Hayadan > Space and astronomy > Astrophysics > Black holes > Page 2
Black holes
- Avi Blizovsky
- February 12, 2022
- 5 תגובות
Holes were able to detect a black hole that matter does not fall into or is not part of a binary system, thus it is not exposed to the eye and to almost any other instrument * Some telescopes that are under construction or ready to be used will be able to detect such individual black holes on a daily basis
- Avi Blizovsky
- December 22, 2021
- 231 תגובות
Very light boson particles are a new type of subatomic particle that scientists have proposed as a compelling possibility for dark matter. But these very light particles, if they exist, are difficult to detect because their mass is very small and only rarely do they create interactions with other matter, this is one of the important properties of dark matter
- Avi Blizovsky
- December 21, 2021
- 4 תגובות
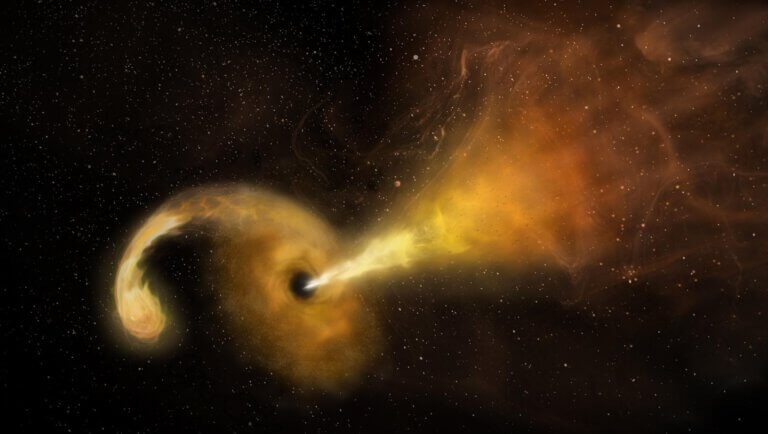
The Hubble Space Telescope photographed a bright knot of gas hit by an invisible jet from the black hole, which is only 15 light years away. The black hole must have looked bright billions of years ago as a quasar, when our young galaxy was fed by lots of infalling gas. But after all this time the black hole is acting sporadically, unwilling to take a nap
- Avi Blizovsky
- November 28, 2021
- 7 תגובות
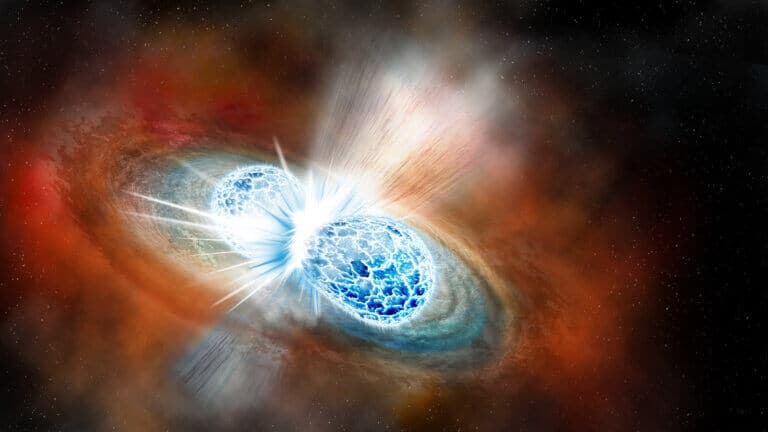
The Laser Interferometer Gravitational Wave Observatory (LIGO) in the US and the Virago Gravitational Wave Observatory in Italy captured the gravitational waves from the death spiral and merger of a neutron star with a black hole, not once but twice. The findings were recently published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters
- Noam Chai
- November 27, 2021
- 9 תגובות
A black hole is a mysterious celestial body. Einstein's theory of relativity taught us a lot about black holes, but many question marks remain about what goes on inside. It is likely that the picture will become clearer as soon as a quantum theory of gravity is discovered, but until then we will content ourselves with the collision of quantum mechanics and general relativity around the event horizon. In this chapter we will discuss the paradox that arose from this collision, the multitude of published solutions and the fascinating developments of the past two years
- Avi Blizovsky
- November 14, 2021
- 7 תגובות
An international team of astrophysicists from South Africa, the UK, France and the US have found a large variation in the brightness of light seen around one of the closest black holes in our galaxy, 9,600 light-years from Earth, and they conclude that it is caused by a massive distortion in its accretion disk
- The Hebrew University
- October 8, 2021
A new international study with the participation of researchers from Tel Aviv University and the Hebrew University confirmed for the first time the existence of the phenomenon of "double cosmic cannibalism" - a rare phenomenon in which a star swallows a compressed object such as a black hole or a neutron star, and the object in turn "devours" the core of the star. The end of the destructive process in a huge explosion in the center of which apparently remains a black hole
- The Hebrew University
- October 7, 2021
- 18 תגובות
- The Hebrew University
- September 16, 2021
A joint study by a pair of researchers from the Hebrew University and Arizona presents a new way to discover the location of medium-sized black holes in the universe. With the help of a reanalysis of X-ray data and observations, the researchers were able to measure for the first time the speed at which the medium-sized black hole rotates, creating an opening for further discoveries and research in the field
- Universe Today
- July 12, 2021
- One response
A rare event that occurred in January 2020 still fascinates scientists, who are trying to learn about the structure of the neutron star with its help
- The Hebrew University
- July 4, 2021
- One response
Researchers from the Hebrew University and France discovered that below the critical size there are factors that prevent black holes from swallowing gas and growing, in galaxies with a mass of more than ten million suns, the attraction is large enough to pull more and more material from the galaxy to the black hole at its center
- Weizmann Institute
- May 1, 2021
Is the origin of a particle that landed at the South Pole in a cosmic event 700 million years old?
- Science site The Conversation
- March 29, 2021
- 9 תגובות
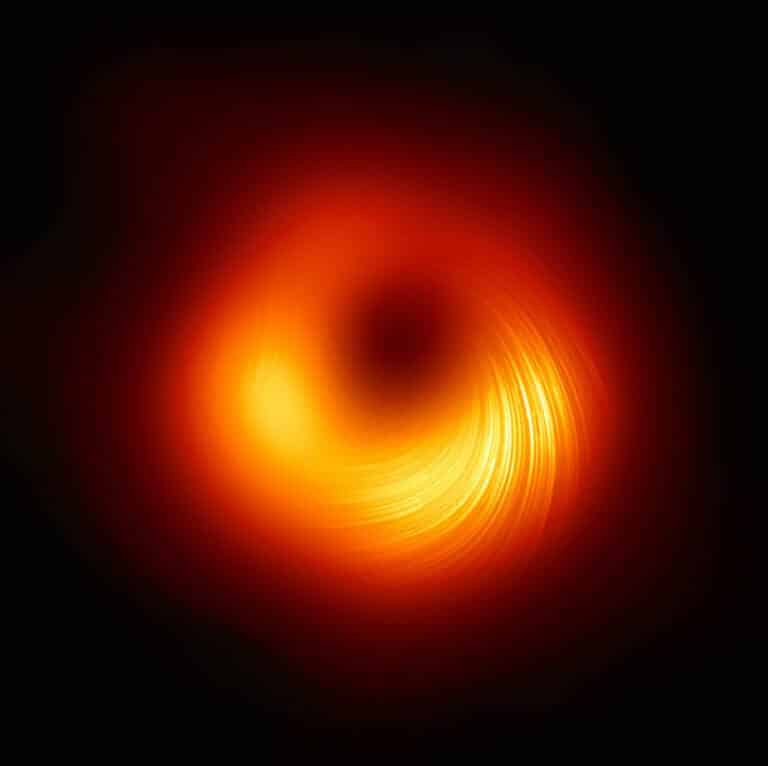
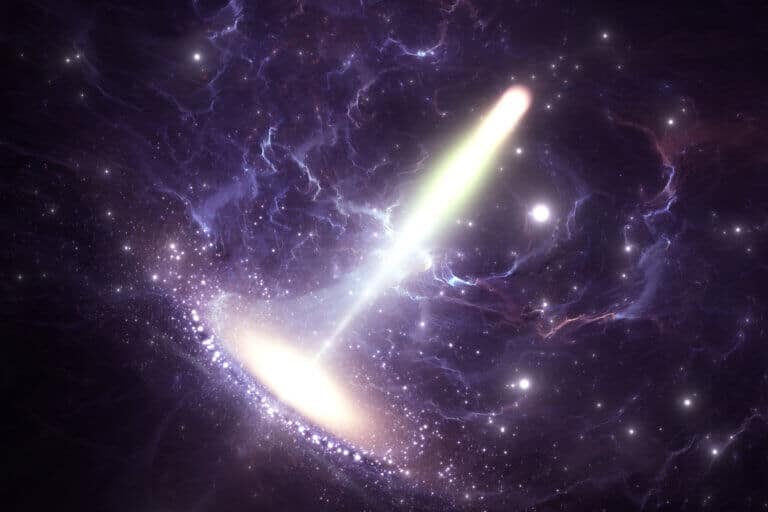
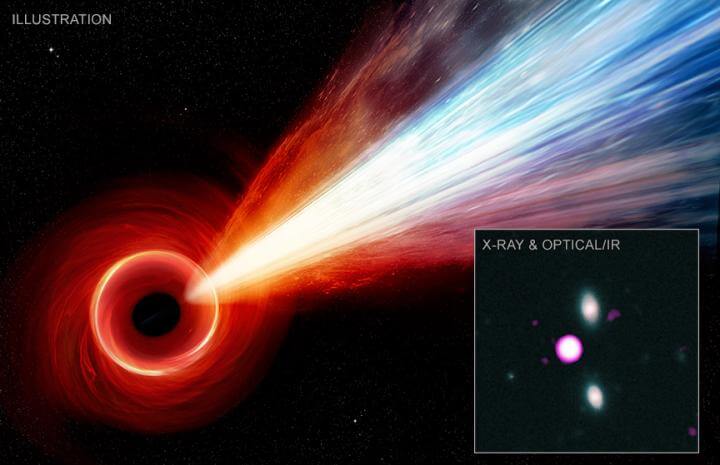
The scientists observed the black hole in the center of the galaxy M87 that was photographed about three years ago by optical means, and now the huge magnetic field around it has been photographed which reveals what happens when matter approaches the speed of light and part of it is swallowed up by the black hole. The writer is one of the scientists who participated in the project
- Universe Today
- March 22, 2021
- No comments
When LIGO and Virgo observe more black star collisions, they may observe many small black stars. If that happens, we may have to examine this idea of darker matter more carefully
- Avi Blizovsky
- March 16, 2021
- 2 תגובות
Physicists from Germany are examining the theoretical possibility of the existence of tunnels in space-time, but only particles can pass through them, and they will immediately close
- Avi Blizovsky
- March 15, 2021
- One response
- The Hebrew University
- February 26, 2021
- 2 תגובות
Dr. Asaf Haresh of the Hebrew University revealed a new and surprising phenomenon concerning the destruction of stars by black holes* so far no researcher has been able to prove that such flashes of radio radiation exist, a relatively long time after the destruction of the star. The research even proves the power of the event and the partial understanding of the scientific world on the subject. The research was published in Nature Astronomy
- The Hebrew University
- February 23, 2021
- 50 תגובות
A group of international researchers, including from the Hebrew University and the Weizmann Institute, discovered the particle that arrived following an emission event that occurred in 2019
- Noam Chai
- October 26, 2020
- 9 תגובות
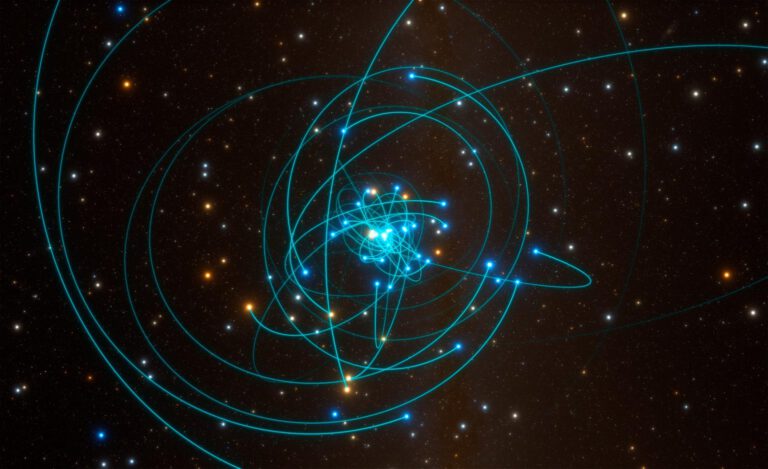
The black hole at the center of the Milky Way is slowly spinning, but what does that mean?
- Avi Blizovsky
- October 8, 2020
- One response
Says Prof. Hagai Netzer from the School of Physics and Astronomy at Tel Aviv University who wrote dozens of joint articles with Ganzel
- Avi Blizovsky
- October 7, 2020
- 5 תגובות
- Dr. Moshe Nahamani
- October 6, 2020
- 11 תגובות
- Avi Blizovsky
- September 6, 2020
- 8 תגובות
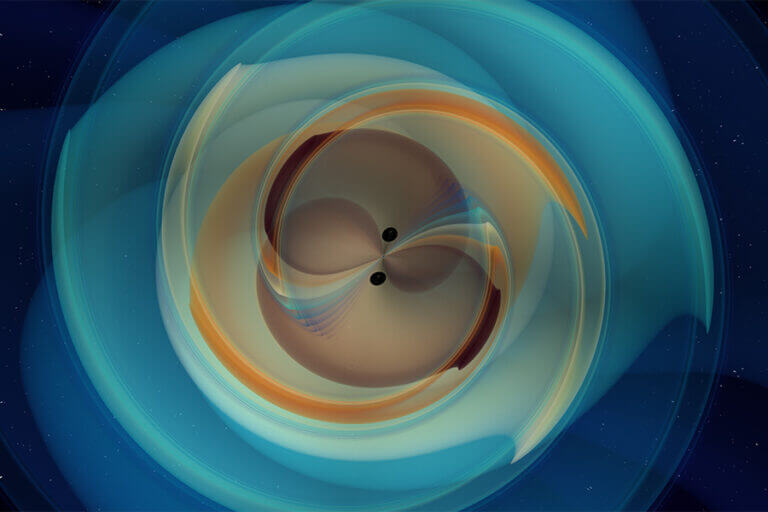
A binary black hole merger probably created gravitational waves equal to the energy of eight suns * "Bang" in the Ligo and Virgo detectors is a signal for the source of the most massive gravitational waves ever
- Avi Blizovsky
- August 26, 2020
- 9 תגובות
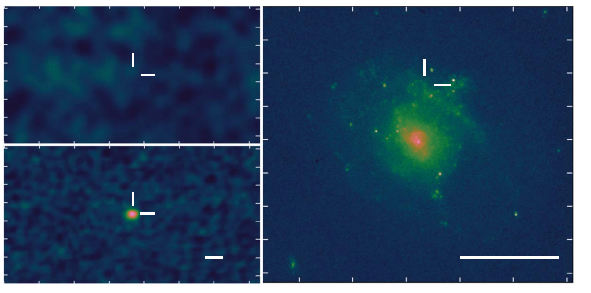
Researchers have identified a star that got too close to the "dinner table" and was swallowed up as well
- Avi Blizovsky
- July 5, 2020
- One response








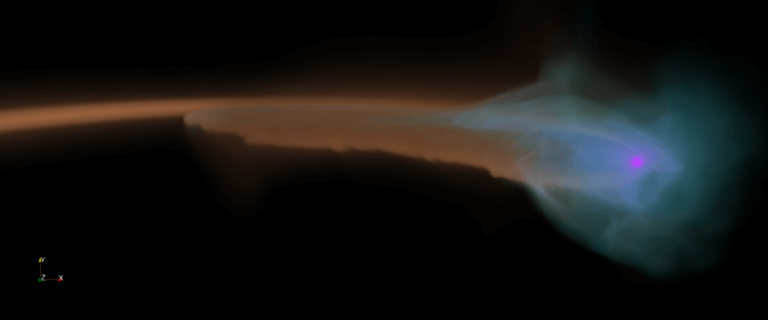








![Illustration of the galaxy and the giant black hole at its center. The black hole converts some of the matter it absorbs into energetic radiation (shaded in blue), while the galaxy continues to form new stars (purple areas). [Image credit: Michael Helfenbein/Yale University - M. Helfenbein / Yale University]](https://www.hayadan.org.il/images/content3/2015/07/Monster_Black_Hole.jpg)