researchers are trying to find a quantum theory of gravity. Here is a chapter number that briefly explains the versions:
http://newphysicsandthemind.net/9.html
Thanks for the examples. was instructive. I have become too accustomed to clean mathematical deductions. These conclusions are less clean (it is possible to think of other mechanisms for reaching the float, and if fossils were not found in Antarctica it would weaken the argument) but these are instructive arguments. I would love to hear about more of these.
First of all, great article.
I've almost lost hope in popular science articles. In my opinion, you bridged the trade-off very nicely between explaining complicated scientific terms and writing fluently for everyone.
A bit about hyperbolic geometry and Minkowski space: Physicists like to describe the world using symmetries. It is both beautiful and educational. We like to say that our universe is homogeneous and isotropic. Homogeneous - the origin of the axes is not important, that is, there is symmetry to the movement. This is equivalent to the linear momentum of a particle in free space being conserved (or the law of constancy, if you will).
Isotropic - there is no preferred direction, meaning everything looks the same at every angle we look at. This is equivalent to the fact that the angular momentum of a particle in free space is conserved (note to professionals - this is exactly Noether's theorem from analytical mechanics: for every continuous symmetry of the Lagrangian, a conserved magnitude can be found).
A bunch is a relatively simple algebraic structure, but you can do a lot of cool things with it. For example - to describe symmetries. We will not go into how and why, but the rotational symmetry (isotropic) can be described by the rotation bundle, which is simply a collection of matrices with certain properties. They can be written so that they contain only sines and cosines of two angles (the circumferential and azimuthal angle) that tell us how many degrees are rotated in each direction.
In the Minkowski space, time comes into play as part of the space. This is not a regular Euclidean space, since its metric (a function that describes the distance between points) is not Euclidean. Moreover, it can be negative. Just as normal rotation preserves size (if I take a pencil and rotate it, its length will not change), so Lorentz transformations preserve the metric of a Minkowski space. The geometry is called hyperbolic because here, too, the collection of transformations also forms a bundle, called a Lorentz bundle. It is also a collection of matrices (this time they are 4 by 4 because there is also the time, instead of 3 by 3 in the rotation bunch) when they can be written as long as they contain only hyperbolic functions (hyperbolic sine and hyperbolic cosine).
A particle that moves slower than the speed of light is called "time-like", and has a positive Minkowski matrix.
A particle that moves faster than the speed of light is called "space-like" and has a negative matrix.
A particle that moves exactly as light is called "light-like" and has a matrix of 0.
Lorentz transformations preserve the metric, so a time-like particle will always remain so (that is, it will not exceed the speed of light), and the same goes for a space-like particle. As for light-like particles, they are never forced to travel at the speed of light. The reason they say that light moves slower in a certain medium is that the photons collide with things in the medium. Some are reflected and some are absorbed, and other photons are emitted in their place. The photons always move at the speed of light, but sometimes they move from Haifa to Tel Aviv via Jerusalem... 🙂
Regarding what scientific theory is: Karl Popper claimed the "principle of refutation", by defining scientific theory in such a way that in principle an experiment can be planned which can confirm or refute the theory. In this sense, psychoanalysis is not a scientific theory, unlike special relativity.
Beyond that, if such an experiment exists, then it provides a certain prediction. If he did not provide a certain prediction, the theory could not be disproved. So it can be rephrased to "a scientific theory is a theory that is consistent with previous observations and provides new testable predictions"
In a sense me, I personally don't recognize string theory as a scientific theory, but that's just me.. 🙂
I hope I was also understood correctly.
Nte
So I do understand evolution….
Here are some predictions:
Australia and America have marsupials. Australia and South America were once connected via Antarctica. It makes sense that fossils of marsupials would be found in Antarctica. And guess what they found?
(I'm not going into the details here - it's from memory) Darwin knew a type of orchid in Madagascar whose nectar is very deep in the flower. Darwin assumed that there was a butterfly in the area that would have a very long tongue. And guess what they found?
There are many more examples……
Miracles The ability to refute goes hand in hand with the ability to predict. You will agree (I hope) that creationism is not a science precisely because it has never had predictions. Nor does she have any internal logic except God determines! The last stop on the earth is silence and basically this closes any possibility of discussion about creationism.
Oops! Come to think of it, I don't know of any prediction of evolution. There is of course great difficulty in predicting: "In 50 years 0.00001% that this crocodile will be longer and 0.00002% that it will be greener". That is, dealing with long periods of time and random mutations. And I would still like to see some statistical prediction. I don't know one.
Evolutionists! I would appreciate help in this matter (which I do not understand here beyond popular and probably inaccurate knowledge)
Neta, change your name to a male name, otherwise you will suffer in life.
Hahahahaha sorry! I have a friend named Neta!
Here it is for you: the aforementioned is written in the female language but is intended for both boys and girls.
Fun!
I'm a boy so please go back and edit all the writing! Thanks I finally got it!
Nte
The whole topic of refutation comes from Karl Popper. He wrote that one of the conditions for a scientific theory to be valid is for there to be an experiment that can disprove the theory. This is beyond two more requirements - the ability to explain observations, and the ability to predict.
There is a problem with this. Think of an experiment to disprove evolution. very hard. It is very easy to think of an observation that would contradict evolution.
of course not. If you dug too deep you would end up in China..
Miracles, of course, the description was for illustration only.
Neta, why not uniform?
And why are we a special point?
Each and every point is special from its point of view, I see myself as the center and you see yourself as the center.
You see the far point as spreading faster because all the points between you and it are also spreading.
The point closest to me, let's call it A, is spreading, let's say at a meter per second.
Now there are 2 meters between me and A, because my point also spreads by a meter.
Now on the other side of A, there is another point, it is B.
B also spreads, and between A and B there are 2 meters in the direction of the spread of each of them in all directions.
That is, last second, I moved away from A by 2 meters, and from B by 4 meters.
From point C beyond B I move 6 meters away, and so on.
I will demonstrate in a more real and dignified way to close this corner completely in case you didn't understand:
Suppose the universe is a sphere with a radius of 5 meters, and it expands/its radius increases by a meter every second.
In a simple equation we write R=5+T
Suppose that there are galaxies/points whose locations:
A = R:2
B=R:3
C=R:4
Putting T=1, it turns out that the radius is 6
And T = 10, which means that after 10 seconds the radius is 15
I will place the new radii:
When R=6, i.e. after a second:
A = 3
B = 2
C = 1.5
When R=15 i.e. after 10 seconds:
A = 7.5
B = 5
C = 3.75
Pay attention, you are at point A
You don't know your position on the ball, you don't know its radius, and you don't know how much it grows every second.
You only know that when you measure B, it is a meter away from you, and 9 seconds later it is 2.5 meters away from you.
So for you, B moves away by 1.5 meters every 9 seconds, but C moves away by the time 2.25 meters away from you!
So the speed of the far point C is greater than the speed of the near point B, and you might think that it is a variable rate of expansion, when the truth is that the rate of expansion is uniform (again, look at the fact that at the beginning we determined that the rate of elongation R is a meter per second).
I hope I didn't dig too much.
I think that "disprovable" means that it has predictions and it doesn't just explain existing data. After all, it is possible to make many theories that explain the same data. A scientific theory should also not contradict existing data, also explain data that until now had no explanation, and also give predictions
maybe yes or no
You write "... you stand at one end, and I at the other, I want you to me at speed C and I to you at speed C we still won't get there,..."
There is no "end" to the universe. Everyone sees themselves in the center.
To Elijah
I don't think every scientific theory is necessarily disprovable. It's not right to dismiss a theory because we don't know how to disprove it.
So the universe is expanding at a non-uniform rate? What is close to us hardly stretches and what is far spreads quickly? After all, this makes our point special and the universe non-uniform according to the laws of physics
Planted, simply.
If the road (universe) stretches at a speed of half C, you stand at one end, and I at the other, I want you to me at a speed C and I to you at a speed C we still won't get there, we are doomed to "remote contact" I know it won't last, but we can try.
The universe expands, that is, each and every point expands, in the form of spreading, like plasticine is spread, it does not produce more plasticine, it does not grow materially, but becomes larger spatially.
It seems as if each point "splits"/"generates" more points from its surroundings.
(), a second later…
(-) and another second.. (—).. (———)…
Let's say that this point, which is a meter long, "creates" 3 meters, and every meter created creates another 3 meters...
Every second this process is carried out.
So you run to me at a speed of 2 meters per second, and I to you, and let's say that the distance between us is 9 meters.
So the second you run 2 meters to me and I run to you, the space has already extended to 27 meters
In other words, we are currently separated by 23 meters...
From 23 meters between us it becomes 69, and you and I are still running... but moving away.
Now when I look at you moving away, it seems to me as if you are moving away at 23 meters per second, and then at 65, it seems as if you are moving in the opposite direction from me.
But after all, it's not you, it's the space.
One day, because of the acceleration of space, it will seem to me as if you exceed the speed of light, you can even go to sleep, or run to me, it will not help you, you will still move away.
Hope I understood correctly.
By the way of what my predecessor said about the galaxies: the meaning is that space expands at a speed higher than the speed of light together with the galaxies within it that supposedly move under the speed of light. It sounds like cleverness and I also didn't really understand how you can "blame" the space that expands faster than the speed of light and still the galaxy will not exceed the speed of light.
I have a 2000 cc Mitsubishi. I put soil with worm holes from the garden + another worm (to be) in the exhaust.
I put my anger in the car, I went up a ramp, I meant a big and full moon, I started and ran to the side... there was some kefir... and nothing happened!
Trust me, it's all regret
Dr. Weinstein: How does the increase in speed manage with a decrease in mass and conservation of energy? Does the mass decrease more "slowly" than the speed increase?
And are there any predictions for the theory? Or some kind of interaction with the normal world? Otherwise it is only an elegant mathematical development. Beautiful maybe but not physically
Guy, it's okay, don't worry. I didn't understand anything either. And there are many more like us
Nadav and others up here, we need to differentiate between the speed of the signal and the speed of light in a vacuum and the speed of light in mediums with a refractive index like the one in dense mediums: one way to move faster than light is to make light move slower. Light in a vacuum moves at speed c. But let's say we take a dense medium like water, glass or another medium. In such a medium the light slows down and then the particles of course move faster than the light. In such a situation, Cherenkov radiation is created.
Let's say we take a rigid body and bend it on one side. Will the other side immediately move at a speed faster than that of light? Yes, but in special relativity there are no rigid bodies. Therefore, there will be no movement or communication with signals that are faster than light.
It is also necessary to distinguish between three speeds: the phase speed, the group speed and the signal speed. We can have a wave packet whose group velocity will be greater than c. But the signal rate does not exceed c because information cannot move faster than the speed of light.
Galaxies: Light takes time to reach a distant galaxy. If we do not take this factor into account, we will come to the conclusion that the light from the galaxy moves at a higher speed than light - according to the optical illusion we get from the galaxy.
Teleportation or the EPR paradox: the information is not transferred quickly over the orit what is paradoxical is the quantum entanglement of the two particles. It's not that quantum mechanics is incomplete and something is missing that we will now look for, and that is why the information passes quickly through Orit. We accept the laws of quantum mechanics as they are - the Copenhagen interpretation - the quantum entanglement, and also therefore accept the laws of special relativity according to which no information passes quickly through a medium.
Wormholes can apparently allow travel from one end of the universe in space-time to another faster than the speed of light, right? To realize wormholes, you need negative energy, exotic matter and all, so apparently wormholes do not exist.
warp drives that warp space-time to allow spaces to travel faster than light: again to create such a thing requires negative energy and exotic matter just like creating a wormhole.
Eliyahu, it is a problem to disprove or test such a theory experimentally because it is a theory that is valid for speeds that are higher than light - that is, for speeds that we in our world cannot reach. Even if we use a particle accelerator that can accelerate neutrinos... they still cannot pass the light speed barrier.
I did not understand anything
Sounds like a necessary expansion - well done
I am,
No, the passage of the signal in a rigid body will actually be the speed of sound in the same medium
Read: http://www.physicsforums.com/showthread.php?t=536289
I have a question -
If two people hold an iron rod and one side pulls in its direction, then the other side immediately feels the pull.
Doesn't this actually mean that they transfer information between them in 0 time? (In other words, information transfer is carried out at infinite speed. Of course there is a DELAY in their brain for this whole story, but that is not the person here)
In quantum entanglement, the information passes the speed of light (does this exist with the help of tachyons?), even though the entangled particle or photon cannot pass the speed of light.
Gali, interesting article, thank you.
Thanks Glee.
Another question should be asked, and it is perhaps the main question,
Is it possible to transfer information between the sub-C universe and the super-C universe? Can a photon for example or another particle pass between the universes.
'Thoughts' such as telepathy and clairvoyance move faster than the speed of light, as we know.
From the new research we can learn that those who are endowed with these qualities can 'disappear' mass...
Some things in modern physics will never "fit" in my head:
Photons are accelerated to the speed of light, or born with it, it doesn't matter. The fact is that it is a muscle speed.
Also the fact that there is a galaxy moving at a relative speed much higher than the speed of light is almost as amazing as the weak explanation that they move at a lower speed, but the empty space that holds them moves faster.
Swallow, terrible explanations.
Is there any way to disprove such a theory through experiment?
If not, then it is not a scientific theory (although not necessarily incorrect).