Hayadan > Space and astronomy > Solar System
Solar System
- Avi Blizovsky
- April 26, 2024
- One response
Astronomers re-examined 37,000 images taken by Hubble over 19 years of objects in deep space. The reward was finding 1701 asteroid orbits in the asteroid belt, of which 1031 are uncatalogued asteroids. About 400 of these uncatalogued asteroids are roughly less than a kilometer in size
- Avi Blizovsky
- April 3, 2024
- One response
In late March 2024, NOAA satellites detected strong solar activity, including a powerful solar flare and coronal mass ejection (CME), which led to the strongest geomagnetic storm since 2017
- Avi Blizovsky
- April 3, 2024
- 2 תגובות
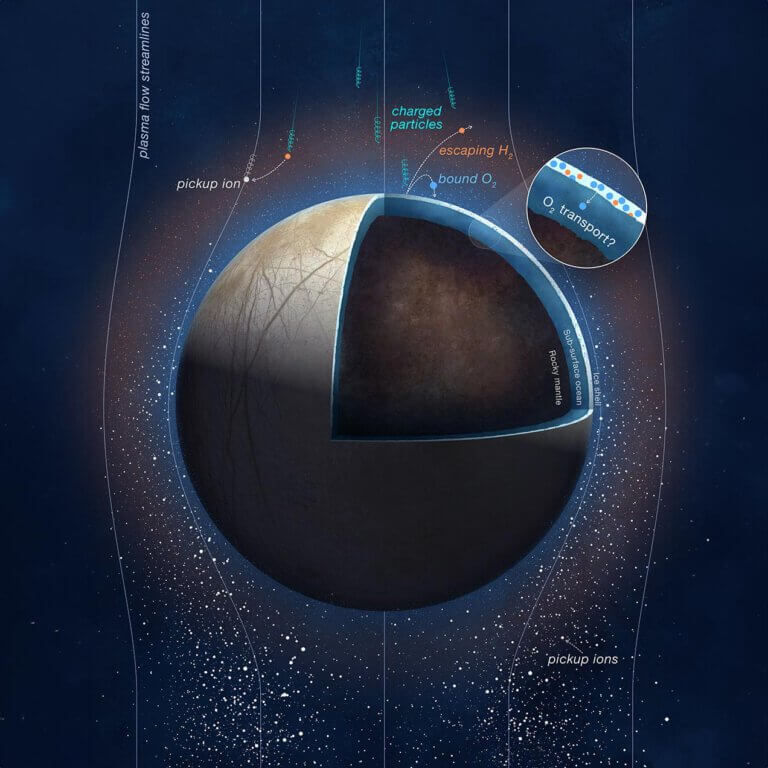
NASA's Juno spacecraft directly measured charged molecules of oxygen and hydrogen from the atmosphere of Europa, one of Jupiter's largest moons. According to a new study by scientists at SwRI and Princeton, these observations provided important constraints on the potential oxidation of its subsurface ocean
- Avi Blizovsky
- April 1, 2024
- One response
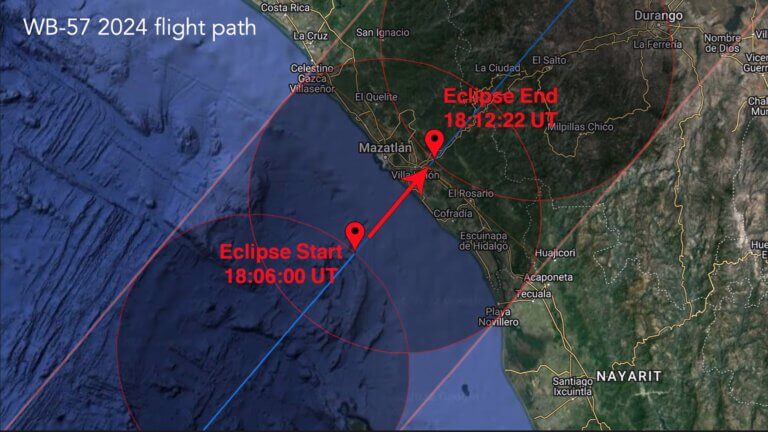
Prof. Caspi, from the University of Colorado presents the results of the experiments in the solar eclipse of 2017, on the multi-channel camera that will fly on a NASA plane
- Avi Blizovsky
- March 19, 2024
- One response
Gallons = small waves. A new international study led by Ben-Gurion University has challenged the prevailing theory that different physical conditions allow the development of galleons that do not exist on Earth
- Avi Blizovsky
- March 4, 2024
- No comments
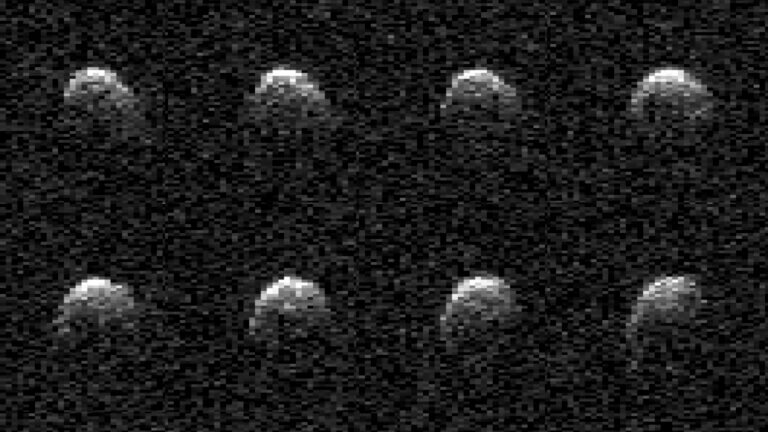
During asteroid 2008 OS7's final approach to Earth on February 2, 2024, the agency's Deep Space Radar collected the first detailed images of the stadium-sized asteroid
- Avi Blizovsky
- March 3, 2024
- One response
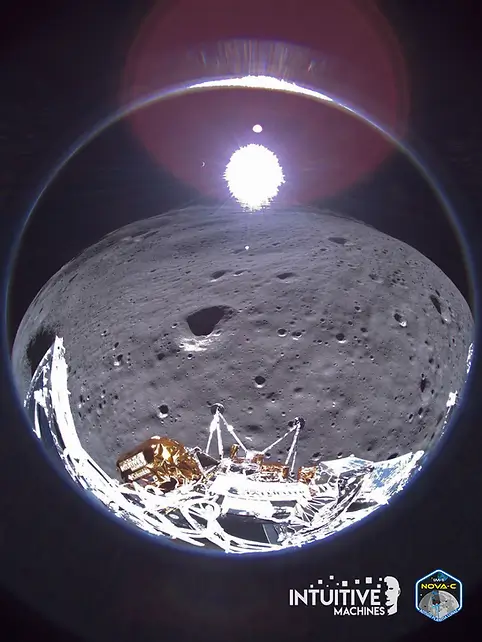
Odysseus landed on its side instead of landing at a vertical angle, which disrupted communication with Earth. Some of the antennas were blocked by the inverted spacecraft, and those that remained exposed were too close to the ground, leading to patchy communications.
- Avi Blizovsky
- February 27, 2024
- One response
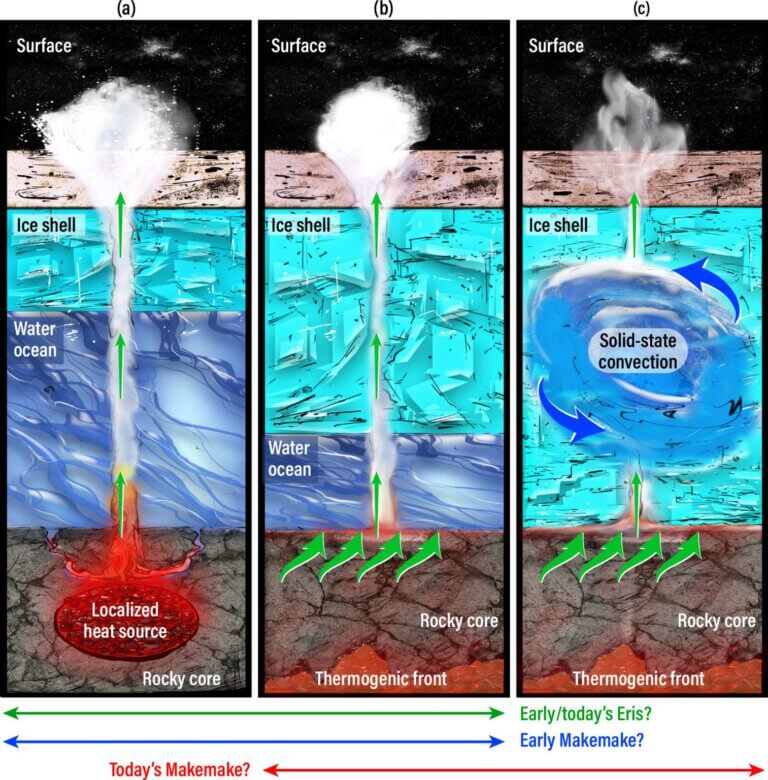
The Webb telescope has observed what appear to be young methane deposits on the surface of Eris and Maki Maki
- Avi Blizovsky
- February 19, 2024
- One response
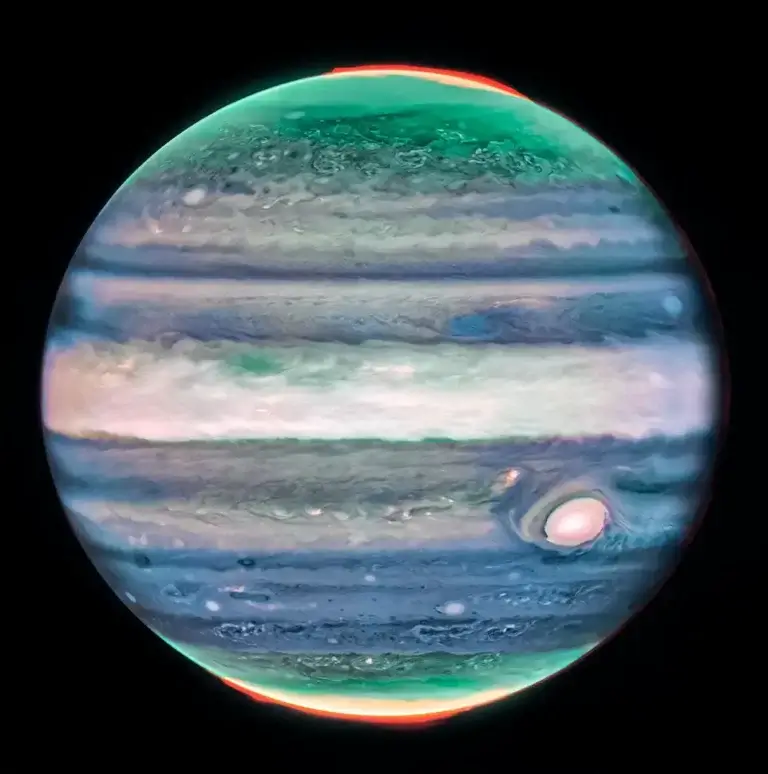
For the first time, NASA activated a tool designed to discover planets many light years away on an object in the solar system, in a study of the winds of Jupiter
- Avi Blizovsky
- December 27, 2023
- 20 תגובות
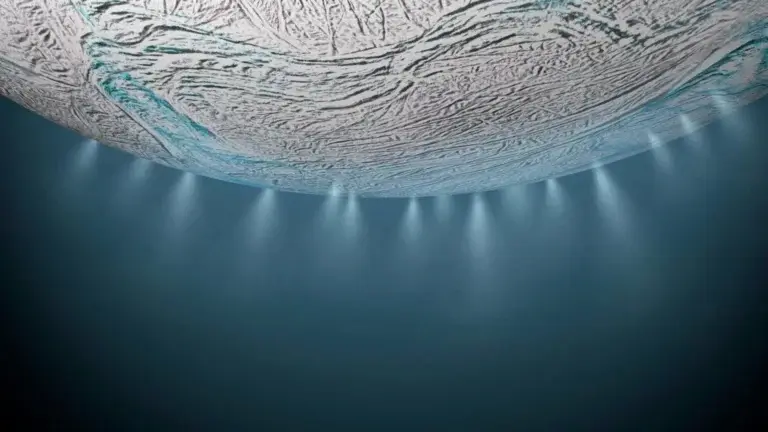
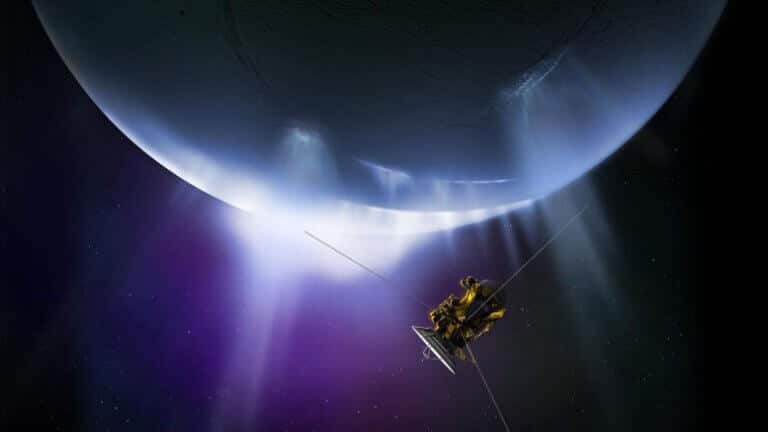
In the new study, evidence for additional sources of chemical energy, much stronger and more diverse than methane production, was discovered: a group of organic compounds was found that were oxidized, and this points to many chemical pathways for the existence of potential life in the subsurface ocean of Enceladus, because oxidation helps to release chemical energy.
- Avi Blizovsky
- November 15, 2023
- 5 תגובות
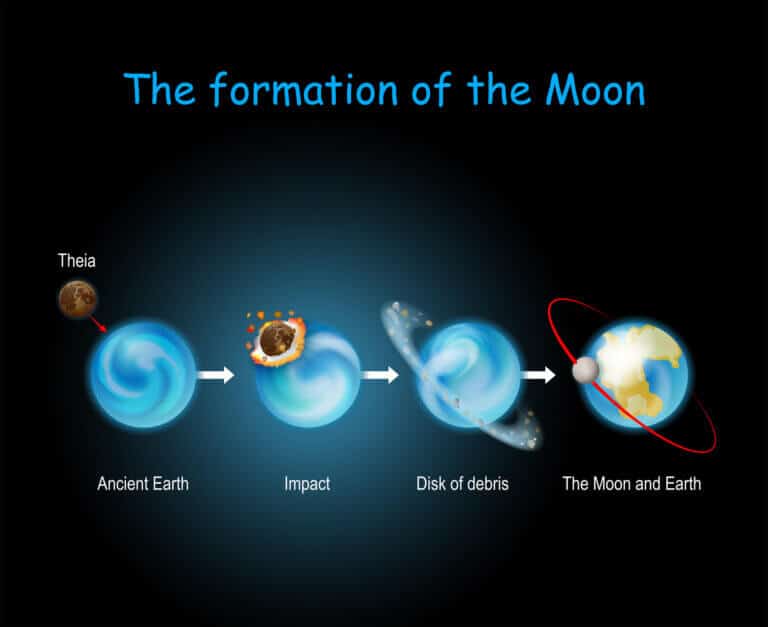
The new research from Calcutta suggests that remnants of that ancient planet known as Theia are still inside the Earth and explain the origin of the "lumps" near the core-mantle boundary. Other remnants of it coalesced to form the moon
- Avi Blizovsky
- November 5, 2023
- One response
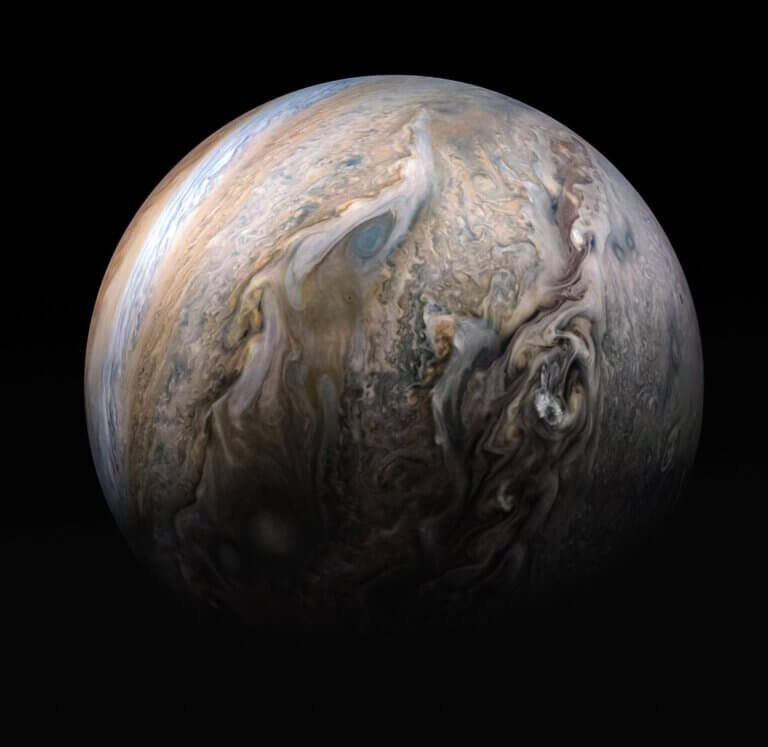
The James Webb Space Telescope discovered a previously unseen jet stream in Jupiter's atmosphere. Similar phenomena have been observed in Saturn, and both may be related to temperature variations in the atmospheres of the gas giants
- Avi Blizovsky
- October 1, 2023
- No comments
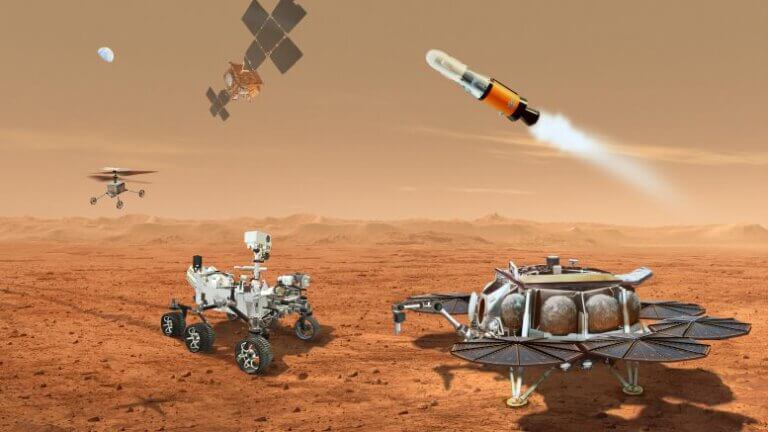
In addition to bringing the first sample collected from Mars to Earth, this very complex mission will include the first launch from the soil of another planet, and also the first rendezvous in orbit around another planet. The return of the samples from Mars is a partnership with ESA (European Space Agency)
- Avi Blizovsky
- September 28, 2023
- No comments
New research reveals mysterious dark and bright spots in Neptune's atmosphere using first ground-based observations with the VLT telescope
- Avi Blizovsky
- August 30, 2023
- 3 תגובות
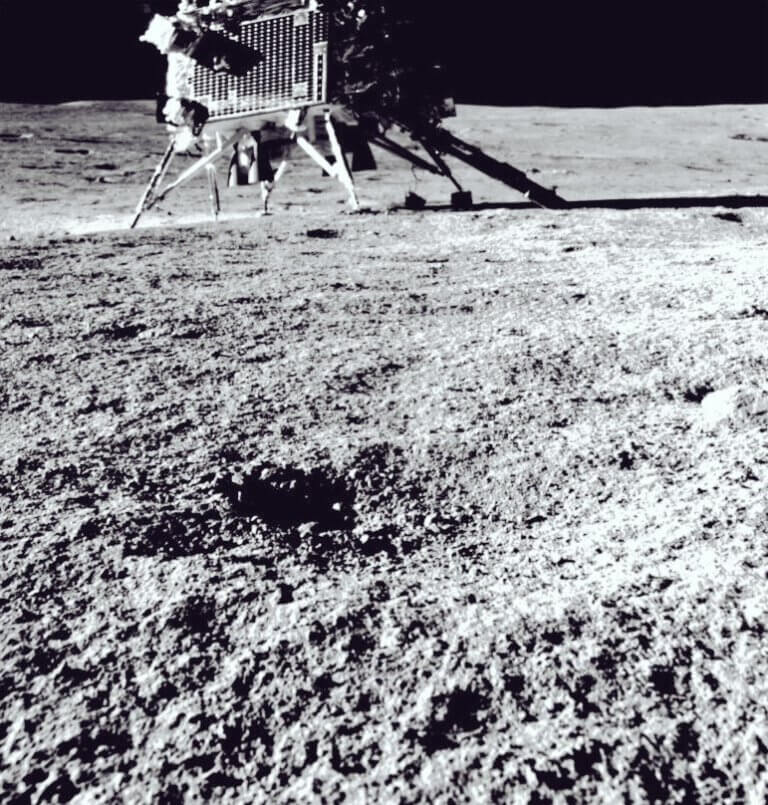
The vehicle discovered a wide variety of heavy elements, but this is the first evidence of the presence of sulfur * The rover will tour the south pole of the moon for two weeks and look for signs of water ice
- Science site The Conversation
- August 22, 2023
- No comments
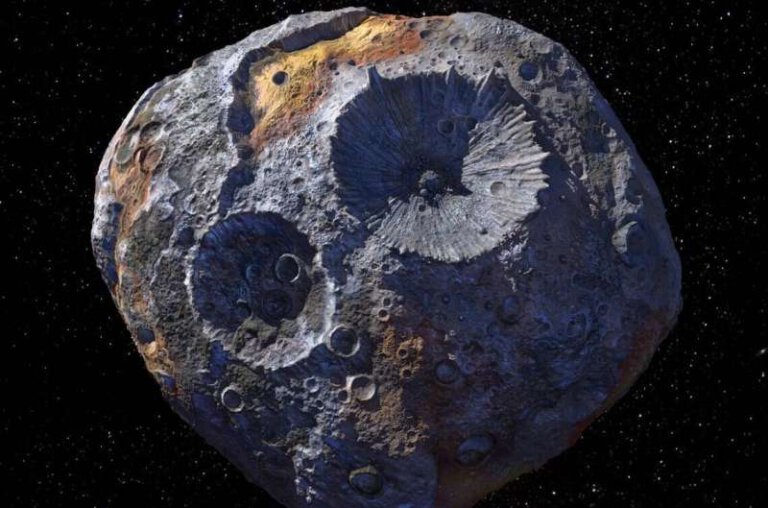
The Psyche spacecraft is launched to the metallic asteroid of the same name to understand what a planet's core looks like
- Avi Blizovsky
- August 12, 2023
- 2 תגובות
The Vera Rubin Observatory's Legacy Survey of Space and Time (LSST) will revolutionize solar system science by discovering a population of previously undiscovered interstellar comets and asteroids passing through our cosmic neighborhood
- Avi Blizovsky
- July 30, 2023
- 2 תגובות
A team led by the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) has created a model of the early impacts on Venus to explain how Earth's sister planet maintained a young surface despite not having plate tectonics.
- Avi Blizovsky
- July 30, 2023
- 3 תגובות
The Bio-SPHERE project investigates potential living and working conditions on the Moon and Mars
- Avi Blizovsky
- July 29, 2023
- 2 תגובות
Io is a raging volcanic world. NASA researchers are specifically looking at a "hot spot" observed by several spacecraft orbiting Jupiter that has grown from snapshot to snapshot
- Avi Blizovsky
- July 21, 2023
- No comments
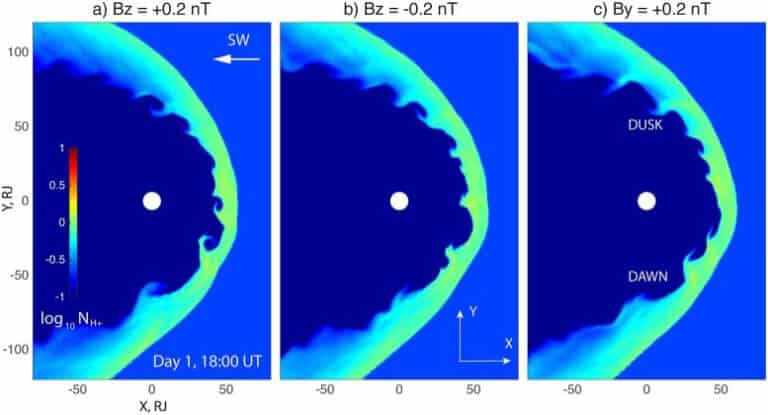
Researchers have discovered that the Juno spacecraft often encounters giant swirling waves at the boundary between the solar wind and Jupiter's magnetosphere
- Avi Blizovsky
- June 14, 2023
- 5 תגובות
This is the first time that such an emission of water has been seen from such a great distance, and in addition, the web allows researchers a direct view, for the first time, of how this emission feeds the water supply of the entire system of Saturn and its rings
- Avi Blizovsky
- April 14, 2023
- 5 תגובות
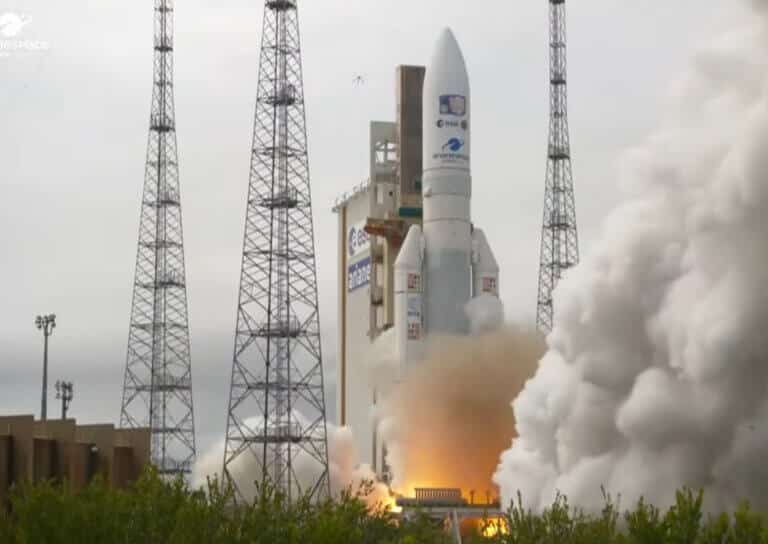
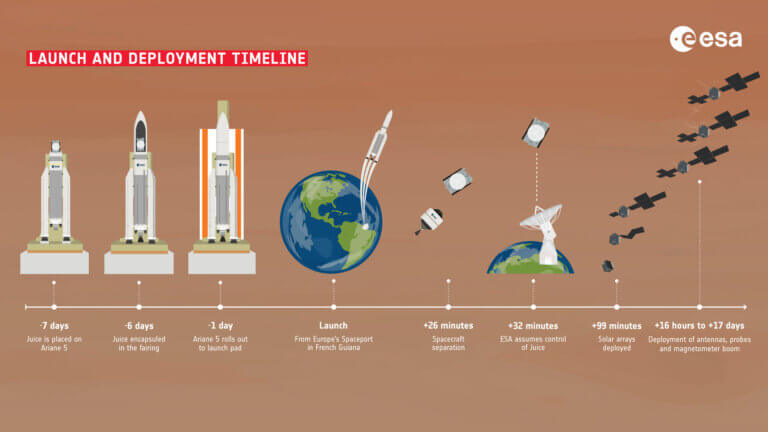
The launch at Coro in French Guiana was postponed from yesterday due to weather conditions * The spacecraft is carrying ten instruments, some of which are also made in Israel * Will arrive in the Zedek system in July 2031
- Avi Blizovsky
- April 13, 2023
- One response
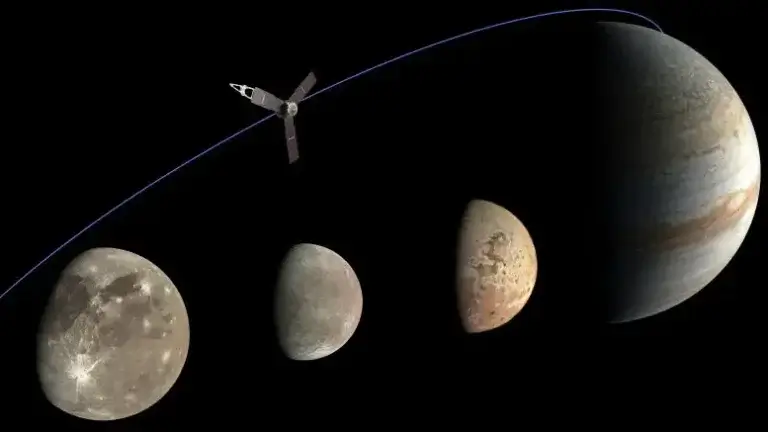
The Juice spacecraft (JUPiter ICy moons Explorer), is a joint project of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Italian Space Agency (ASI), planned to explore three of Jupiter's icy moons: Ganymede, Europa and Callisto. The mission is scheduled to reach Jupiter in 2031
- Avi Blizovsky
- April 10, 2023
- No comments
The purpose of the operation - to find out if the oceans hidden beneath the surface of Jupiter's icy moons have the potential to support extraterrestrial life