Summary: Amyloid-beta proteins formed in the liver are carried in the bloodstream by lipoproteins to the brain. This causes neurodegradation, brain degeneration and inflammation, common features of Alzheimer's disease
Source: PLOS Processing: Gilat Simon
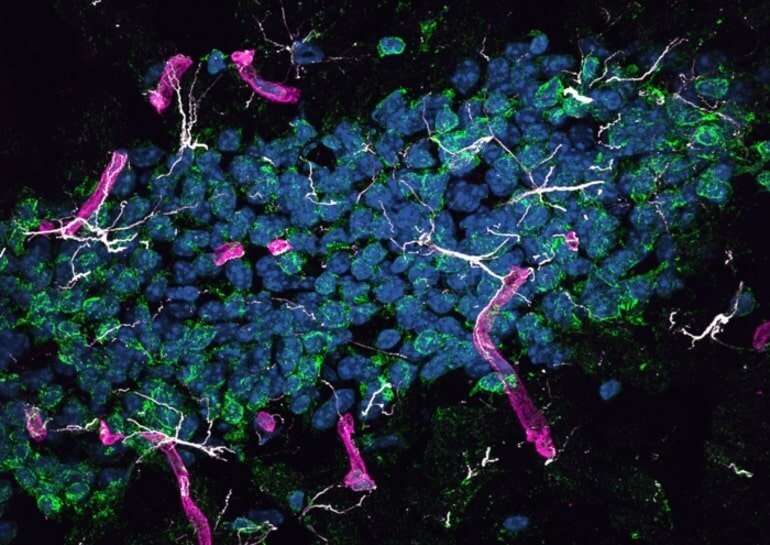
Amyloid protein formed in the liver may cause neurodegradation in the brain, according to a new study published in the journal PLOS Biology, by John Mamo from Curtin University in Australia and his colleagues. Since this protein is considered after the main contributors to the development of Alzheimer's disease, the findings show that liver plays an important role in the onset or progression of the disease.
Amyloid-beta (A-beta) deposits in the brain are one of the pathological hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease and are involved in neurodegeneration both in human patients and in animal models of the disease.
Testing this hypothesis is difficult, since the brain also produces amyloid-beta, and distinguishing between the proteins from the different sources (liver and brain) is challenging.
In the present study, the authors overcame this challenge by developing a mouse that produces beta-human amyloid only in the liver cells. They showed that the protein is carried in the bloodstream by lipoproteins rich in triglycerides, just as occurs in humans, and is transported from the periphery of the body to the brain.
They found that mice developed neurodegeneration and brain atrophy, accompanied by neurovascular inflammation and cerebral capillary dysfunction, common symptoms in Alzheimer's disease. Diseased mice performed poorly in learning tests that depend on the proper functioning of the hippocampus, the brain structure essential for forming new memories.
The findings from this study indicate that amyloid-beta formed in the periphery of the body has the ability to cause neurodegeneration and suggest that amyloid-beta formed in the liver is a potential contributor to the human disease. If this contribution is significant, the findings may have a major impact on understanding the disease.
Today, most salting-out models focus on the overproduction of amyloid-beta in the brain itself, which mimics the rare cases of hereditary Alzheimer's disease in humans. However, in most cases of Alzheimer's disease, the overproduction of amyloid-beta in the brain is not considered the main factor in the etiology of the disease (etiology - a branch of research that deals with the study of the causes of the disease). Instead, various lifestyle factors are given greater importance, including a diet rich in fat, which may increase amyloid-beta production in the liver.
The effects of peripheral amyloid-beta on brain capillaries may be critical in the disease process, Mammo adds. "While it is now necessary to conduct more studies, the current findings show that it is possible that specific treatment of these toxic protein deposits, amyloid lipoproteins in the blood, through diet and drugs may slow the development of Alzheimer's disease."
More of the topic in Hayadan:
